Roger Cheng
Contrastive-mixup learning for improved speaker verification
Feb 22, 2022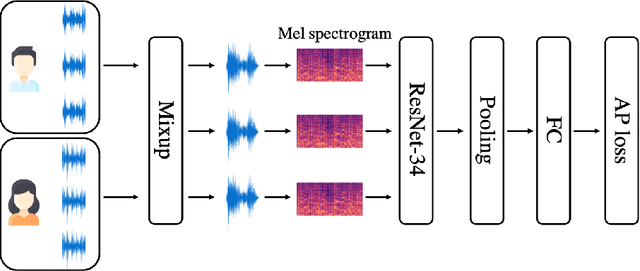
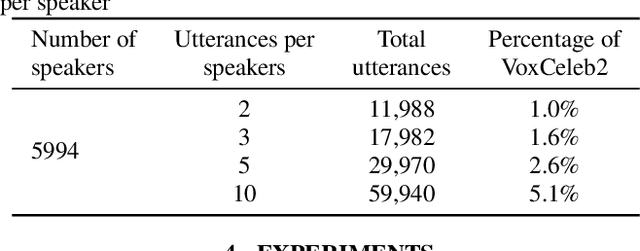
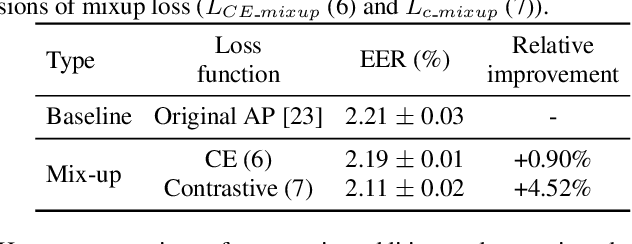
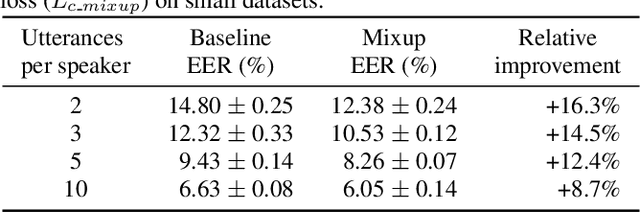
Abstract:This paper proposes a novel formulation of prototypical loss with mixup for speaker verification. Mixup is a simple yet efficient data augmentation technique that fabricates a weighted combination of random data point and label pairs for deep neural network training. Mixup has attracted increasing attention due to its ability to improve robustness and generalization of deep neural networks. Although mixup has shown success in diverse domains, most applications have centered around closed-set classification tasks. In this work, we propose contrastive-mixup, a novel augmentation strategy that learns distinguishing representations based on a distance metric. During training, mixup operations generate convex interpolations of both inputs and virtual labels. Moreover, we have reformulated the prototypical loss function such that mixup is enabled on metric learning objectives. To demonstrate its generalization given limited training data, we conduct experiments by varying the number of available utterances from each speaker in the VoxCeleb database. Experimental results show that applying contrastive-mixup outperforms the existing baseline, reducing error rate by 16% relatively, especially when the number of training utterances per speaker is limited.
The INTERSPEECH 2020 Deep Noise Suppression Challenge: Datasets, Subjective Testing Framework, and Challenge Results
May 29, 2020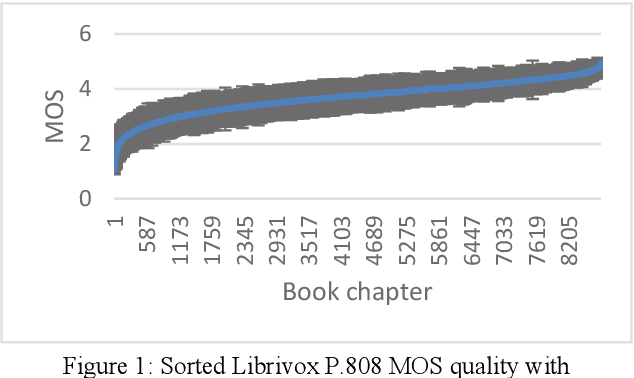

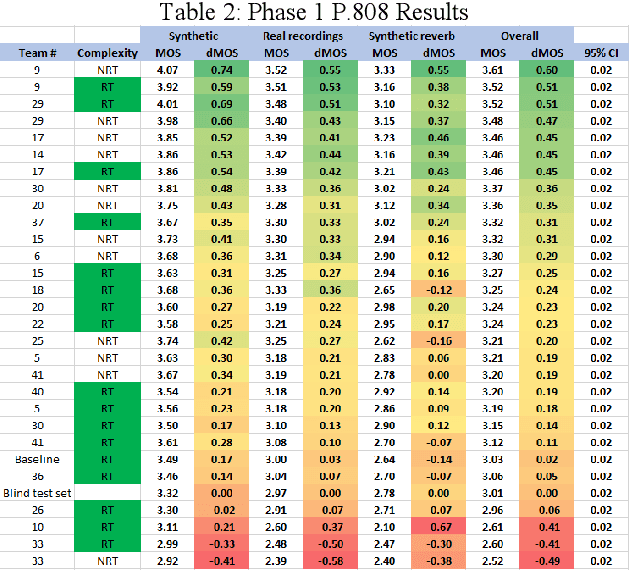
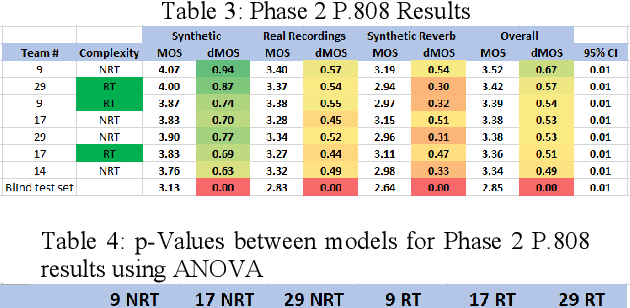
Abstract:The INTERSPEECH 2020 Deep Noise Suppression (DNS) Challenge is intended to promote collaborative research in real-time single-channel Speech Enhancement aimed to maximize the subjective (perceptual) quality of the enhanced speech. A typical approach to evaluate the noise suppression methods is to use objective metrics on the test set obtained by splitting the original dataset. While the performance is good on the synthetic test set, often the model performance degrades significantly on real recordings. Also, most of the conventional objective metrics do not correlate well with subjective tests and lab subjective tests are not scalable for a large test set. In this challenge, we open-sourced a large clean speech and noise corpus for training the noise suppression models and a representative test set to real-world scenarios consisting of both synthetic and real recordings. We also open-sourced an online subjective test framework based on ITU-T P.808 for researchers to reliably test their developments. We evaluated the results using P.808 on a blind test set. The results and the key learnings from the challenge are discussed. The datasets and scripts can be found here for quick access https://github.com/microsoft/DNS-Challenge.
The INTERSPEECH 2020 Deep Noise Suppression Challenge: Datasets, Subjective Speech Quality and Testing Framework
Jan 23, 2020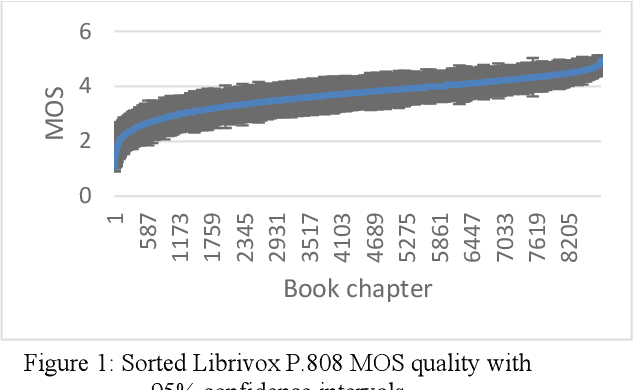

Abstract:The INTERSPEECH 2020 Deep Noise Suppression Challenge is intended to promote collaborative research in real-time single-channel Speech Enhancement aimed to maximize the subjective (perceptual) quality of the enhanced speech. A typical approach to evaluate the noise suppression methods is to use objective metrics on the test set obtained by splitting the original dataset. Many publications report reasonable performance on the synthetic test set drawn from the same distribution as that of the training set. However, often the model performance degrades significantly on real recordings. Also, most of the conventional objective metrics do not correlate well with subjective tests and lab subjective tests are not scalable for a large test set. In this challenge, we open-source a large clean speech and noise corpus for training the noise suppression models and a representative test set to real-world scenarios consisting of both synthetic and real recordings. We also open source an online subjective test framework based on ITU-T P.808 for researchers to quickly test their developments. The winners of this challenge will be selected based on subjective evaluation on a representative test set using P.808 framework.
Identifying Bias in AI using Simulation
Sep 30, 2018



Abstract:Machine learned models exhibit bias, often because the datasets used to train them are biased. This presents a serious problem for the deployment of such technology, as the resulting models might perform poorly on populations that are minorities within the training set and ultimately present higher risks to them. We propose to use high-fidelity computer simulations to interrogate and diagnose biases within ML classifiers. We present a framework that leverages Bayesian parameter search to efficiently characterize the high dimensional feature space and more quickly identify weakness in performance. We apply our approach to an example domain, face detection, and show that it can be used to help identify demographic biases in commercial face application programming interfaces (APIs).
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge