Ricardo Silveira Cabral
Jack
Gaia2: Benchmarking LLM Agents on Dynamic and Asynchronous Environments
Feb 12, 2026Abstract:We introduce Gaia2, a benchmark for evaluating large language model agents in realistic, asynchronous environments. Unlike prior static or synchronous evaluations, Gaia2 introduces scenarios where environments evolve independently of agent actions, requiring agents to operate under temporal constraints, adapt to noisy and dynamic events, resolve ambiguity, and collaborate with other agents. Each scenario is paired with a write-action verifier, enabling fine-grained, action-level evaluation and making Gaia2 directly usable for reinforcement learning from verifiable rewards. Our evaluation of state-of-the-art proprietary and open-source models shows that no model dominates across capabilities: GPT-5 (high) reaches the strongest overall score of 42% pass@1 but fails on time-sensitive tasks, Claude-4 Sonnet trades accuracy and speed for cost, Kimi-K2 leads among open-source models with 21% pass@1. These results highlight fundamental trade-offs between reasoning, efficiency, robustness, and expose challenges in closing the "sim2real" gap. Gaia2 is built on a consumer environment with the open-source Agents Research Environments platform and designed to be easy to extend. By releasing Gaia2 alongside the foundational ARE framework, we aim to provide the community with a flexible infrastructure for developing, benchmarking, and training the next generation of practical agent systems.
The Llama 4 Herd: Architecture, Training, Evaluation, and Deployment Notes
Jan 15, 2026Abstract:This document consolidates publicly reported technical details about Metas Llama 4 model family. It summarizes (i) released variants (Scout and Maverick) and the broader herd context including the previewed Behemoth teacher model, (ii) architectural characteristics beyond a high-level MoE description covering routed/shared-expert structure, early-fusion multimodality, and long-context design elements reported for Scout (iRoPE and length generalization strategies), (iii) training disclosures spanning pre-training, mid-training for long-context extension, and post-training methodology (lightweight SFT, online RL, and lightweight DPO) as described in release materials, (iv) developer-reported benchmark results for both base and instruction-tuned checkpoints, and (v) practical deployment constraints observed across major serving environments, including provider-specific context limits and quantization packaging. The manuscript also summarizes licensing obligations relevant to redistribution and derivative naming, and reviews publicly described safeguards and evaluation practices. The goal is to provide a compact technical reference for researchers and practitioners who need precise, source-backed facts about Llama 4.
MLGym: A New Framework and Benchmark for Advancing AI Research Agents
Feb 20, 2025



Abstract:We introduce Meta MLGym and MLGym-Bench, a new framework and benchmark for evaluating and developing LLM agents on AI research tasks. This is the first Gym environment for machine learning (ML) tasks, enabling research on reinforcement learning (RL) algorithms for training such agents. MLGym-bench consists of 13 diverse and open-ended AI research tasks from diverse domains such as computer vision, natural language processing, reinforcement learning, and game theory. Solving these tasks requires real-world AI research skills such as generating new ideas and hypotheses, creating and processing data, implementing ML methods, training models, running experiments, analyzing the results, and iterating through this process to improve on a given task. We evaluate a number of frontier large language models (LLMs) on our benchmarks such as Claude-3.5-Sonnet, Llama-3.1 405B, GPT-4o, o1-preview, and Gemini-1.5 Pro. Our MLGym framework makes it easy to add new tasks, integrate and evaluate models or agents, generate synthetic data at scale, as well as develop new learning algorithms for training agents on AI research tasks. We find that current frontier models can improve on the given baselines, usually by finding better hyperparameters, but do not generate novel hypotheses, algorithms, architectures, or substantial improvements. We open-source our framework and benchmark to facilitate future research in advancing the AI research capabilities of LLM agents.
The Llama 3 Herd of Models
Jul 31, 2024Abstract:Modern artificial intelligence (AI) systems are powered by foundation models. This paper presents a new set of foundation models, called Llama 3. It is a herd of language models that natively support multilinguality, coding, reasoning, and tool usage. Our largest model is a dense Transformer with 405B parameters and a context window of up to 128K tokens. This paper presents an extensive empirical evaluation of Llama 3. We find that Llama 3 delivers comparable quality to leading language models such as GPT-4 on a plethora of tasks. We publicly release Llama 3, including pre-trained and post-trained versions of the 405B parameter language model and our Llama Guard 3 model for input and output safety. The paper also presents the results of experiments in which we integrate image, video, and speech capabilities into Llama 3 via a compositional approach. We observe this approach performs competitively with the state-of-the-art on image, video, and speech recognition tasks. The resulting models are not yet being broadly released as they are still under development.
PINs: Progressive Implicit Networks for Multi-Scale Neural Representations
Feb 09, 2022


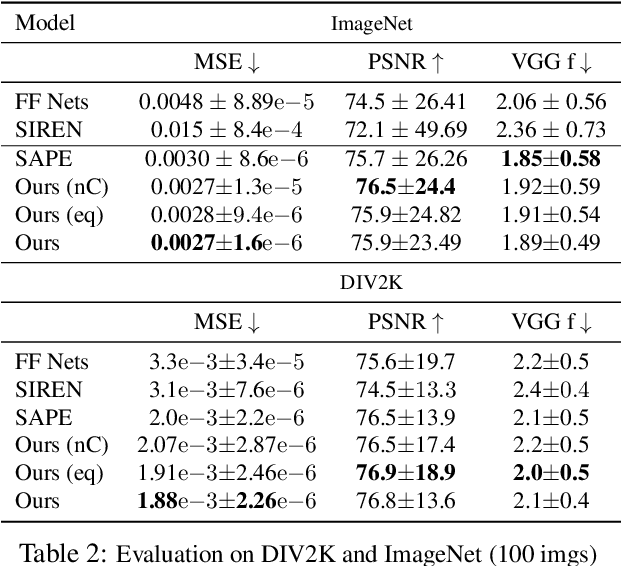
Abstract:Multi-layer perceptrons (MLP) have proven to be effective scene encoders when combined with higher-dimensional projections of the input, commonly referred to as \textit{positional encoding}. However, scenes with a wide frequency spectrum remain a challenge: choosing high frequencies for positional encoding introduces noise in low structure areas, while low frequencies result in poor fitting of detailed regions. To address this, we propose a progressive positional encoding, exposing a hierarchical MLP structure to incremental sets of frequency encodings. Our model accurately reconstructs scenes with wide frequency bands and learns a scene representation at progressive level of detail \textit{without explicit per-level supervision}. The architecture is modular: each level encodes a continuous implicit representation that can be leveraged separately for its respective resolution, meaning a smaller network for coarser reconstructions. Experiments on several 2D and 3D datasets show improvements in reconstruction accuracy, representational capacity and training speed compared to baselines.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge