Randall O'Reilly
Towards Reverse-Engineering the Brain: Brain-Derived Neuromorphic Computing Approach with Photonic, Electronic, and Ionic Dynamicity in 3D integrated circuits
Mar 28, 2024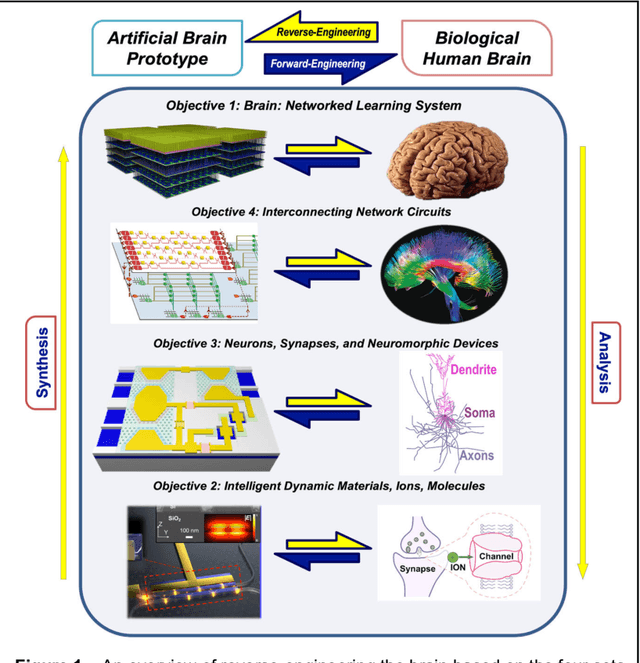
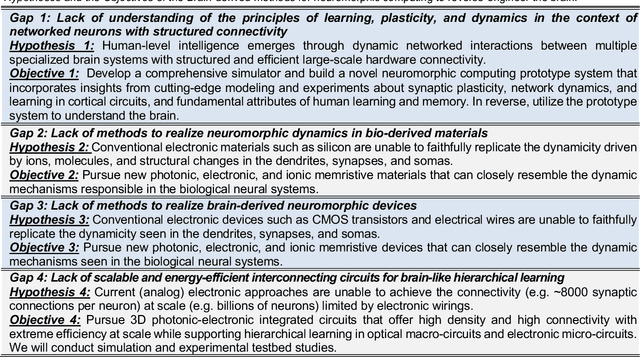
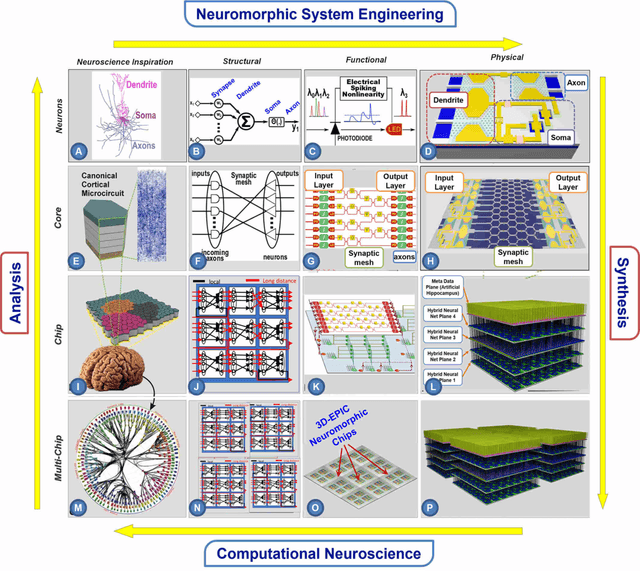
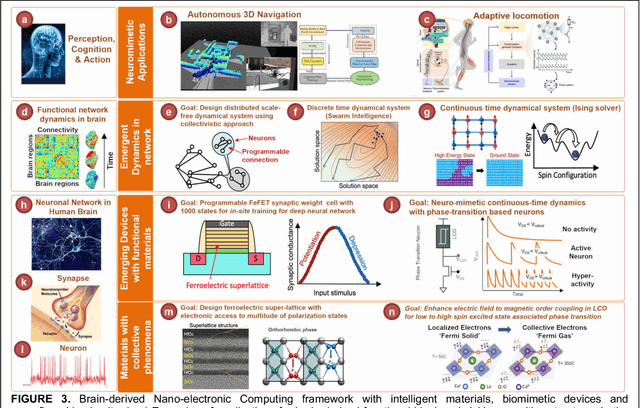
Abstract:The human brain has immense learning capabilities at extreme energy efficiencies and scale that no artificial system has been able to match. For decades, reverse engineering the brain has been one of the top priorities of science and technology research. Despite numerous efforts, conventional electronics-based methods have failed to match the scalability, energy efficiency, and self-supervised learning capabilities of the human brain. On the other hand, very recent progress in the development of new generations of photonic and electronic memristive materials, device technologies, and 3D electronic-photonic integrated circuits (3D EPIC ) promise to realize new brain-derived neuromorphic systems with comparable connectivity, density, energy-efficiency, and scalability. When combined with bio-realistic learning algorithms and architectures, it may be possible to realize an 'artificial brain' prototype with general self-learning capabilities. This paper argues the possibility of reverse-engineering the brain through architecting a prototype of a brain-derived neuromorphic computing system consisting of artificial electronic, ionic, photonic materials, devices, and circuits with dynamicity resembling the bio-plausible molecular, neuro/synaptic, neuro-circuit, and multi-structural hierarchical macro-circuits of the brain based on well-tested computational models. We further argue the importance of bio-plausible local learning algorithms applicable to the neuromorphic computing system that capture the flexible and adaptive unsupervised and self-supervised learning mechanisms central to human intelligence. Most importantly, we emphasize that the unique capabilities in brain-derived neuromorphic computing prototype systems will enable us to understand links between specific neuronal and network-level properties with system-level functioning and behavior.
The Relational Bottleneck as an Inductive Bias for Efficient Abstraction
Sep 12, 2023

Abstract:A central challenge for cognitive science is to explain how abstract concepts are acquired from limited experience. This effort has often been framed in terms of a dichotomy between empiricist and nativist approaches, most recently embodied by debates concerning deep neural networks and symbolic cognitive models. Here, we highlight a recently emerging line of work that suggests a novel reconciliation of these approaches, by exploiting an inductive bias that we term the relational bottleneck. We review a family of models that employ this approach to induce abstractions in a data-efficient manner, emphasizing their potential as candidate models for the acquisition of abstract concepts in the human mind and brain.
Adaptive Synaptic Failure Enables Sampling from Posterior Predictive Distributions in the Brain
Oct 04, 2022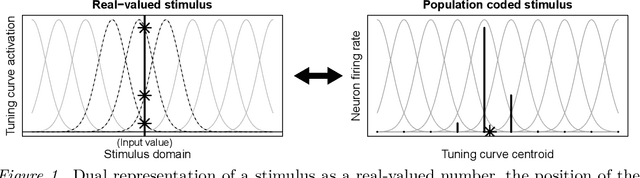
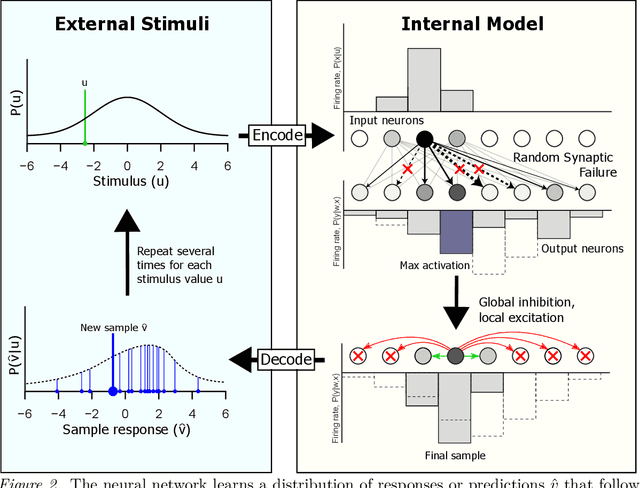
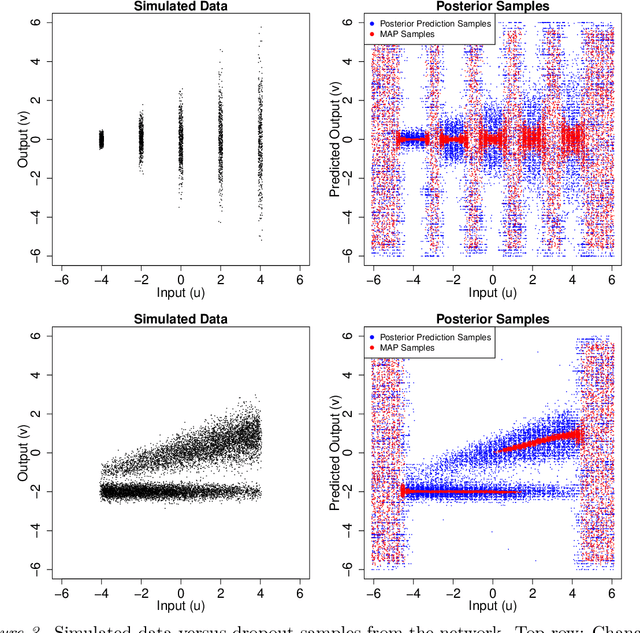
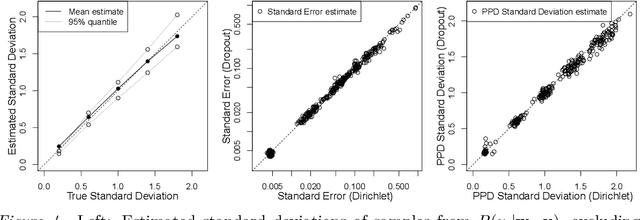
Abstract:Bayesian interpretations of neural processing require that biological mechanisms represent and operate upon probability distributions in accordance with Bayes' theorem. Many have speculated that synaptic failure constitutes a mechanism of variational, i.e., approximate, Bayesian inference in the brain. Whereas models have previously used synaptic failure to sample over uncertainty in model parameters, we demonstrate that by adapting transmission probabilities to learned network weights, synaptic failure can sample not only over model uncertainty, but complete posterior predictive distributions as well. Our results potentially explain the brain's ability to perform probabilistic searches and to approximate complex integrals. These operations are involved in numerous calculations, including likelihood evaluation and state value estimation for complex planning.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge