Rahul Mishra
Shadow Unlearning: A Neuro-Semantic Approach to Fidelity-Preserving Faceless Forgetting in LLMs
Jan 07, 2026Abstract:Machine unlearning aims to selectively remove the influence of specific training samples to satisfy privacy regulations such as the GDPR's 'Right to be Forgotten'. However, many existing methods require access to the data being removed, exposing it to membership inference attacks and potential misuse of Personally Identifiable Information (PII). We address this critical challenge by proposing Shadow Unlearning, a novel paradigm of approximate unlearning, that performs machine unlearning on anonymized forget data without exposing PII. We further propose a novel privacy-preserving framework, Neuro-Semantic Projector Unlearning (NSPU) to achieve Shadow unlearning. To evaluate our method, we compile Multi-domain Fictitious Unlearning (MuFU) forget set across five diverse domains and introduce an evaluation stack to quantify the trade-off between knowledge retention and unlearning effectiveness. Experimental results on various LLMs show that NSPU achieves superior unlearning performance, preserves model utility, and enhances user privacy. Additionally, the proposed approach is at least 10 times more computationally efficient than standard unlearning approaches. Our findings foster a new direction for privacy-aware machine unlearning that balances data protection and model fidelity.
SpectralKrum: A Spectral-Geometric Defense Against Byzantine Attacks in Federated Learning
Dec 12, 2025



Abstract:Federated Learning (FL) distributes model training across clients who retain their data locally, but this architecture exposes a fundamental vulnerability: Byzantine clients can inject arbitrarily corrupted updates that degrade or subvert the global model. While robust aggregation methods (including Krum, Bulyan, and coordinate-wise defenses) offer theoretical guarantees under idealized assumptions, their effectiveness erodes substantially when client data distributions are heterogeneous (non-IID) and adversaries can observe or approximate the defense mechanism. This paper introduces SpectralKrum, a defense that fuses spectral subspace estimation with geometric neighbor-based selection. The core insight is that benign optimization trajectories, despite per-client heterogeneity, concentrate near a low-dimensional manifold that can be estimated from historical aggregates. SpectralKrum projects incoming updates into this learned subspace, applies Krum selection in compressed coordinates, and filters candidates whose orthogonal residual energy exceeds a data-driven threshold. The method requires no auxiliary data, operates entirely on model updates, and preserves FL privacy properties. We evaluate SpectralKrum against eight robust baselines across seven attack scenarios on CIFAR-10 with Dirichlet-distributed non-IID partitions (alpha = 0.1). Experiments spanning over 56,000 training rounds show that SpectralKrum is competitive against directional and subspace-aware attacks (adaptive-steer, buffer-drift), but offers limited advantage under label-flip and min-max attacks where malicious updates remain spectrally indistinguishable from benign ones.
i-Mask: An Intelligent Mask for Breath-Driven Activity Recognition
Sep 04, 2025



Abstract:The patterns of inhalation and exhalation contain important physiological signals that can be used to anticipate human behavior, health trends, and vital parameters. Human activity recognition (HAR) is fundamentally connected to these vital signs, providing deeper insights into well-being and enabling real-time health monitoring. This work presents i-Mask, a novel HAR approach that leverages exhaled breath patterns captured using a custom-developed mask equipped with integrated sensors. Data collected from volunteers wearing the mask undergoes noise filtering, time-series decomposition, and labeling to train predictive models. Our experimental results validate the effectiveness of the approach, achieving over 95\% accuracy and highlighting its potential in healthcare and fitness applications.
HalluCounter: Reference-free LLM Hallucination Detection in the Wild!
Mar 06, 2025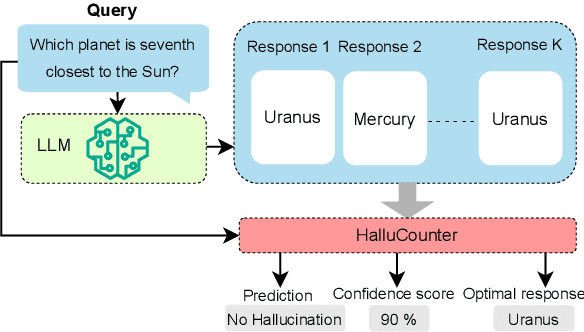

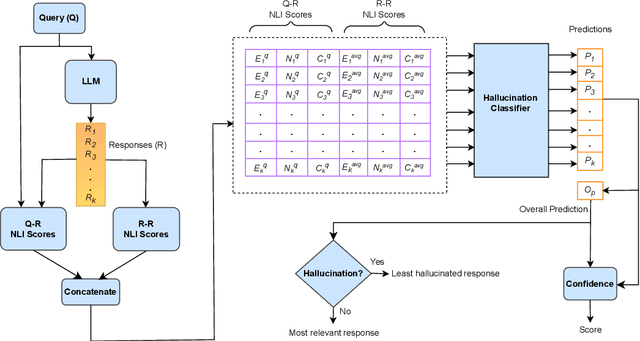
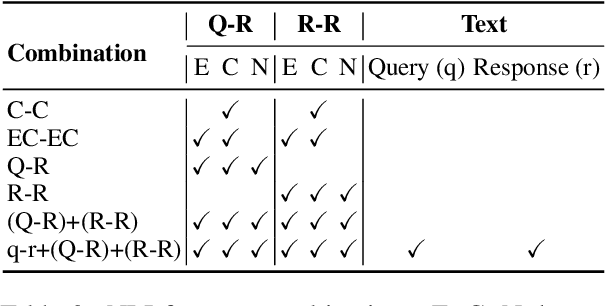
Abstract:Response consistency-based, reference-free hallucination detection (RFHD) methods do not depend on internal model states, such as generation probabilities or gradients, which Grey-box models typically rely on but are inaccessible in closed-source LLMs. However, their inability to capture query-response alignment patterns often results in lower detection accuracy. Additionally, the lack of large-scale benchmark datasets spanning diverse domains remains a challenge, as most existing datasets are limited in size and scope. To this end, we propose HalluCounter, a novel reference-free hallucination detection method that utilizes both response-response and query-response consistency and alignment patterns. This enables the training of a classifier that detects hallucinations and provides a confidence score and an optimal response for user queries. Furthermore, we introduce HalluCounterEval, a benchmark dataset comprising both synthetically generated and human-curated samples across multiple domains. Our method outperforms state-of-the-art approaches by a significant margin, achieving over 90\% average confidence in hallucination detection across datasets.
One Arrow, Many Targets: Probing LLMs for Multi-Attribute Controllable Text Summarization
Nov 02, 2024



Abstract:Text summarization is a well-established task within the natural language processing (NLP) community. However, the focus on controllable summarization tailored to user requirements is gaining traction only recently. While several efforts explore controllability in text summarization, the investigation of Multi-Attribute Controllable Summarization (MACS) remains limited. This work addresses this gap by examining the MACS task through the lens of large language models (LLMs), using various learning paradigms, particularly low-rank adapters. We experiment with different popular adapter fine-tuning strategies to assess the effectiveness of the resulting models in retaining cues and patterns associated with multiple controllable attributes. Additionally, we propose and evaluate a novel hierarchical adapter fusion technique to integrate learnings from two distinct controllable attributes. Subsquently, we present our findings, discuss the challenges encountered, and suggest potential avenues for advancing the MACS task.
KTCR: Improving Implicit Hate Detection with Knowledge Transfer driven Concept Refinement
Oct 20, 2024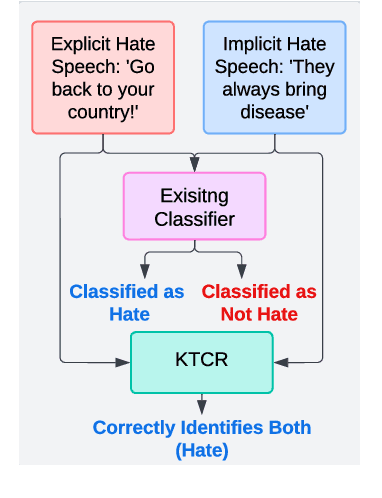
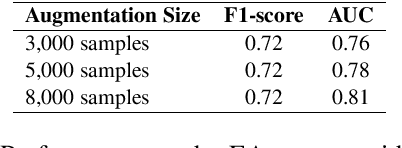
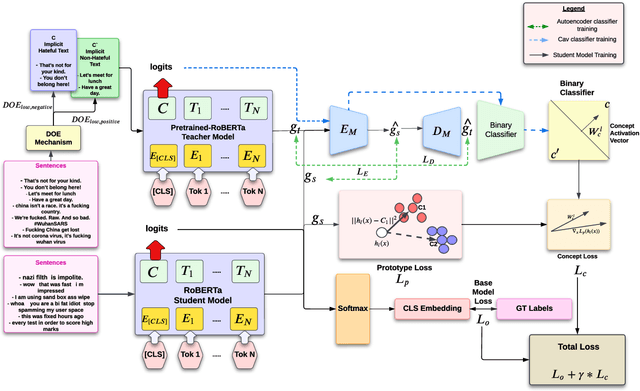
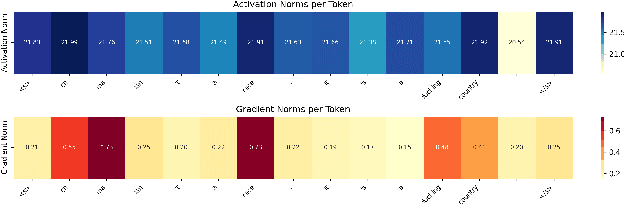
Abstract:The constant shifts in social and political contexts, driven by emerging social movements and political events, lead to new forms of hate content and previously unrecognized hate patterns that machine learning models may not have captured. Some recent literature proposes the data augmentation-based techniques to enrich existing hate datasets by incorporating samples that reveal new implicit hate patterns. This approach aims to improve the model's performance on out-of-domain implicit hate instances. It is observed, that further addition of more samples for augmentation results in the decrease of the performance of the model. In this work, we propose a Knowledge Transfer-driven Concept Refinement method that distills and refines the concepts related to implicit hate samples through novel prototype alignment and concept losses, alongside data augmentation based on concept activation vectors. Experiments with several publicly available datasets show that incorporating additional implicit samples reflecting new hate patterns through concept refinement enhances the model's performance, surpassing baseline results while maintaining cross-dataset generalization capabilities.\footnote{DISCLAIMER: This paper contains explicit statements that are potentially offensive.}
SceneGraMMi: Scene Graph-boosted Hybrid-fusion for Multi-Modal Misinformation Veracity Prediction
Oct 20, 2024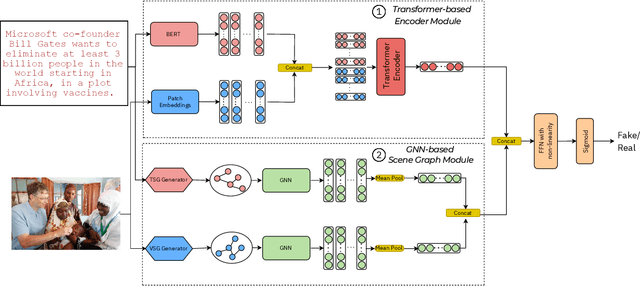

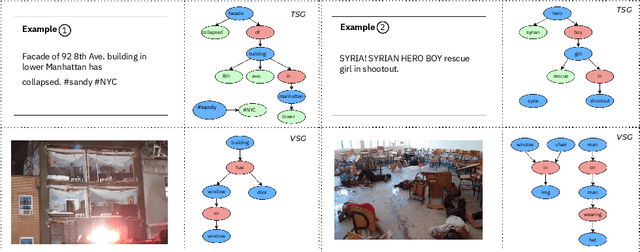
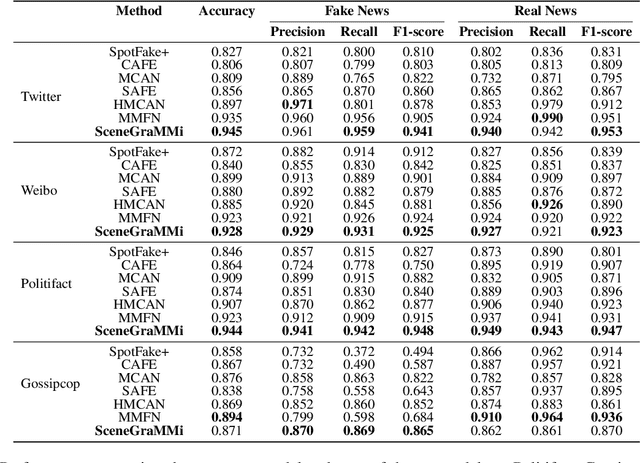
Abstract:Misinformation undermines individual knowledge and affects broader societal narratives. Despite growing interest in the research community in multi-modal misinformation detection, existing methods exhibit limitations in capturing semantic cues, key regions, and cross-modal similarities within multi-modal datasets. We propose SceneGraMMi, a Scene Graph-boosted Hybrid-fusion approach for Multi-modal Misinformation veracity prediction, which integrates scene graphs across different modalities to improve detection performance. Experimental results across four benchmark datasets show that SceneGraMMi consistently outperforms state-of-the-art methods. In a comprehensive ablation study, we highlight the contribution of each component, while Shapley values are employed to examine the explainability of the model's decision-making process.
DiscoGraMS: Enhancing Movie Screen-Play Summarization using Movie Character-Aware Discourse Graph
Oct 18, 2024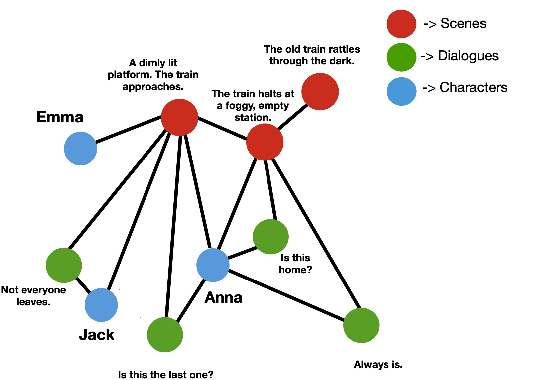
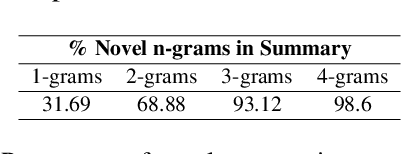
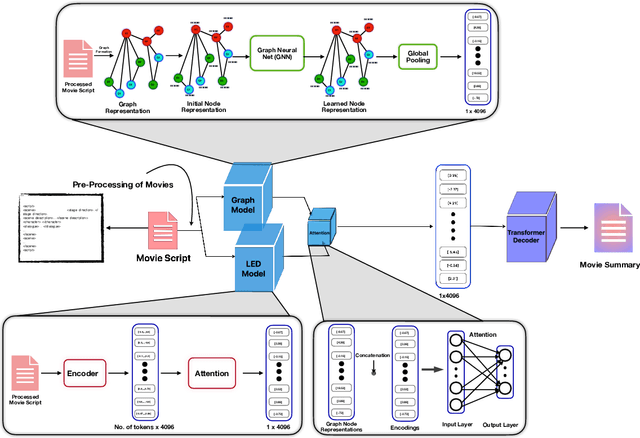
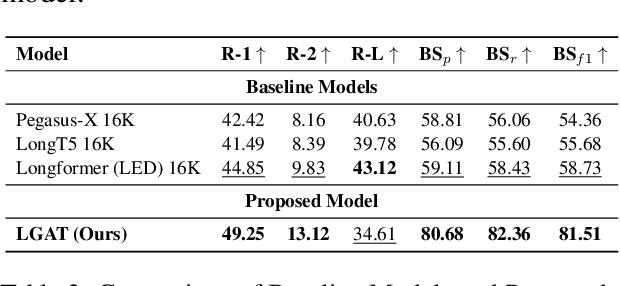
Abstract:Summarizing movie screenplays presents a unique set of challenges compared to standard document summarization. Screenplays are not only lengthy, but also feature a complex interplay of characters, dialogues, and scenes, with numerous direct and subtle relationships and contextual nuances that are difficult for machine learning models to accurately capture and comprehend. Recent attempts at screenplay summarization focus on fine-tuning transformer-based pre-trained models, but these models often fall short in capturing long-term dependencies and latent relationships, and frequently encounter the "lost in the middle" issue. To address these challenges, we introduce DiscoGraMS, a novel resource that represents movie scripts as a movie character-aware discourse graph (CaD Graph). This approach is well-suited for various downstream tasks, such as summarization, question-answering, and salience detection. The model aims to preserve all salient information, offering a more comprehensive and faithful representation of the screenplay's content. We further explore a baseline method that combines the CaD Graph with the corresponding movie script through a late fusion of graph and text modalities, and we present very initial promising results.
Utilizing Transfer Learning and pre-trained Models for Effective Forest Fire Detection: A Case Study of Uttarakhand
Oct 09, 2024
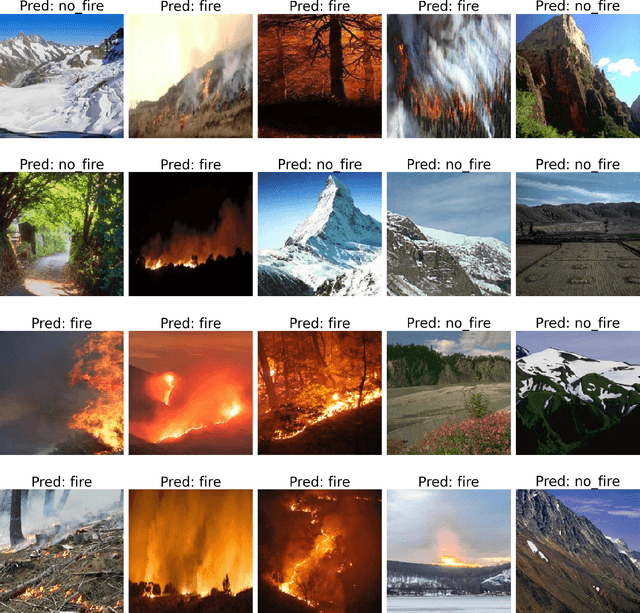
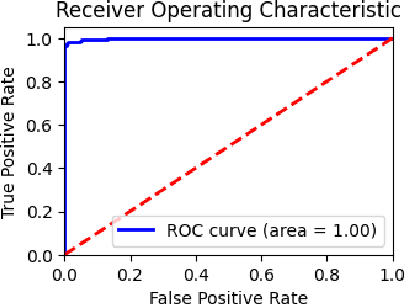
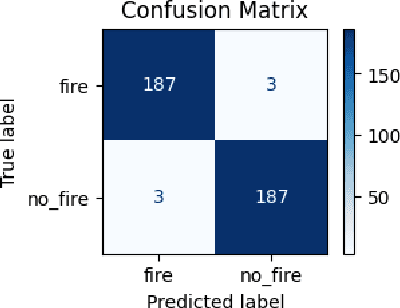
Abstract:Forest fires pose a significant threat to the environment, human life, and property. Early detection and response are crucial to mitigating the impact of these disasters. However, traditional forest fire detection methods are often hindered by our reliability on manual observation and satellite imagery with low spatial resolution. This paper emphasizes the role of transfer learning in enhancing forest fire detection in India, particularly in overcoming data collection challenges and improving model accuracy across various regions. We compare traditional learning methods with transfer learning, focusing on the unique challenges posed by regional differences in terrain, climate, and vegetation. Transfer learning can be categorized into several types based on the similarity between the source and target tasks, as well as the type of knowledge transferred. One key method is utilizing pre-trained models for efficient transfer learning, which significantly reduces the need for extensive labeled data. We outline the transfer learning process, demonstrating how researchers can adapt pre-trained models like MobileNetV2 for specific tasks such as forest fire detection. Finally, we present experimental results from training and evaluating a deep learning model using the Uttarakhand forest fire dataset, showcasing the effectiveness of transfer learning in this context.
Seg-HGNN: Unsupervised and Light-Weight Image Segmentation with Hyperbolic Graph Neural Networks
Sep 10, 2024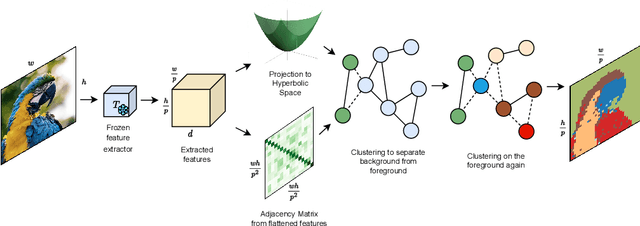
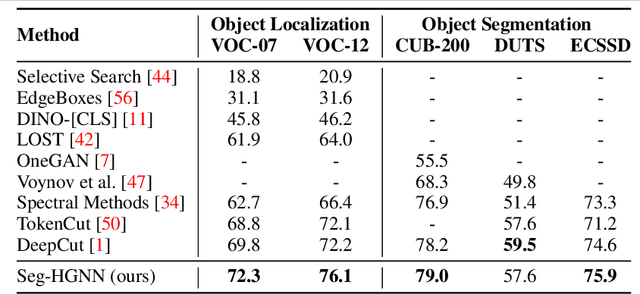

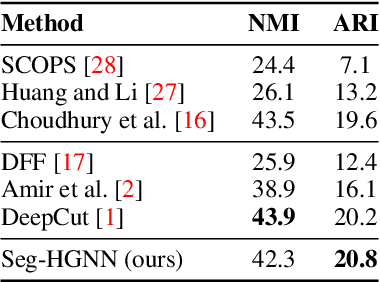
Abstract:Image analysis in the euclidean space through linear hyperspaces is well studied. However, in the quest for more effective image representations, we turn to hyperbolic manifolds. They provide a compelling alternative to capture complex hierarchical relationships in images with remarkably small dimensionality. To demonstrate hyperbolic embeddings' competence, we introduce a light-weight hyperbolic graph neural network for image segmentation, encompassing patch-level features in a very small embedding size. Our solution, Seg-HGNN, surpasses the current best unsupervised method by 2.5\%, 4\% on VOC-07, VOC-12 for localization, and by 0.8\%, 1.3\% on CUB-200, ECSSD for segmentation, respectively. With less than 7.5k trainable parameters, Seg-HGNN delivers effective and fast ($\approx 2$ images/second) results on very standard GPUs like the GTX1650. This empirical evaluation presents compelling evidence of the efficacy and potential of hyperbolic representations for vision tasks.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge