Rajeev Thakur
Who Gets the Reward, Who Gets the Blame? Evaluation-Aligned Training Signals for Multi-LLM Agents
Nov 17, 2025Abstract:Large Language Models (LLMs) in multi-agent systems (MAS) have shown promise for complex tasks, yet current training methods lack principled ways to connect system-level evaluation with agent-level and message-level learning. We propose a theoretical framework that unifies cooperative game-theoretic attribution with process reward modeling to transform system evaluation into agent credit and then into response-level signals. Unlike prior approaches that rely only on attribution (e.g., Shapley) or step-level labels (e.g., PRM), our method produces local, signed, and credit-conserving signals. In success cases, Shapley-based credit assignment fairly allocates outcomes across agents and is refined into per-message rewards that promote cooperation while discouraging redundancy or sabotage. In failure cases, first-error localization yields repair-aware preferences that penalize harmful steps while rewarding corrective attempts. The resulting signals are bounded, cooperative, and directly compatible with reinforcement-based or preference-based post-training, providing a unified and auditable pathway from global evaluation to local supervision in LLM multi-agent training. Our contribution is conceptual: we present a theoretical foundation and training signals, leaving empirical validation for future work.
Employing Artificial Intelligence to Steer Exascale Workflows with Colmena
Aug 26, 2024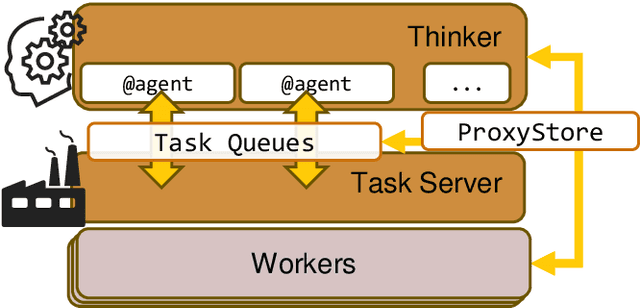
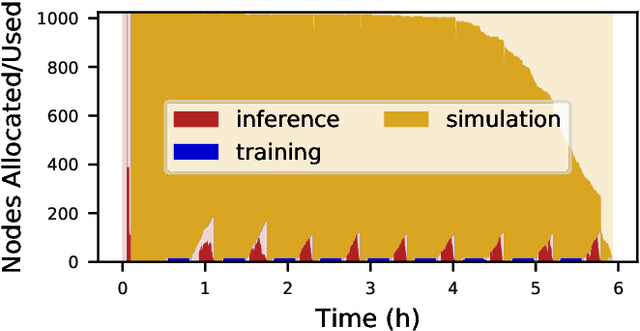
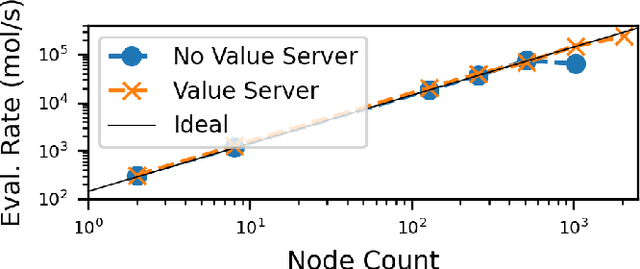
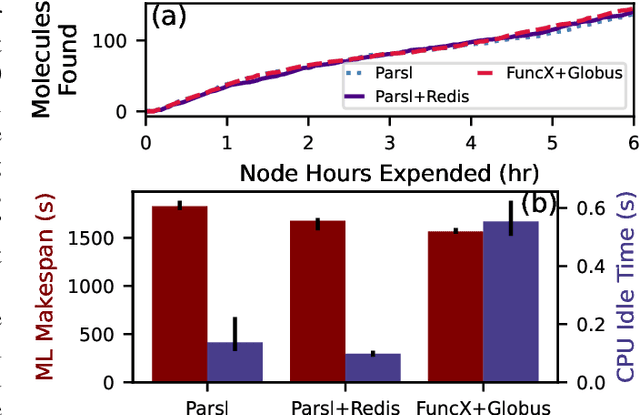
Abstract:Computational workflows are a common class of application on supercomputers, yet the loosely coupled and heterogeneous nature of workflows often fails to take full advantage of their capabilities. We created Colmena to leverage the massive parallelism of a supercomputer by using Artificial Intelligence (AI) to learn from and adapt a workflow as it executes. Colmena allows scientists to define how their application should respond to events (e.g., task completion) as a series of cooperative agents. In this paper, we describe the design of Colmena, the challenges we overcame while deploying applications on exascale systems, and the science workflows we have enhanced through interweaving AI. The scaling challenges we discuss include developing steering strategies that maximize node utilization, introducing data fabrics that reduce communication overhead of data-intensive tasks, and implementing workflow tasks that cache costly operations between invocations. These innovations coupled with a variety of application patterns accessible through our agent-based steering model have enabled science advances in chemistry, biophysics, and materials science using different types of AI. Our vision is that Colmena will spur creative solutions that harness AI across many domains of scientific computing.
A Comprehensive Performance Study of Large Language Models on Novel AI Accelerators
Oct 06, 2023Abstract:Artificial intelligence (AI) methods have become critical in scientific applications to help accelerate scientific discovery. Large language models (LLMs) are being considered as a promising approach to address some of the challenging problems because of their superior generalization capabilities across domains. The effectiveness of the models and the accuracy of the applications is contingent upon their efficient execution on the underlying hardware infrastructure. Specialized AI accelerator hardware systems have recently become available for accelerating AI applications. However, the comparative performance of these AI accelerators on large language models has not been previously studied. In this paper, we systematically study LLMs on multiple AI accelerators and GPUs and evaluate their performance characteristics for these models. We evaluate these systems with (i) a micro-benchmark using a core transformer block, (ii) a GPT- 2 model, and (iii) an LLM-driven science use case, GenSLM. We present our findings and analyses of the models' performance to better understand the intrinsic capabilities of AI accelerators. Furthermore, our analysis takes into account key factors such as sequence lengths, scaling behavior, sparsity, and sensitivity to gradient accumulation steps.
Cloud Services Enable Efficient AI-Guided Simulation Workflows across Heterogeneous Resources
Mar 15, 2023Abstract:Applications that fuse machine learning and simulation can benefit from the use of multiple computing resources, with, for example, simulation codes running on highly parallel supercomputers and AI training and inference tasks on specialized accelerators. Here, we present our experiences deploying two AI-guided simulation workflows across such heterogeneous systems. A unique aspect of our approach is our use of cloud-hosted management services to manage challenging aspects of cross-resource authentication and authorization, function-as-a-service (FaaS) function invocation, and data transfer. We show that these methods can achieve performance parity with systems that rely on direct connection between resources. We achieve parity by integrating the FaaS system and data transfer capabilities with a system that passes data by reference among managers and workers, and a user-configurable steering algorithm to hide data transfer latencies. We anticipate that this ease of use can enable routine use of heterogeneous resources in computational science.
Colmena: Scalable Machine-Learning-Based Steering of Ensemble Simulations for High Performance Computing
Oct 06, 2021



Abstract:Scientific applications that involve simulation ensembles can be accelerated greatly by using experiment design methods to select the best simulations to perform. Methods that use machine learning (ML) to create proxy models of simulations show particular promise for guiding ensembles but are challenging to deploy because of the need to coordinate dynamic mixes of simulation and learning tasks. We present Colmena, an open-source Python framework that allows users to steer campaigns by providing just the implementations of individual tasks plus the logic used to choose which tasks to execute when. Colmena handles task dispatch, results collation, ML model invocation, and ML model (re)training, using Parsl to execute tasks on HPC systems. We describe the design of Colmena and illustrate its capabilities by applying it to electrolyte design, where it both scales to 65536 CPUs and accelerates the discovery rate for high-performance molecules by a factor of 100 over unguided searches.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge