Rida Qadri
The Case for "Thick Evaluations" of Cultural Representation in AI
Mar 24, 2025Abstract:Generative AI image models have been increasingly evaluated for their (in)ability to represent non-Western cultures. We argue that these evaluations operate through reductive ideals of representation, abstracted from how people define their own representation and neglecting the inherently interpretive and contextual nature of cultural representation. In contrast to these 'thin' evaluations, we introduce the idea of 'thick evaluations': a more granular, situated, and discursive measurement framework for evaluating representations of social worlds in AI images, steeped in communities' own understandings of representation. We develop this evaluation framework through workshops in South Asia, by studying the 'thick' ways in which people interpret and assign meaning to images of their own cultures. We introduce practices for thicker evaluations of representation that expand the understanding of representation underpinning AI evaluations and by co-constructing metrics with communities, bringing measurement in line with the experiences of communities on the ground.
Risks of Cultural Erasure in Large Language Models
Jan 02, 2025



Abstract:Large language models are increasingly being integrated into applications that shape the production and discovery of societal knowledge such as search, online education, and travel planning. As a result, language models will shape how people learn about, perceive and interact with global cultures making it important to consider whose knowledge systems and perspectives are represented in models. Recognizing this importance, increasingly work in Machine Learning and NLP has focused on evaluating gaps in global cultural representational distribution within outputs. However, more work is needed on developing benchmarks for cross-cultural impacts of language models that stem from a nuanced sociologically-aware conceptualization of cultural impact or harm. We join this line of work arguing for the need of metricizable evaluations of language technologies that interrogate and account for historical power inequities and differential impacts of representation on global cultures, particularly for cultures already under-represented in the digital corpora. We look at two concepts of erasure: omission: where cultures are not represented at all and simplification i.e. when cultural complexity is erased by presenting one-dimensional views of a rich culture. The former focuses on whether something is represented, and the latter on how it is represented. We focus our analysis on two task contexts with the potential to influence global cultural production. First, we probe representations that a language model produces about different places around the world when asked to describe these contexts. Second, we analyze the cultures represented in the travel recommendations produced by a set of language model applications. Our study shows ways in which the NLP community and application developers can begin to operationalize complex socio-cultural considerations into standard evaluations and benchmarks.
Dialogue with the Machine and Dialogue with the Art World: Evaluating Generative AI for Culturally-Situated Creativity
Dec 18, 2024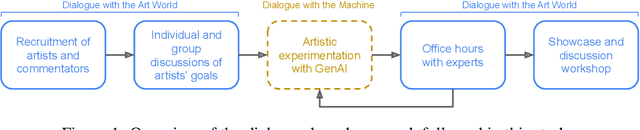
Abstract:This paper proposes dialogue as a method for evaluating generative AI tools for culturally-situated creative practice, that recognizes the socially situated nature of art. Drawing on sociologist Howard Becker's concept of Art Worlds, this method expands the scope of traditional AI and creativity evaluations beyond benchmarks, user studies with crowd-workers, or focus groups conducted with artists. Our method involves two mutually informed dialogues: 1) 'dialogues with art worlds' placing artists in conversation with experts such as art historians, curators, and archivists, and 2)'dialogues with the machine,' facilitated through structured artist- and critic-led experimentation with state-of-the-art generative AI tools. We demonstrate the value of this method through a case study with artists and experts steeped in non-western art worlds, specifically the Persian Gulf. We trace how these dialogues help create culturally rich and situated forms of evaluation for representational possibilities of generative AI that mimic the reception of generative artwork in the broader art ecosystem. Putting artists in conversation with commentators also allow artists to shift their use of the tools to respond to their cultural and creative context. Our study can provide generative AI researchers an understanding of the complex dynamics of technology, human creativity and the socio-politics of art worlds, to build more inclusive machines for diverse art worlds.
Beyond the Surface: A Global-Scale Analysis of Visual Stereotypes in Text-to-Image Generation
Jan 12, 2024



Abstract:Recent studies have highlighted the issue of stereotypical depictions for people of different identity groups in Text-to-Image (T2I) model generations. However, these existing approaches have several key limitations, including a noticeable lack of coverage of global identity groups in their evaluation, and the range of their associated stereotypes. Additionally, they often lack a critical distinction between inherently visual stereotypes, such as `underweight' or `sombrero', and culturally dependent stereotypes like `attractive' or `terrorist'. In this work, we address these limitations with a multifaceted approach that leverages existing textual resources to ground our evaluation of geo-cultural stereotypes in the generated images from T2I models. We employ existing stereotype benchmarks to identify and evaluate visual stereotypes at a global scale, spanning 135 nationality-based identity groups. We demonstrate that stereotypical attributes are thrice as likely to be present in images of these identities as compared to other attributes. We further investigate how disparately offensive the depictions of generated images are for different nationalities. Finally, through a detailed case study, we reveal how the 'default' representations of all identity groups have a stereotypical appearance. Moreover, for the Global South, images across different attributes are visually similar, even when explicitly prompted otherwise. CONTENT WARNING: Some examples may contain offensive stereotypes.
AI's Regimes of Representation: A Community-centered Study of Text-to-Image Models in South Asia
May 19, 2023



Abstract:This paper presents a community-centered study of cultural limitations of text-to-image (T2I) models in the South Asian context. We theorize these failures using scholarship on dominant media regimes of representations and locate them within participants' reporting of their existing social marginalizations. We thus show how generative AI can reproduce an outsiders gaze for viewing South Asian cultures, shaped by global and regional power inequities. By centering communities as experts and soliciting their perspectives on T2I limitations, our study adds rich nuance into existing evaluative frameworks and deepens our understanding of the culturally-specific ways AI technologies can fail in non-Western and Global South settings. We distill lessons for responsible development of T2I models, recommending concrete pathways forward that can allow for recognition of structural inequalities.
Cultural Incongruencies in Artificial Intelligence
Nov 19, 2022Abstract:Artificial intelligence (AI) systems attempt to imitate human behavior. How well they do this imitation is often used to assess their utility and to attribute human-like (or artificial) intelligence to them. However, most work on AI refers to and relies on human intelligence without accounting for the fact that human behavior is inherently shaped by the cultural contexts they are embedded in, the values and beliefs they hold, and the social practices they follow. Additionally, since AI technologies are mostly conceived and developed in just a handful of countries, they embed the cultural values and practices of these countries. Similarly, the data that is used to train the models also fails to equitably represent global cultural diversity. Problems therefore arise when these technologies interact with globally diverse societies and cultures, with different values and interpretive practices. In this position paper, we describe a set of cultural dependencies and incongruencies in the context of AI-based language and vision technologies, and reflect on the possibilities of and potential strategies towards addressing these incongruencies.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge