Qucheng Peng
Lifelong Domain Adaptive 3D Human Pose Estimation
Dec 29, 2025Abstract:3D Human Pose Estimation (3D HPE) is vital in various applications, from person re-identification and action recognition to virtual reality. However, the reliance on annotated 3D data collected in controlled environments poses challenges for generalization to diverse in-the-wild scenarios. Existing domain adaptation (DA) paradigms like general DA and source-free DA for 3D HPE overlook the issues of non-stationary target pose datasets. To address these challenges, we propose a novel task named lifelong domain adaptive 3D HPE. To our knowledge, we are the first to introduce the lifelong domain adaptation to the 3D HPE task. In this lifelong DA setting, the pose estimator is pretrained on the source domain and subsequently adapted to distinct target domains. Moreover, during adaptation to the current target domain, the pose estimator cannot access the source and all the previous target domains. The lifelong DA for 3D HPE involves overcoming challenges in adapting to current domain poses and preserving knowledge from previous domains, particularly combating catastrophic forgetting. We present an innovative Generative Adversarial Network (GAN) framework, which incorporates 3D pose generators, a 2D pose discriminator, and a 3D pose estimator. This framework effectively mitigates domain shifts and aligns original and augmented poses. Moreover, we construct a novel 3D pose generator paradigm, integrating pose-aware, temporal-aware, and domain-aware knowledge to enhance the current domain's adaptation and alleviate catastrophic forgetting on previous domains. Our method demonstrates superior performance through extensive experiments on diverse domain adaptive 3D HPE datasets.
Exploiting Aggregation and Segregation of Representations for Domain Adaptive Human Pose Estimation
Dec 29, 2024Abstract:Human pose estimation (HPE) has received increasing attention recently due to its wide application in motion analysis, virtual reality, healthcare, etc. However, it suffers from the lack of labeled diverse real-world datasets due to the time- and labor-intensive annotation. To cope with the label deficiency issue, one common solution is to train the HPE models with easily available synthetic datasets (source) and apply them to real-world data (target) through domain adaptation (DA). Unfortunately, prevailing domain adaptation techniques within the HPE domain remain predominantly fixated on effecting alignment and aggregation between source and target features, often sidestepping the crucial task of excluding domain-specific representations. To rectify this, we introduce a novel framework that capitalizes on both representation aggregation and segregation for domain adaptive human pose estimation. Within this framework, we address the network architecture aspect by disentangling representations into distinct domain-invariant and domain-specific components, facilitating aggregation of domain-invariant features while simultaneously segregating domain-specific ones. Moreover, we tackle the discrepancy measurement facet by delving into various keypoint relationships and applying separate aggregation or segregation mechanisms to enhance alignment. Extensive experiments on various benchmarks, e.g., Human3.6M, LSP, H3D, and FreiHand, show that our method consistently achieves state-of-the-art performance. The project is available at \url{https://github.com/davidpengucf/EPIC}.
3D Vision-Language Gaussian Splatting
Oct 10, 2024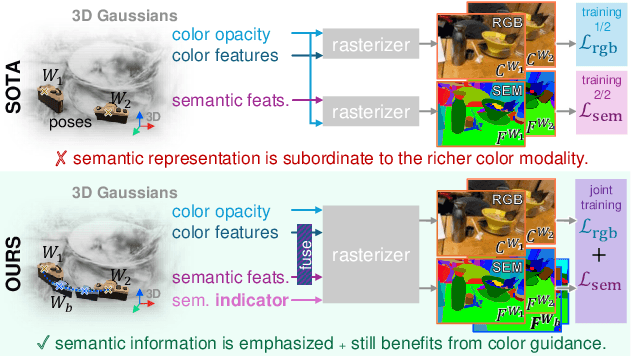
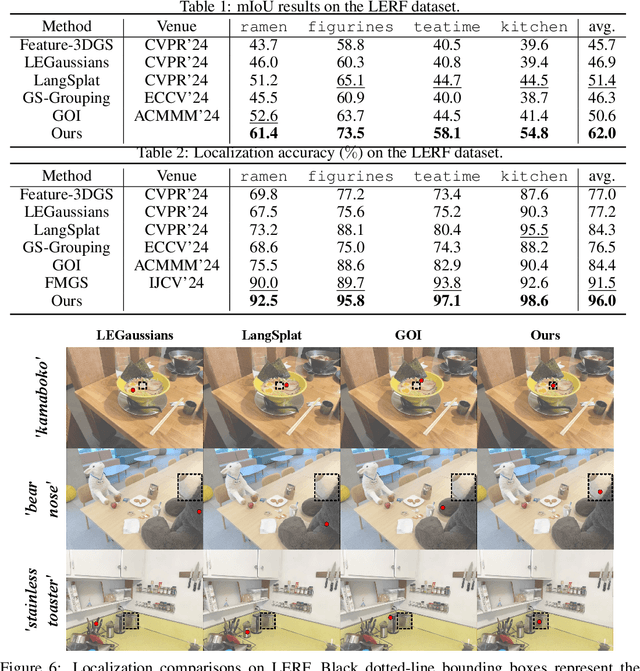
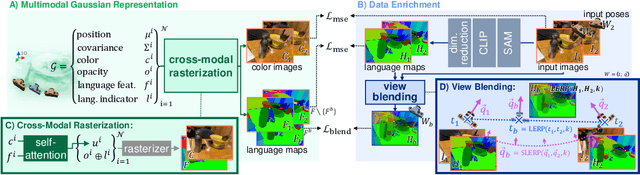
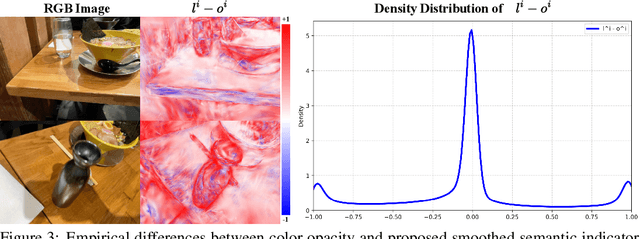
Abstract:Recent advancements in 3D reconstruction methods and vision-language models have propelled the development of multi-modal 3D scene understanding, which has vital applications in robotics, autonomous driving, and virtual/augmented reality. However, current multi-modal scene understanding approaches have naively embedded semantic representations into 3D reconstruction methods without striking a balance between visual and language modalities, which leads to unsatisfying semantic rasterization of translucent or reflective objects, as well as over-fitting on color modality. To alleviate these limitations, we propose a solution that adequately handles the distinct visual and semantic modalities, i.e., a 3D vision-language Gaussian splatting model for scene understanding, to put emphasis on the representation learning of language modality. We propose a novel cross-modal rasterizer, using modality fusion along with a smoothed semantic indicator for enhancing semantic rasterization. We also employ a camera-view blending technique to improve semantic consistency between existing and synthesized views, thereby effectively mitigating over-fitting. Extensive experiments demonstrate that our method achieves state-of-the-art performance in open-vocabulary semantic segmentation, surpassing existing methods by a significant margin.
A Dual-Augmentor Framework for Domain Generalization in 3D Human Pose Estimation
Mar 20, 2024



Abstract:3D human pose data collected in controlled laboratory settings present challenges for pose estimators that generalize across diverse scenarios. To address this, domain generalization is employed. Current methodologies in domain generalization for 3D human pose estimation typically utilize adversarial training to generate synthetic poses for training. Nonetheless, these approaches exhibit several limitations. First, the lack of prior information about the target domain complicates the application of suitable augmentation through a single pose augmentor, affecting generalization on target domains. Moreover, adversarial training's discriminator tends to enforce similarity between source and synthesized poses, impeding the exploration of out-of-source distributions. Furthermore, the pose estimator's optimization is not exposed to domain shifts, limiting its overall generalization ability. To address these limitations, we propose a novel framework featuring two pose augmentors: the weak and the strong augmentors. Our framework employs differential strategies for generation and discrimination processes, facilitating the preservation of knowledge related to source poses and the exploration of out-of-source distributions without prior information about target poses. Besides, we leverage meta-optimization to simulate domain shifts in the optimization process of the pose estimator, thereby improving its generalization ability. Our proposed approach significantly outperforms existing methods, as demonstrated through comprehensive experiments on various benchmark datasets.Our code will be released at \url{https://github.com/davidpengucf/DAF-DG}.
Source-free Domain Adaptive Human Pose Estimation
Aug 18, 2023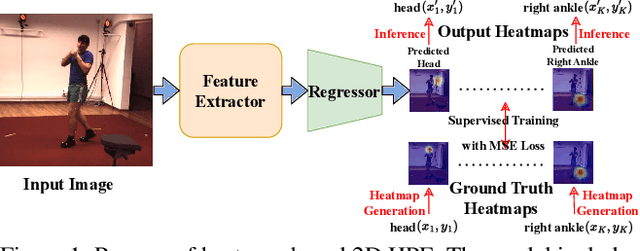
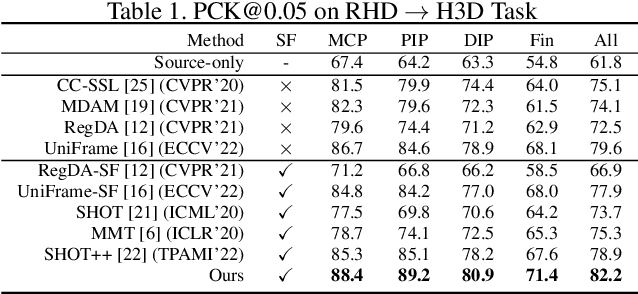
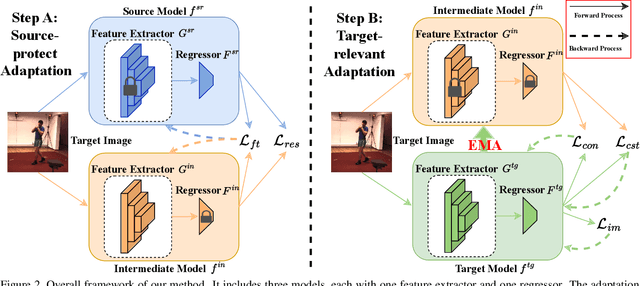
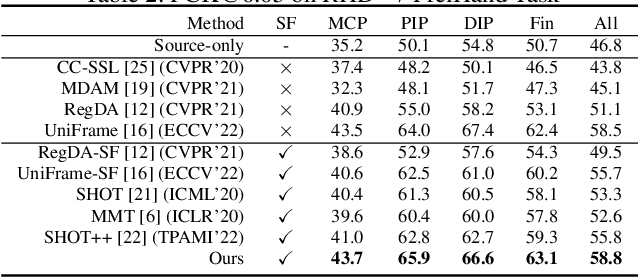
Abstract:Human Pose Estimation (HPE) is widely used in various fields, including motion analysis, healthcare, and virtual reality. However, the great expenses of labeled real-world datasets present a significant challenge for HPE. To overcome this, one approach is to train HPE models on synthetic datasets and then perform domain adaptation (DA) on real-world data. Unfortunately, existing DA methods for HPE neglect data privacy and security by using both source and target data in the adaptation process. To this end, we propose a new task, named source-free domain adaptive HPE, which aims to address the challenges of cross-domain learning of HPE without access to source data during the adaptation process. We further propose a novel framework that consists of three models: source model, intermediate model, and target model, which explores the task from both source-protect and target-relevant perspectives. The source-protect module preserves source information more effectively while resisting noise, and the target-relevant module reduces the sparsity of spatial representations by building a novel spatial probability space, and pose-specific contrastive learning and information maximization are proposed on the basis of this space. Comprehensive experiments on several domain adaptive HPE benchmarks show that the proposed method outperforms existing approaches by a considerable margin. The codes are available at https://github.com/davidpengucf/SFDAHPE.
GaitSADA: Self-Aligned Domain Adaptation for mmWave Gait Recognition
Feb 01, 2023



Abstract:mmWave radar-based gait recognition is a novel user identification method that captures human gait biometrics from mmWave radar return signals. This technology offers privacy protection and is resilient to weather and lighting conditions. However, its generalization performance is yet unknown and limits its practical deployment. To address this problem, in this paper, a non-synthetic dataset is collected and analyzed to reveal the presence of spatial and temporal domain shifts in mmWave gait biometric data, which significantly impacts identification accuracy. To address this issue, a novel self-aligned domain adaptation method called GaitSADA is proposed. GaitSADA improves system generalization performance by using a two-stage semi-supervised model training approach. The first stage uses semi-supervised contrastive learning and the second stage uses semi-supervised consistency training with centroid alignment. Extensive experiments show that GaitSADA outperforms representative domain adaptation methods by an average of 15.41% in low data regimes.
Toward Better Target Representation for Source-Free and Black-Box Domain Adaptation
Aug 22, 2022



Abstract:Domain adaptation aims at aligning the labeled source domain and the unlabeled target domain, and most existing approaches assume the source data is accessible. Unfortunately, this paradigm raises concerns in data privacy and security. Recent studies try to dispel these concerns by the Source-Free setting, which adapts the source-trained model towards target domain without exposing the source data. However, the Source-Free paradigm is still at risk of data leakage due to adversarial attacks to the source model. Hence, the Black-Box setting is proposed, where only the outputs of source model can be utilized. In this paper, we address both the Source-Free adaptation and the Black-Box adaptation, proposing a novel method named better target representation from Frequency Mixup and Mutual Learning (FMML). Specifically, we introduce a new data augmentation technique as Frequency MixUp, which highlights task-relevant objects in the interpolations, thus enhancing class-consistency and linear behavior for target models. Moreover, we introduce a network regularization method called Mutual Learning to the domain adaptation problem. It transfers knowledge inside the target model via self-knowledge distillation and thus alleviates overfitting on the source domain by learning multi-scale target representations. Extensive experiments show that our method achieves state-of-the-art performance on several benchmark datasets under both settings.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge