Rajmund Nagy
Towards a GENEA Leaderboard -- an Extended, Living Benchmark for Evaluating and Advancing Conversational Motion Synthesis
Oct 08, 2024


Abstract:Current evaluation practices in speech-driven gesture generation lack standardisation and focus on aspects that are easy to measure over aspects that actually matter. This leads to a situation where it is impossible to know what is the state of the art, or to know which method works better for which purpose when comparing two publications. In this position paper, we review and give details on issues with existing gesture-generation evaluation, and present a novel proposal for remedying them. Specifically, we announce an upcoming living leaderboard to benchmark progress in conversational motion synthesis. Unlike earlier gesture-generation challenges, the leaderboard will be updated with large-scale user studies of new gesture-generation systems multiple times per year, and systems on the leaderboard can be submitted to any publication venue that their authors prefer. By evolving the leaderboard evaluation data and tasks over time, the effort can keep driving progress towards the most important end goals identified by the community. We actively seek community involvement across the entire evaluation pipeline: from data and tasks for the evaluation, via tooling, to the systems evaluated. In other words, our proposal will not only make it easier for researchers to perform good evaluations, but their collective input and contributions will also help drive the future of gesture-generation research.
The GENEA Challenge 2023: A large scale evaluation of gesture generation models in monadic and dyadic settings
Aug 24, 2023Abstract:This paper reports on the GENEA Challenge 2023, in which participating teams built speech-driven gesture-generation systems using the same speech and motion dataset, followed by a joint evaluation. This year's challenge provided data on both sides of a dyadic interaction, allowing teams to generate full-body motion for an agent given its speech (text and audio) and the speech and motion of the interlocutor. We evaluated 12 submissions and 2 baselines together with held-out motion-capture data in several large-scale user studies. The studies focused on three aspects: 1) the human-likeness of the motion, 2) the appropriateness of the motion for the agent's own speech whilst controlling for the human-likeness of the motion, and 3) the appropriateness of the motion for the behaviour of the interlocutor in the interaction, using a setup that controls for both the human-likeness of the motion and the agent's own speech. We found a large span in human-likeness between challenge submissions, with a few systems rated close to human mocap. Appropriateness seems far from being solved, with most submissions performing in a narrow range slightly above chance, far behind natural motion. The effect of the interlocutor is even more subtle, with submitted systems at best performing barely above chance. Interestingly, a dyadic system being highly appropriate for agent speech does not necessarily imply high appropriateness for the interlocutor. Additional material is available via the project website at https://svito-zar.github.io/GENEAchallenge2023/ .
Listen, denoise, action! Audio-driven motion synthesis with diffusion models
Nov 17, 2022
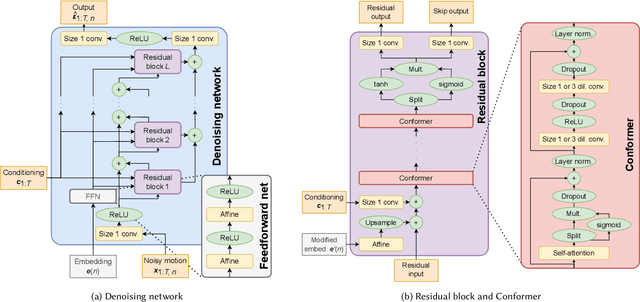
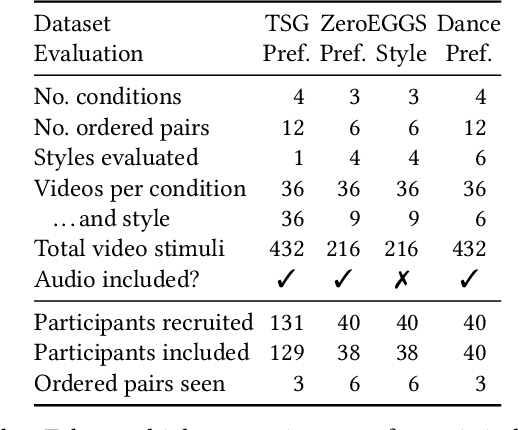
Abstract:Diffusion models have experienced a surge of interest as highly expressive yet efficiently trainable probabilistic models. We show that these models are an excellent fit for synthesising human motion that co-occurs with audio, for example co-speech gesticulation, since motion is complex and highly ambiguous given audio, calling for a probabilistic description. Specifically, we adapt the DiffWave architecture to model 3D pose sequences, putting Conformers in place of dilated convolutions for improved accuracy. We also demonstrate control over motion style, using classifier-free guidance to adjust the strength of the stylistic expression. Gesture-generation experiments on the Trinity Speech-Gesture and ZeroEGGS datasets confirm that the proposed method achieves top-of-the-line motion quality, with distinctive styles whose expression can be made more or less pronounced. We also synthesise dance motion and path-driven locomotion using the same model architecture. Finally, we extend the guidance procedure to perform style interpolation in a manner that is appealing for synthesis tasks and has connections to product-of-experts models, a contribution we believe is of independent interest. Video examples are available at https://www.speech.kth.se/research/listen-denoise-action/
Multimodal analysis of the predictability of hand-gesture properties
Aug 12, 2021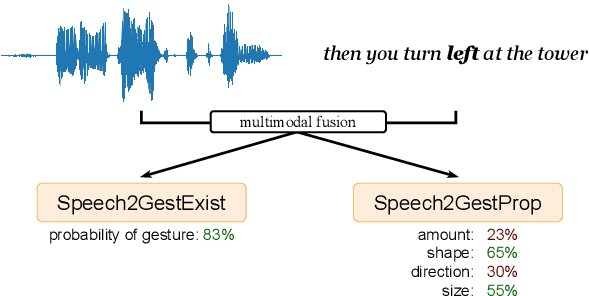
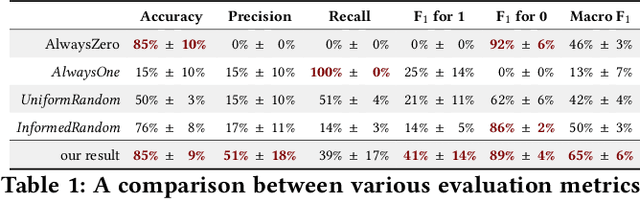
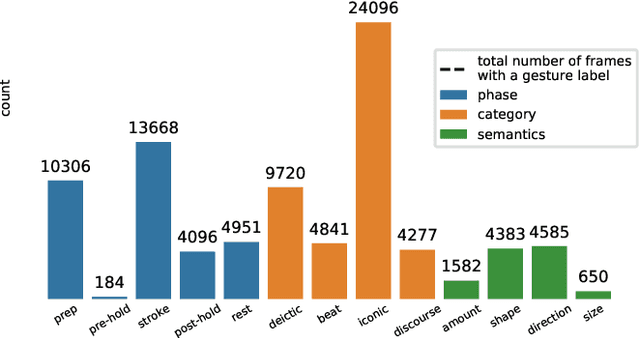
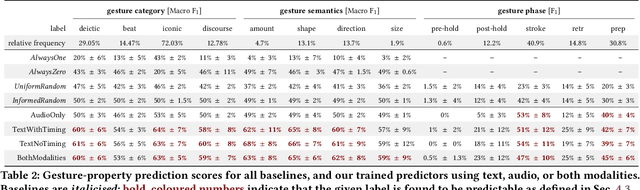
Abstract:Embodied conversational agents benefit from being able to accompany their speech with gestures. Although many data-driven approaches to gesture generation have been proposed in recent years, it is still unclear whether such systems can consistently generate gestures that convey meaning. We investigate which gesture properties (phase, category, and semantics) can be predicted from speech text and/or audio using contemporary deep learning. In extensive experiments, we show that gesture properties related to gesture meaning (semantics and category) are predictable from text features (time-aligned BERT embeddings) alone, but not from prosodic audio features, while rhythm-related gesture properties (phase) on the other hand can be predicted from either audio, text (with word-level timing information), or both. These results are encouraging as they indicate that it is possible to equip an embodied agent with content-wise meaningful co-speech gestures using a machine-learning model.
Speech2Properties2Gestures: Gesture-Property Prediction as a Tool for Generating Representational Gestures from Speech
Jun 28, 2021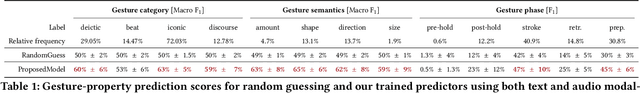
Abstract:We propose a new framework for gesture generation, aiming to allow data-driven approaches to produce more semantically rich gestures. Our approach first predicts whether to gesture, followed by a prediction of the gesture properties. Those properties are then used as conditioning for a modern probabilistic gesture-generation model capable of high-quality output. This empowers the approach to generate gestures that are both diverse and representational.
A Framework for Integrating Gesture Generation Models into Interactive Conversational Agents
Feb 24, 2021Abstract:Embodied conversational agents (ECAs) benefit from non-verbal behavior for natural and efficient interaction with users. Gesticulation - hand and arm movements accompanying speech - is an essential part of non-verbal behavior. Gesture generation models have been developed for several decades: starting with rule-based and ending with mainly data-driven methods. To date, recent end-to-end gesture generation methods have not been evaluated in a real-time interaction with users. We present a proof-of-concept framework, which is intended to facilitate evaluation of modern gesture generation models in interaction. We demonstrate an extensible open-source framework that contains three components: 1) a 3D interactive agent; 2) a chatbot backend; 3) a gesticulating system. Each component can be replaced, making the proposed framework applicable for investigating the effect of different gesturing models in real-time interactions with different communication modalities, chatbot backends, or different agent appearances. The code and video are available at the project page https://nagyrajmund.github.io/project/gesturebot.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge