Raphael C. -W. Phan
MD-BERT: Action Recognition in Dark Videos via Dynamic Multi-Stream Fusion and Temporal Modeling
Feb 06, 2025



Abstract:Action recognition in dark, low-light (under-exposed) or noisy videos is a challenging task due to visibility degradation, which can hinder critical spatiotemporal details. This paper proposes MD-BERT, a novel multi-stream approach that integrates complementary pre-processing techniques such as gamma correction and histogram equalization alongside raw dark frames to address these challenges. We introduce the Dynamic Feature Fusion (DFF) module, extending existing attentional fusion methods to a three-stream setting, thereby capturing fine-grained and global contextual information across different brightness and contrast enhancements. The fused spatiotemporal features are then processed by a BERT-based temporal model, which leverages its bidirectional self-attention to effectively capture long-range dependencies and contextual relationships across frames. Extensive experiments on the ARID V1.0 and ARID V1.5 dark video datasets show that MD-BERT outperforms existing methods, establishing a new state-of-the-art performance. Ablation studies further highlight the individual contributions of each input stream and the effectiveness of the proposed DFF and BERT modules. The official website of this work is available at: https://github.com/HrishavBakulBarua/DarkBERT
SFC-GAN: A Generative Adversarial Network for Brain Functional and Structural Connectome Translation
Jan 13, 2025Abstract:Modern brain imaging technologies have enabled the detailed reconstruction of human brain connectomes, capturing structural connectivity (SC) from diffusion MRI and functional connectivity (FC) from functional MRI. Understanding the intricate relationships between SC and FC is vital for gaining deeper insights into the brain's functional and organizational mechanisms. However, obtaining both SC and FC modalities simultaneously remains challenging, hindering comprehensive analyses. Existing deep generative models typically focus on synthesizing a single modality or unidirectional translation between FC and SC, thereby missing the potential benefits of bi-directional translation, especially in scenarios where only one connectome is available. Therefore, we propose Structural-Functional Connectivity GAN (SFC-GAN), a novel framework for bidirectional translation between SC and FC. This approach leverages the CycleGAN architecture, incorporating convolutional layers to effectively capture the spatial structures of brain connectomes. To preserve the topological integrity of these connectomes, we employ a structure-preserving loss that guides the model in capturing both global and local connectome patterns while maintaining symmetry. Our framework demonstrates superior performance in translating between SC and FC, outperforming baseline models in similarity and graph property evaluations compared to ground truth data, each translated modality can be effectively utilized for downstream classification.
Variational Potential Flow: A Novel Probabilistic Framework for Energy-Based Generative Modelling
Jul 21, 2024



Abstract:Energy based models (EBMs) are appealing for their generality and simplicity in data likelihood modeling, but have conventionally been difficult to train due to the unstable and time-consuming implicit MCMC sampling during contrastive divergence training. In this paper, we present a novel energy-based generative framework, Variational Potential Flow (VAPO), that entirely dispenses with implicit MCMC sampling and does not rely on complementary latent models or cooperative training. The VAPO framework aims to learn a potential energy function whose gradient (flow) guides the prior samples, so that their density evolution closely follows an approximate data likelihood homotopy. An energy loss function is then formulated to minimize the Kullback-Leibler divergence between density evolution of the flow-driven prior and the data likelihood homotopy. Images can be generated after training the potential energy, by initializing the samples from Gaussian prior and solving the ODE governing the potential flow on a fixed time interval using generic ODE solvers. Experiment results show that the proposed VAPO framework is capable of generating realistic images on various image datasets. In particular, our proposed framework achieves competitive FID scores for unconditional image generation on the CIFAR-10 and CelebA datasets.
ActNetFormer: Transformer-ResNet Hybrid Method for Semi-Supervised Action Recognition in Videos
Apr 09, 2024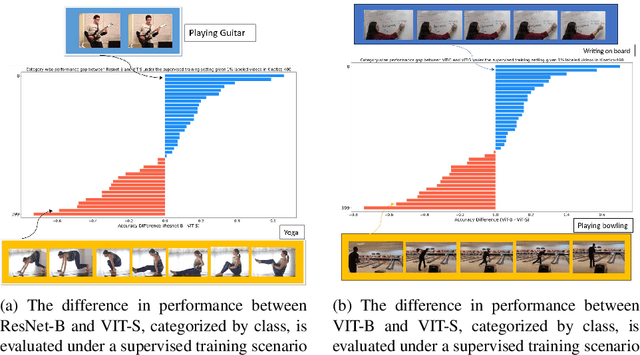

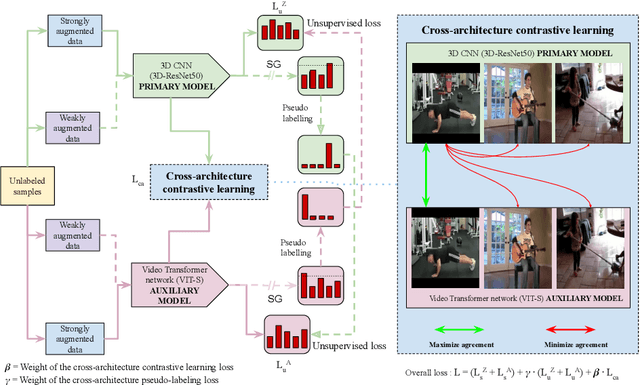

Abstract:Human action or activity recognition in videos is a fundamental task in computer vision with applications in surveillance and monitoring, self-driving cars, sports analytics, human-robot interaction and many more. Traditional supervised methods require large annotated datasets for training, which are expensive and time-consuming to acquire. This work proposes a novel approach using Cross-Architecture Pseudo-Labeling with contrastive learning for semi-supervised action recognition. Our framework leverages both labeled and unlabelled data to robustly learn action representations in videos, combining pseudo-labeling with contrastive learning for effective learning from both types of samples. We introduce a novel cross-architecture approach where 3D Convolutional Neural Networks (3D CNNs) and video transformers (VIT) are utilised to capture different aspects of action representations; hence we call it ActNetFormer. The 3D CNNs excel at capturing spatial features and local dependencies in the temporal domain, while VIT excels at capturing long-range dependencies across frames. By integrating these complementary architectures within the ActNetFormer framework, our approach can effectively capture both local and global contextual information of an action. This comprehensive representation learning enables the model to achieve better performance in semi-supervised action recognition tasks by leveraging the strengths of each of these architectures. Experimental results on standard action recognition datasets demonstrate that our approach performs better than the existing methods, achieving state-of-the-art performance with only a fraction of labeled data. The official website of this work is available at: https://github.com/rana2149/ActNetFormer.
Transferable Class-Modelling for Decentralized Source Attribution of GAN-Generated Images
Mar 18, 2022
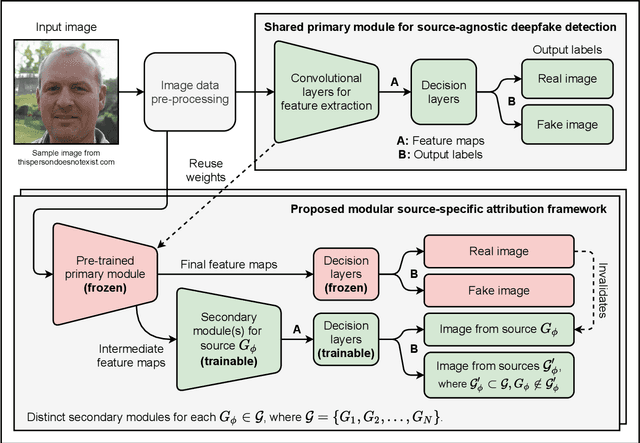
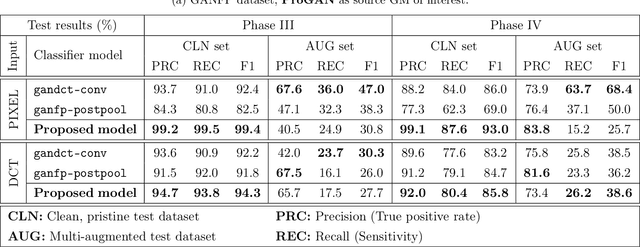
Abstract:GAN-generated deepfakes as a genre of digital images are gaining ground as both catalysts of artistic expression and malicious forms of deception, therefore demanding systems to enforce and accredit their ethical use. Existing techniques for the source attribution of synthetic images identify subtle intrinsic fingerprints using multiclass classification neural nets limited in functionality and scalability. Hence, we redefine the deepfake detection and source attribution problems as a series of related binary classification tasks. We leverage transfer learning to rapidly adapt forgery detection networks for multiple independent attribution problems, by proposing a semi-decentralized modular design to solve them simultaneously and efficiently. Class activation mapping is also demonstrated as an effective means of feature localization for model interpretation. Our models are determined via experimentation to be competitive with current benchmarks, and capable of decent performance on human portraits in ideal conditions. Decentralized fingerprint-based attribution is found to retain validity in the presence of novel sources, but is more susceptible to type II errors that intensify with image perturbations and attributive uncertainty. We describe both our conceptual framework and model prototypes for further enhancement when investigating the technical limits of reactive deepfake attribution.
Graph Autoencoders for Embedding Learning in Brain Networks and Major Depressive Disorder Identification
Jul 27, 2021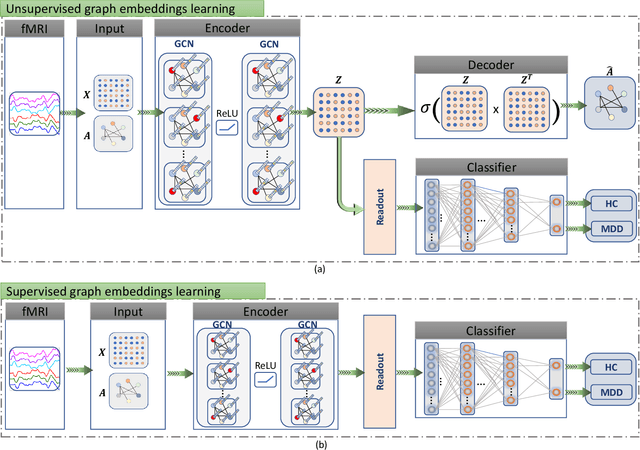
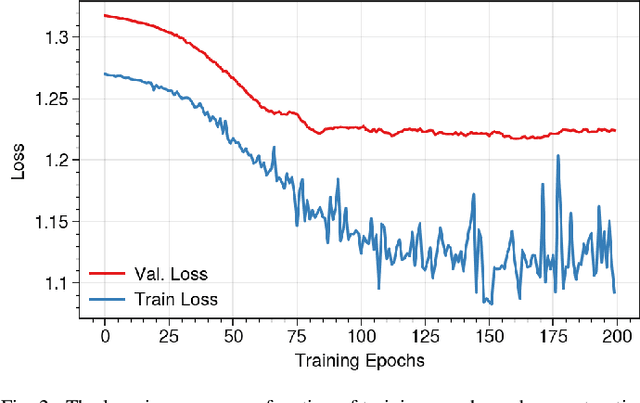
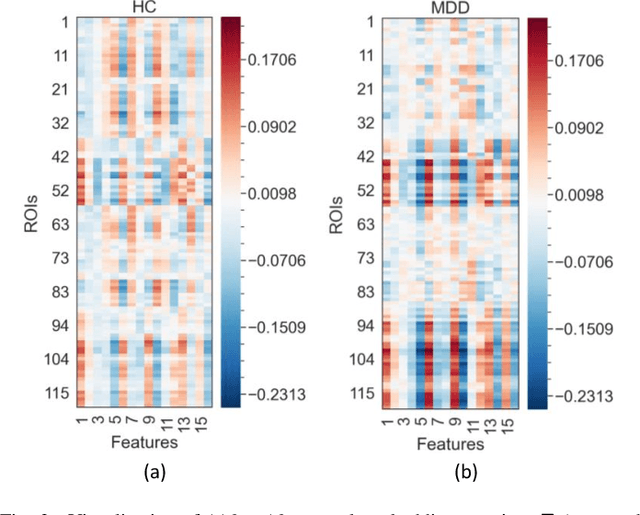
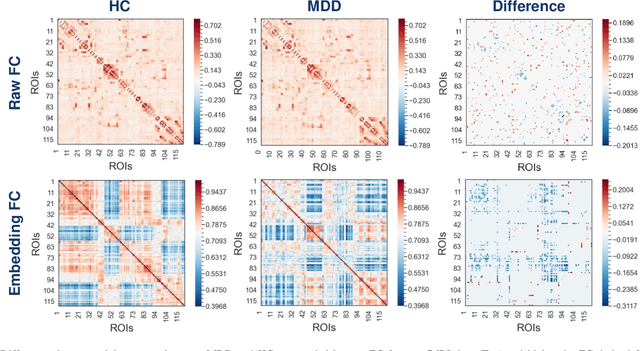
Abstract:Brain functional connectivity (FC) reveals biomarkers for identification of various neuropsychiatric disorders. Recent application of deep neural networks (DNNs) to connectome-based classification mostly relies on traditional convolutional neural networks using input connectivity matrices on a regular Euclidean grid. We propose a graph deep learning framework to incorporate the non-Euclidean information about graph structure for classifying functional magnetic resonance imaging (fMRI)- derived brain networks in major depressive disorder (MDD). We design a novel graph autoencoder (GAE) architecture based on the graph convolutional networks (GCNs) to embed the topological structure and node content of large-sized fMRI networks into low-dimensional latent representations. In network construction, we employ the Ledoit-Wolf (LDW) shrinkage method to estimate the high-dimensional FC metrics efficiently from fMRI data. We consider both supervised and unsupervised approaches for the graph embedded learning. The learned embeddings are then used as feature inputs for a deep fully-connected neural network (FCNN) to discriminate MDD from healthy controls. Evaluated on a resting-state fMRI MDD dataset with 43 subjects, results show that the proposed GAE-FCNN model significantly outperforms several state-of-the-art DNN methods for brain connectome classification, achieving accuracy of 72.50% using the LDW-FC metrics as node features. The graph embeddings of fMRI FC networks learned by the GAE also reveal apparent group differences between MDD and HC. Our new framework demonstrates feasibility of learning graph embeddings on brain networks to provide discriminative information for diagnosis of brain disorders.
Less is More: Micro-expression Recognition from Video using Apex Frame
Feb 15, 2018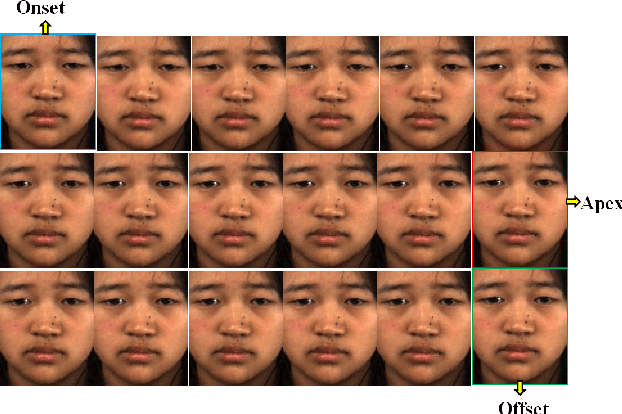
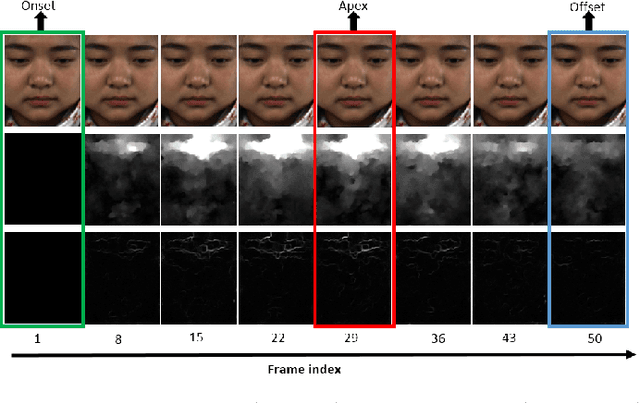
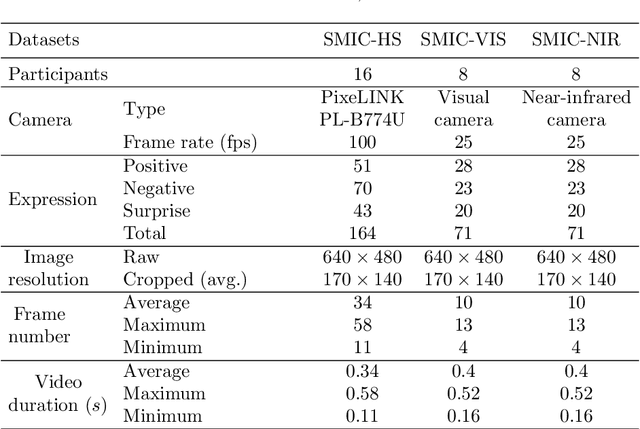

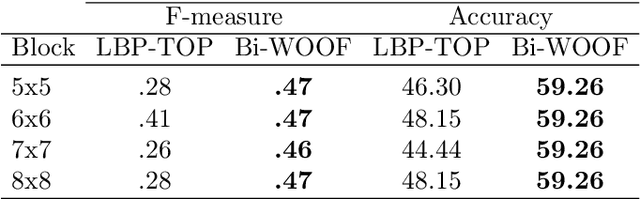
Abstract:Despite recent interest and advances in facial micro-expression research, there is still plenty room for improvement in terms of micro-expression recognition. Conventional feature extraction approaches for micro-expression video consider either the whole video sequence or a part of it, for representation. However, with the high-speed video capture of micro-expressions (100-200 fps), are all frames necessary to provide a sufficiently meaningful representation? Is the luxury of data a bane to accurate recognition? A novel proposition is presented in this paper, whereby we utilize only two images per video: the apex frame and the onset frame. The apex frame of a video contains the highest intensity of expression changes among all frames, while the onset is the perfect choice of a reference frame with neutral expression. A new feature extractor, Bi-Weighted Oriented Optical Flow (Bi-WOOF) is proposed to encode essential expressiveness of the apex frame. We evaluated the proposed method on five micro-expression databases: CAS(ME)$^2$, CASME II, SMIC-HS, SMIC-NIR and SMIC-VIS. Our experiments lend credence to our hypothesis, with our proposed technique achieving a state-of-the-art F1-score recognition performance of 61% and 62% in the high frame rate CASME II and SMIC-HS databases respectively.
* 14 pages double-column, author affiliations updated, acknowledgment of grant support added
Spontaneous expression classification in the encrypted domain
Mar 14, 2014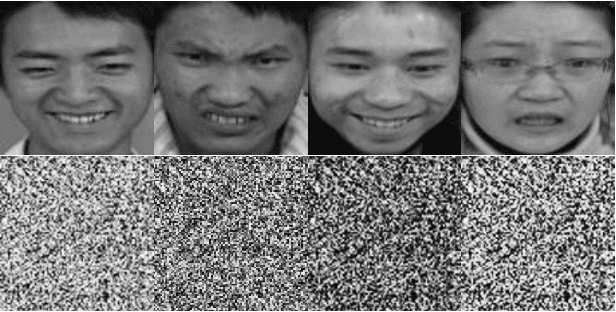
Abstract:To date, most facial expression analysis have been based on posed image databases and is carried out without being able to protect the identity of the subjects whose expressions are being recognised. In this paper, we propose and implement a system for classifying facial expressions of images in the encrypted domain based on a Paillier cryptosystem implementation of Fisher Linear Discriminant Analysis and k-nearest neighbour (FLDA + kNN). We present results of experiments carried out on a recently developed natural visible and infrared facial expression (NVIE) database of spontaneous images. To the best of our knowledge, this is the first system that will allow the recog-nition of encrypted spontaneous facial expressions by a remote server on behalf of a client.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge