Roger K. Moore
The Influence of Facial Features on the Perceived Trustworthiness of a Social Robot
Sep 17, 2025Abstract:Trust and the perception of trustworthiness play an important role in decision-making and our behaviour towards others, and this is true not only of human-human interactions but also of human-robot interactions. While significant advances have been made in recent years in the field of social robotics, there is still some way to go before we fully understand the factors that influence human trust in robots. This paper presents the results of a study into the first impressions created by a social robot's facial features, based on the hypothesis that a `babyface' engenders trust. By manipulating the back-projected face of a Furhat robot, the study confirms that eye shape and size have a significant impact on the perception of trustworthiness. The work thus contributes to an understanding of the design choices that need to be made when developing social robots so as to optimise the effectiveness of human-robot interaction.
Towards deployment-centric multimodal AI beyond vision and language
Apr 04, 2025Abstract:Multimodal artificial intelligence (AI) integrates diverse types of data via machine learning to improve understanding, prediction, and decision-making across disciplines such as healthcare, science, and engineering. However, most multimodal AI advances focus on models for vision and language data, while their deployability remains a key challenge. We advocate a deployment-centric workflow that incorporates deployment constraints early to reduce the likelihood of undeployable solutions, complementing data-centric and model-centric approaches. We also emphasise deeper integration across multiple levels of multimodality and multidisciplinary collaboration to significantly broaden the research scope beyond vision and language. To facilitate this approach, we identify common multimodal-AI-specific challenges shared across disciplines and examine three real-world use cases: pandemic response, self-driving car design, and climate change adaptation, drawing expertise from healthcare, social science, engineering, science, sustainability, and finance. By fostering multidisciplinary dialogue and open research practices, our community can accelerate deployment-centric development for broad societal impact.
One Size Does not Fit All: Personalised Affordance Design for Social Robots
Dec 11, 2023Abstract:Personalisation is essential to achieve more acceptable and effective results in human-robot interaction. Placing users in the central role, many studies have focused on enhancing the abilities of social robots to perceive and understand users. However, little is known about improving user perceptions and interpretation of a social robot in spoken interactions. The work described in the paper aims to find out what affects the personalisation of affordance of a social robot, namely its appearance, voice and language behaviours. The experimental data presented here is based on an ongoing project. It demonstrates the many and varied ways in which people change their preferences for the affordance of a social robot under different circumstances. It also examines the relationship between such preferences and expectations of characteristics of a social robot, like competence and warmth. It also shows that individuals have different perceptions of the language behaviours of the same robot. These results demonstrate that one-sized personalisation does not fit all. Personalisation should be considered a comprehensive approach, including appropriate affordance design, to suit the user expectations of social roles.
Adapting the NICT-JLE Corpus for Disfluency Detection Models
Aug 04, 2023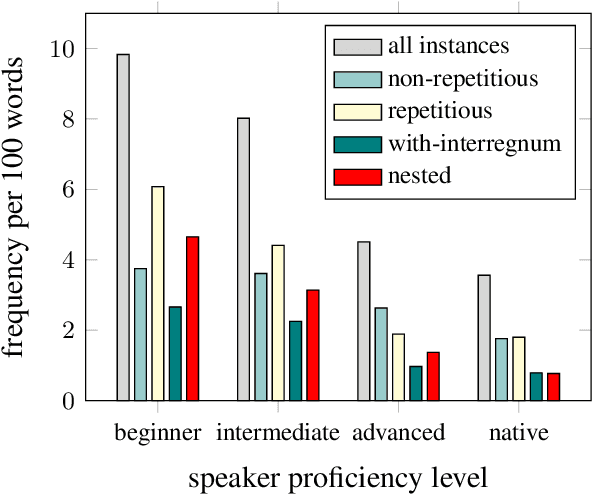
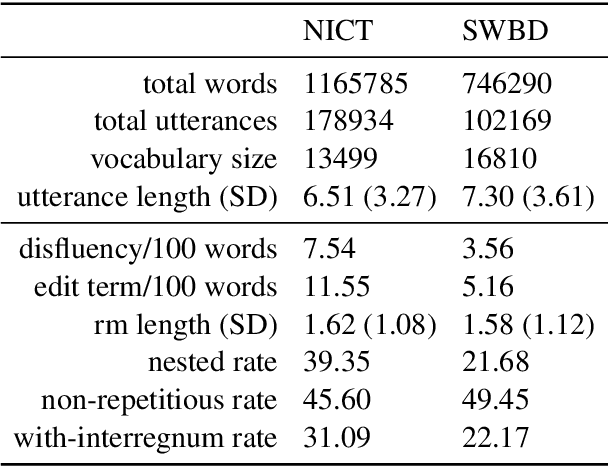

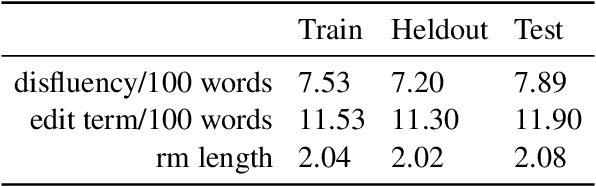
Abstract:The detection of disfluencies such as hesitations, repetitions and false starts commonly found in speech is a widely studied area of research. With a standardised process for evaluation using the Switchboard Corpus, model performance can be easily compared across approaches. This is not the case for disfluency detection research on learner speech, however, where such datasets have restricted access policies, making comparison and subsequent development of improved models more challenging. To address this issue, this paper describes the adaptation of the NICT-JLE corpus, containing approximately 300 hours of English learners' oral proficiency tests, to a format that is suitable for disfluency detection model training and evaluation. Points of difference between the NICT-JLE and Switchboard corpora are explored, followed by a detailed overview of adaptations to the tag set and meta-features of the NICT-JLE corpus. The result of this work provides a standardised train, heldout and test set for use in future research on disfluency detection for learner speech.
Local Minima Drive Communications in Cooperative Interaction
Jul 18, 2023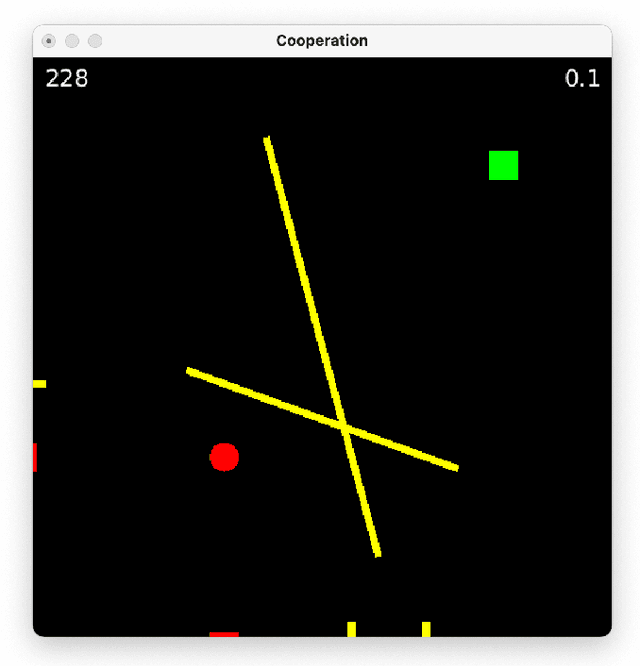
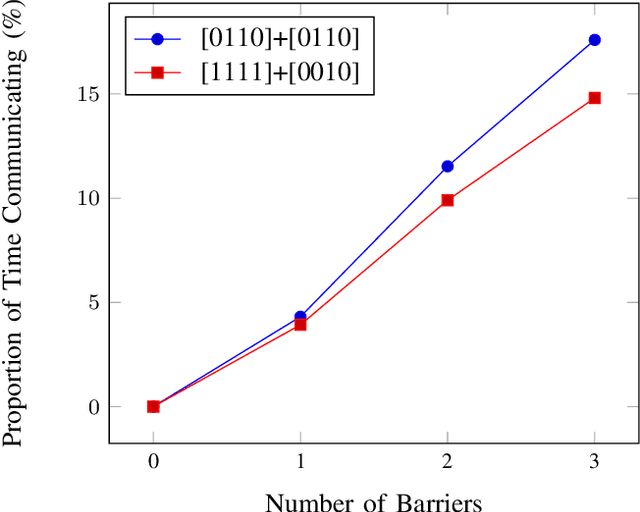
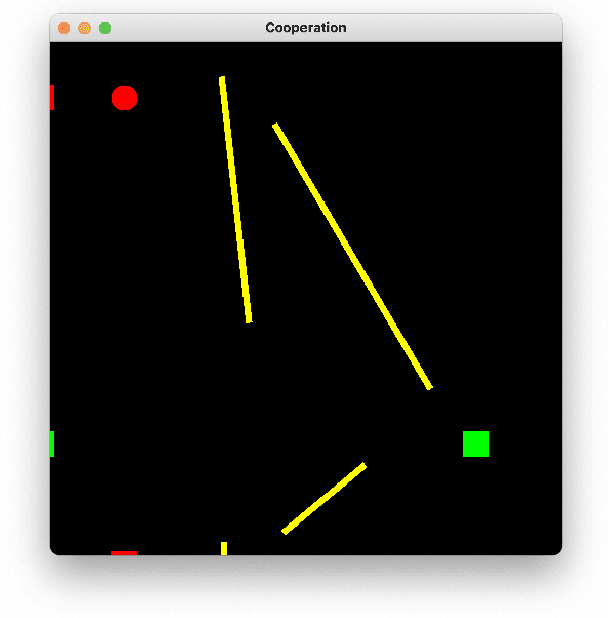
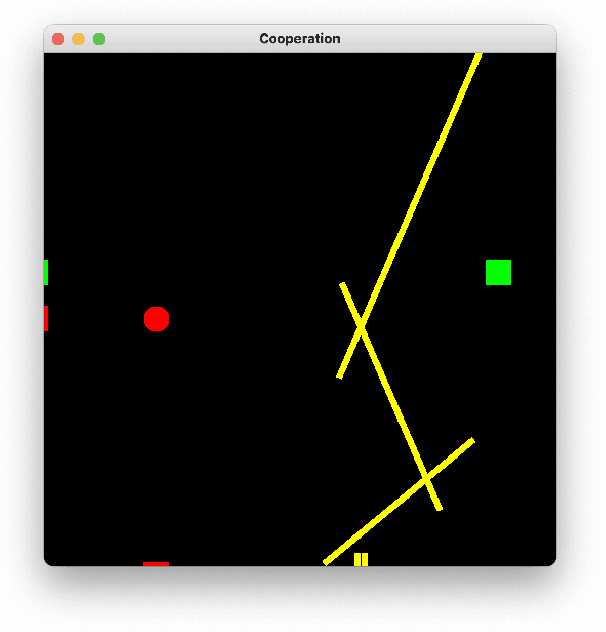
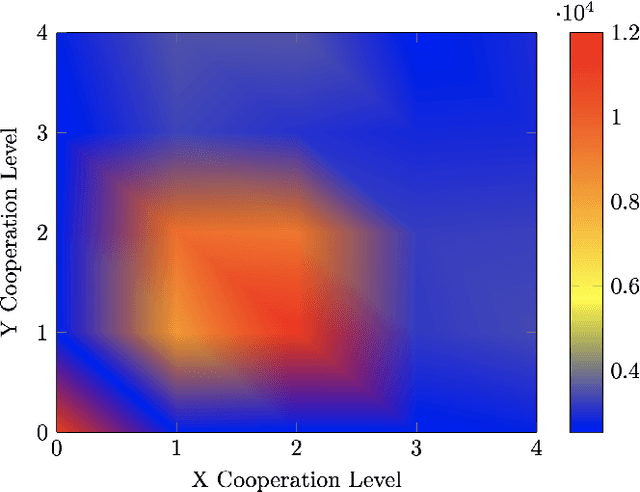
Abstract:An important open question in human-robot interaction (HRI) is precisely when an agent should decide to communicate, particularly in a cooperative task. Perceptual Control Theory (PCT) tells us that agents are able to cooperate on a joint task simply by sharing the same 'intention', thereby distributing the effort required to complete the task among the agents. This is even true for agents that do not possess the same abilities, so long as the goal is observable, the combined actions are sufficient to complete the task, and there is no local minimum in the search space. If these conditions hold, then a cooperative task can be accomplished without any communication between the contributing agents. However, for tasks that do contain local minima, the global solution can only be reached if at least one of the agents adapts its intention at the appropriate moments, and this can only be achieved by appropriately timed communication. In other words, it is hypothesised that in cooperative tasks, the function of communication is to coordinate actions in a complex search space that contains local minima. These principles have been verified in a computer-based simulation environment in which two independent one-dimensional agents are obliged to cooperate in order to solve a two-dimensional path-finding task.
Whither the Priors for (Vocal) Interactivity?
Mar 16, 2022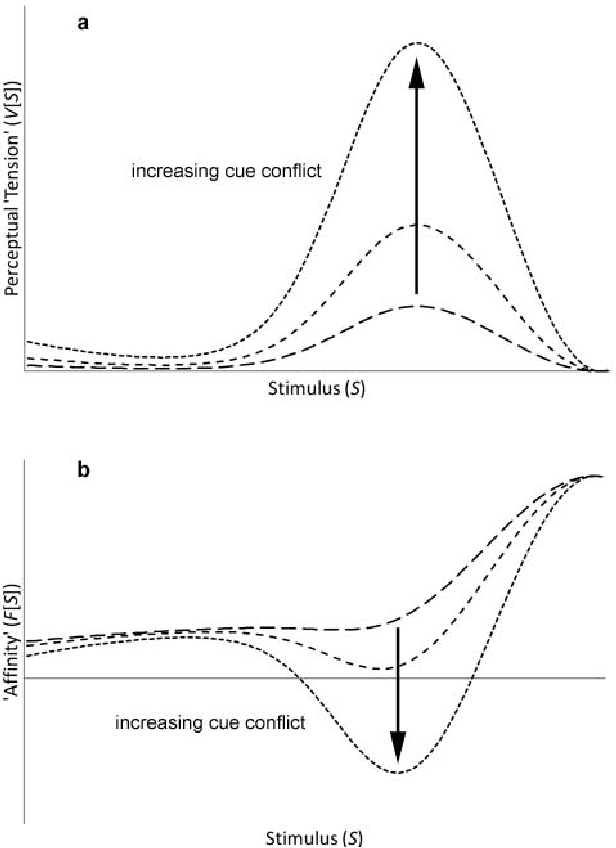
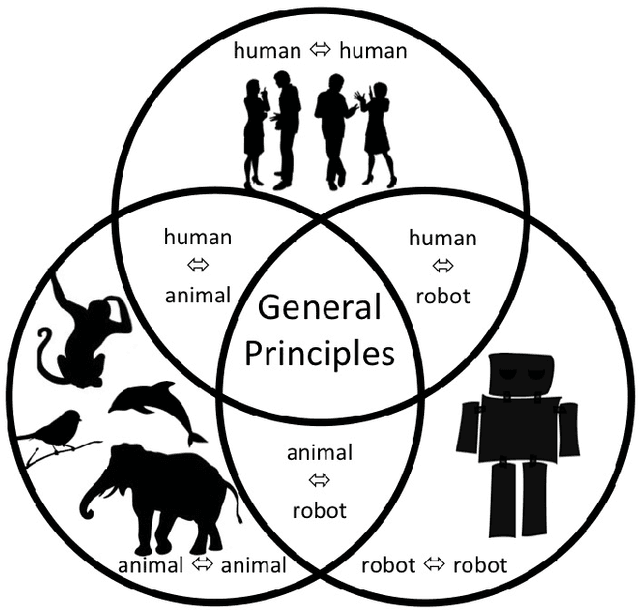
Abstract:Voice-based communication is often cited as one of the most `natural' ways in which humans and robots might interact, and the recent availability of accurate automatic speech recognition and intelligible speech synthesis has enabled researchers to integrate advanced off-the-shelf spoken language technology components into their robot platforms. Despite this, the resulting interactions are anything but `natural'. It transpires that simply giving a robot a voice doesn't mean that a user will know how (or when) to talk to it, and the resulting `conversations' tend to be stilted, one-sided and short. On the surface, these difficulties might appear to be fairly trivial consequences of users' unfamiliarity with robots (and \emph{vice versa}), and that any problems would be mitigated by long-term use by the human, coupled with `deep learning' by the robot. However, it is argued here that such communication failures are indicative of a deeper malaise: a fundamental lack of basic principles -- \emph{priors} -- underpinning not only speech-based interaction in particular, but (vocal) interactivity in general. This is evidenced not only by the fact that contemporary spoken language systems already require training data sets that are orders-of-magnitude greater than that experienced by a young child, but also by the lack of design principles for creating effective communicative human-robot interaction. This short position paper identifies some of the key areas where theoretical insights might help overcome these shortfalls.
Investigating Deep Neural Structures and their Interpretability in the Domain of Voice Conversion
Feb 22, 2021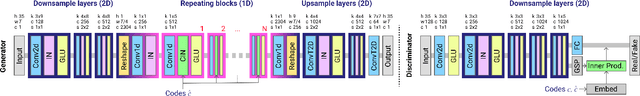
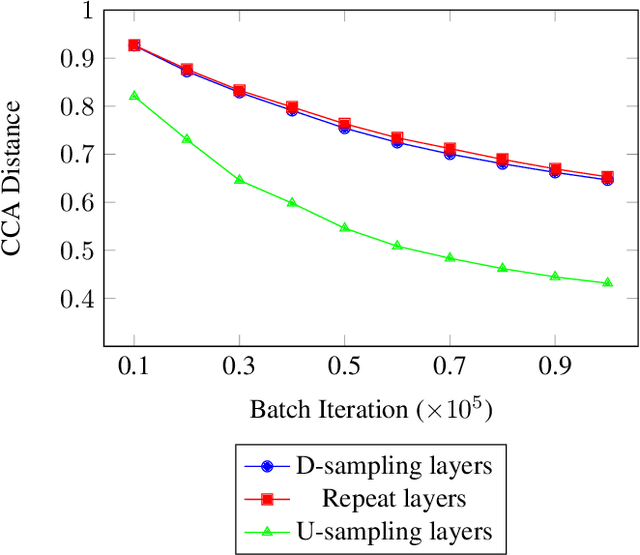


Abstract:Generative Adversarial Networks (GANs) are machine learning networks based around creating synthetic data. Voice Conversion (VC) is a subset of voice translation that involves translating the paralinguistic features of a source speaker to a target speaker while preserving the linguistic information. The aim of non-parallel conditional GANs for VC is to translate an acoustic speech feature sequence from one domain to another without the use of paired data. In the study reported here, we investigated the interpretability of state-of-the-art implementations of non-parallel GANs in the domain of VC. We show that the learned representations in the repeating layers of a particular GAN architecture remain close to their original random initialised parameters, demonstrating that it is the number of repeating layers that is more responsible for the quality of the output. We also analysed the learned representations of a model trained on one particular dataset when used during transfer learning on another dataset. This showed extremely high levels of similarity across the entire network. Together, these results provide new insight into how the learned representations of deep generative networks change during learning and the importance in the number of layers.
Talking with Robots: Opportunities and Challenges
Dec 01, 2019
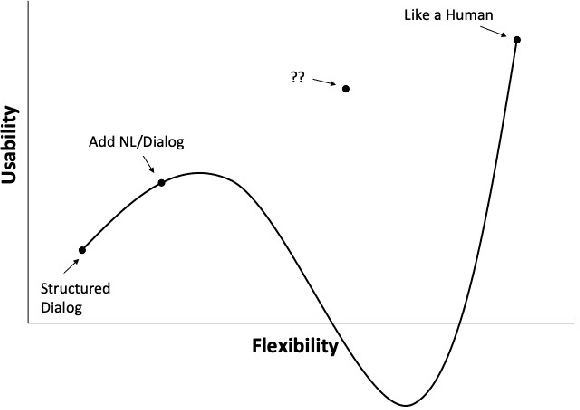
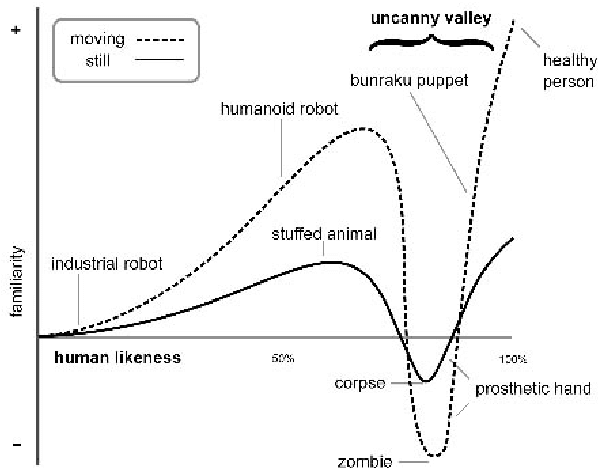
Abstract:Notwithstanding the tremendous progress that is taking place in spoken language technology, effective speech-based human-robot interaction still raises a number of important challenges. Not only do the fields of robotics and spoken language technology present their own special problems, but their combination raises an additional set of issues. In particular, there is a large gap between the formulaic speech that typifies contemporary spoken dialogue systems and the flexible nature of human-human conversation. It is pointed out that grounded and situated speech-based human-robot interaction may lead to deeper insights into the pragmatics of language usage, thereby overcoming the current `habitability gap'.
Vocal Interactivity in Crowds, Flocks and Swarms: Implications for Voice User Interfaces
Jul 26, 2019
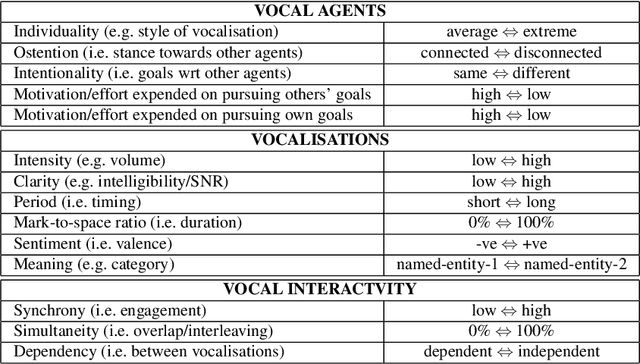
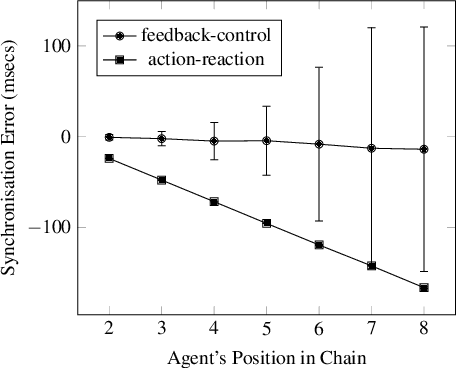
Abstract:Recent years have seen an explosion in the availability of Voice User Interfaces. However, user surveys suggest that there are issues with respect to usability, and it has been hypothesised that contemporary voice-enabled systems are missing crucial behaviours relating to user engagement and vocal interactivity. However, it is well established that such ostensive behaviours are ubiquitous in the animal kingdom, and that vocalisation provides a means through which interaction may be coordinated and managed between individuals and within groups. Hence, this paper reports results from a study aimed at identifying generic mechanisms that might underpin coordinated collective vocal behaviour with a particular focus on closed-loop negative-feedback control as a powerful regulatory process. A computer-based real-time simulation of vocal interactivity is described which has provided a number of insights, including the enumeration of a number of key control variables that may be worthy of further investigation.
On the Use/Misuse of the Term 'Phoneme'
Jul 26, 2019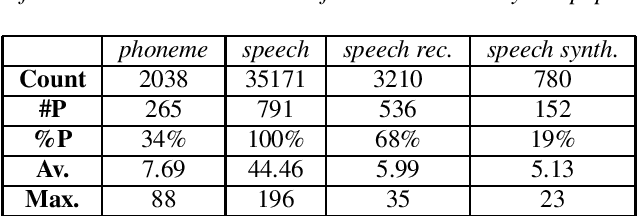

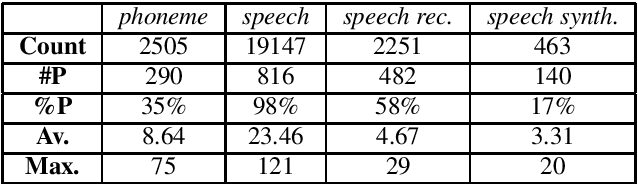

Abstract:The term 'phoneme' lies at the heart of speech science and technology, and yet it is not clear that the research community fully appreciates its meaning and implications. In particular, it is suspected that many researchers use the term in a casual sense to refer to the sounds of speech, rather than as a well defined abstract concept. If true, this means that some sections of the community may be missing an opportunity to understand and exploit the implications of this important psychological phenomenon. Here we review the correct meaning of the term 'phoneme' and report the results of an investigation into its use/misuse in the accepted papers at INTERSPEECH-2018. It is confirmed that a significant proportion of the community (i) may not be aware of the critical difference between `phonetic' and 'phonemic' levels of description, (ii) may not fully understand the significance of 'phonemic contrast', and as a consequence, (iii) consistently misuse the term 'phoneme'. These findings are discussed, and recommendations are made as to how this situation might be mitigated.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge