Prathmesh Madhu
ARIN: Adaptive Resampling and Instance Normalization for Robust Blind Inpainting of Dunhuang Cave Paintings
Feb 25, 2024Abstract:Image enhancement algorithms are very useful for real world computer vision tasks where image resolution is often physically limited by the sensor size. While state-of-the-art deep neural networks show impressive results for image enhancement, they often struggle to enhance real-world images. In this work, we tackle a real-world setting: inpainting of images from Dunhuang caves. The Dunhuang dataset consists of murals, half of which suffer from corrosion and aging. These murals feature a range of rich content, such as Buddha statues, bodhisattvas, sponsors, architecture, dance, music, and decorative patterns designed by different artists spanning ten centuries, which makes manual restoration challenging. We modify two different existing methods (CAR, HINet) that are based upon state-of-the-art (SOTA) super resolution and deblurring networks. We show that those can successfully inpaint and enhance these deteriorated cave paintings. We further show that a novel combination of CAR and HINet, resulting in our proposed inpainting network (ARIN), is very robust to external noise, especially Gaussian noise. To this end, we present a quantitative and qualitative comparison of our proposed approach with existing SOTA networks and winners of the Dunhuang challenge. One of the proposed methods HINet) represents the new state of the art and outperforms the 1st place of the Dunhuang Challenge, while our combination ARIN, which is robust to noise, is comparable to the 1st place. We also present and discuss qualitative results showing the impact of our method for inpainting on Dunhuang cave images.
Attention-Guided Erasing: A Novel Augmentation Method for Enhancing Downstream Breast Density Classification
Jan 08, 2024Abstract:The assessment of breast density is crucial in the context of breast cancer screening, especially in populations with a higher percentage of dense breast tissues. This study introduces a novel data augmentation technique termed Attention-Guided Erasing (AGE), devised to enhance the downstream classification of four distinct breast density categories in mammography following the BI-RADS recommendation in the Vietnamese cohort. The proposed method integrates supplementary information during transfer learning, utilizing visual attention maps derived from a vision transformer backbone trained using the self-supervised DINO method. These maps are utilized to erase background regions in the mammogram images, unveiling only the potential areas of dense breast tissues to the network. Through the incorporation of AGE during transfer learning with varying random probabilities, we consistently surpass classification performance compared to scenarios without AGE and the traditional random erasing transformation. We validate our methodology using the publicly available VinDr-Mammo dataset. Specifically, we attain a mean F1-score of 0.5910, outperforming values of 0.5594 and 0.5691 corresponding to scenarios without AGE and with random erasing (RE), respectively. This superiority is further substantiated by t-tests, revealing a p-value of p<0.0001, underscoring the statistical significance of our approach.
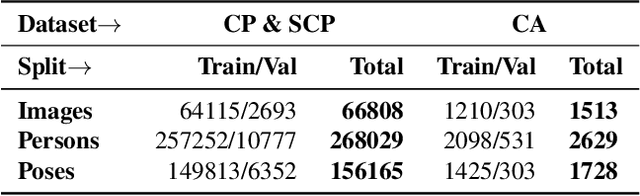
SniffyArt: The Dataset of Smelling Persons
Nov 20, 2023



Abstract:Smell gestures play a crucial role in the investigation of past smells in the visual arts yet their automated recognition poses significant challenges. This paper introduces the SniffyArt dataset, consisting of 1941 individuals represented in 441 historical artworks. Each person is annotated with a tightly fitting bounding box, 17 pose keypoints, and a gesture label. By integrating these annotations, the dataset enables the development of hybrid classification approaches for smell gesture recognition. The datasets high-quality human pose estimation keypoints are achieved through the merging of five separate sets of keypoint annotations per person. The paper also presents a baseline analysis, evaluating the performance of representative algorithms for detection, keypoint estimation, and classification tasks, showcasing the potential of combining keypoint estimation with smell gesture classification. The SniffyArt dataset lays a solid foundation for future research and the exploration of multi-task approaches leveraging pose keypoints and person boxes to advance human gesture and olfactory dimension analysis in historical artworks.
* 10 pages, 8 figures
Transfer Learning for Olfactory Object Detection
Jan 24, 2023Abstract:We investigate the effect of style and category similarity in multiple datasets used for object detection pretraining. We find that including an additional stage of object-detection pretraining can increase the detection performance considerably. While our experiments suggest that style similarities between pre-training and target datasets are less important than matching categories, further experiments are needed to verify this hypothesis.
* 6 pages, 4 figures
ODOR: The ICPR2022 ODeuropa Challenge on Olfactory Object Recognition
Jan 24, 2023Abstract:The Odeuropa Challenge on Olfactory Object Recognition aims to foster the development of object detection in the visual arts and to promote an olfactory perspective on digital heritage. Object detection in historical artworks is particularly challenging due to varying styles and artistic periods. Moreover, the task is complicated due to the particularity and historical variance of predefined target objects, which exhibit a large intra-class variance, and the long tail distribution of the dataset labels, with some objects having only very few training examples. These challenges should encourage participants to create innovative approaches using domain adaptation or few-shot learning. We provide a dataset of 2647 artworks annotated with 20 120 tightly fit bounding boxes that are split into a training and validation set (public). A test set containing 1140 artworks and 15 480 annotations is kept private for the challenge evaluation.
* 6 pages, 6 figures
Classification of Luminal Subtypes in Full Mammogram Images Using Transfer Learning
Jan 23, 2023Abstract:Automatic identification of patients with luminal and non-luminal subtypes during a routine mammography screening can support clinicians in streamlining breast cancer therapy planning. Recent machine learning techniques have shown promising results in molecular subtype classification in mammography; however, they are highly dependent on pixel-level annotations, handcrafted, and radiomic features. In this work, we provide initial insights into the luminal subtype classification in full mammogram images trained using only image-level labels. Transfer learning is applied from a breast abnormality classification task, to finetune a ResNet-18-based luminal versus non-luminal subtype classification task. We present and compare our results on the publicly available CMMD dataset and show that our approach significantly outperforms the baseline classifier by achieving a mean AUC score of 0.6688 and a mean F1 score of 0.6693 on the test dataset. The improvement over baseline is statistically significant, with a p-value of p<0.0001.
An unobtrusive quality supervision approach for medical image annotation
Nov 22, 2022Abstract:Image annotation is one essential prior step to enable data-driven algorithms. In medical imaging, having large and reliably annotated data sets is crucial to recognize various diseases robustly. However, annotator performance varies immensely, thus impacts model training. Therefore, often multiple annotators should be employed, which is however expensive and resource-intensive. Hence, it is desirable that users should annotate unseen data and have an automated system to unobtrusively rate their performance during this process. We examine such a system based on whole slide images (WSIs) showing lung fluid cells. We evaluate two methods the generation of synthetic individual cell images: conditional Generative Adversarial Networks and Diffusion Models (DM). For qualitative and quantitative evaluation, we conduct a user study to highlight the suitability of generated cells. Users could not detect 52.12% of generated images by DM proofing the feasibility to replace the original cells with synthetic cells without being noticed.
ICC++: Explainable Image Retrieval for Art Historical Corpora using Image Composition Canvas
Jun 22, 2022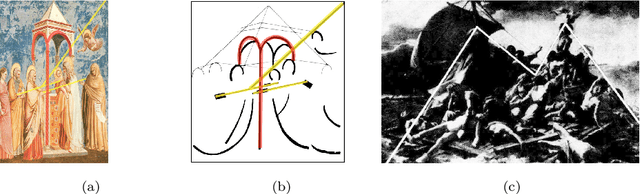
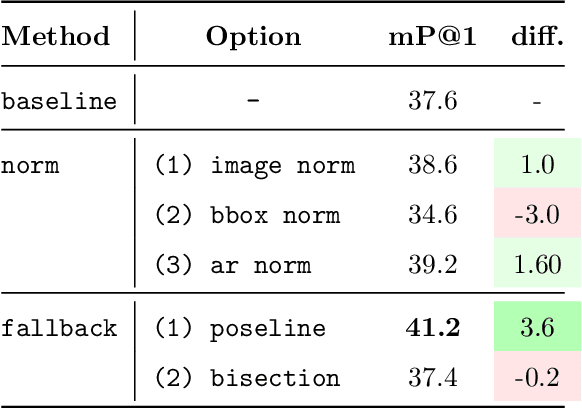
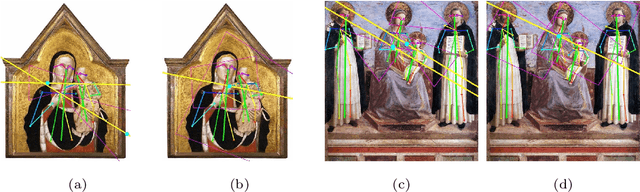
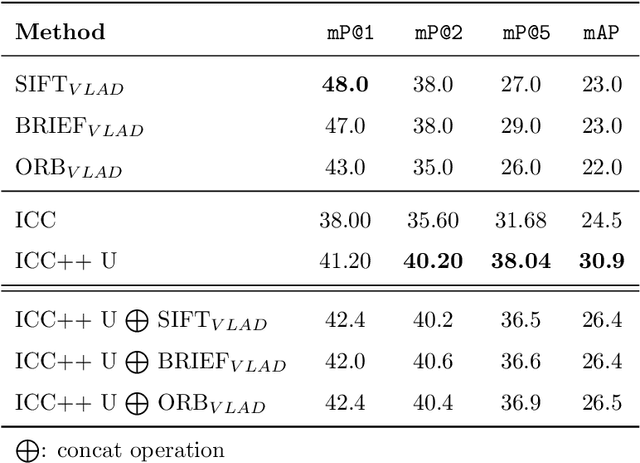
Abstract:Image compositions are helpful in the study of image structures and assist in discovering the semantics of the underlying scene portrayed across art forms and styles. With the digitization of artworks in recent years, thousands of images of a particular scene or narrative could potentially be linked together. However, manually linking this data with consistent objectiveness can be a highly challenging and time-consuming task. In this work, we present a novel approach called Image Composition Canvas (ICC++) to compare and retrieve images having similar compositional elements. ICC++ is an improvement over ICC specializing in generating low and high-level features (compositional elements) motivated by Max Imdahl's work. To this end, we present a rigorous quantitative and qualitative comparison of our approach with traditional and state-of-the-art (SOTA) methods showing that our proposed method outperforms all of them. In combination with deep features, our method outperforms the best deep learning-based method, opening the research direction for explainable machine learning for digital humanities. We will release the code and the data post-publication.
Effect of Random Histogram Equalization on Breast Calcification Analysis Using Deep Learning
May 03, 2022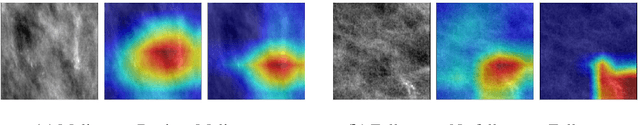
Abstract:Early detection and analysis of calcifications in mammogram images is crucial in a breast cancer diagnosis workflow. Management of calcifications that require immediate follow-up and further analyzing its benignancy or malignancy can result in a better prognosis. Recent studies have shown that deep learning-based algorithms can learn robust representations to analyze suspicious calcifications in mammography. In this work, we demonstrate that randomly equalizing the histograms of calcification patches as a data augmentation technique can significantly improve the classification performance for analyzing suspicious calcifications. We validate our approach by using the CBIS-DDSM dataset for two classification tasks. The results on both the tasks show that the proposed methodology gains more than 1% mean accuracy and F1-score when equalizing the data with a probability of 0.4 when compared to not using histogram equalization. This is further supported by the t-tests, where we obtain a p-value of p<0.0001, thus showing the statistical significance of our approach.
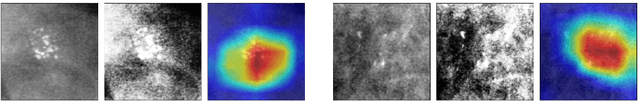
Enhancing Human Pose Estimation in Ancient Vase Paintings via Perceptually-grounded Style Transfer Learning
Dec 10, 2020

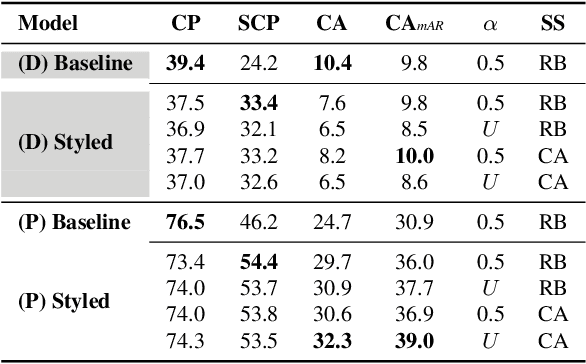
Abstract:Human pose estimation (HPE) is a central part of understanding the visual narration and body movements of characters depicted in artwork collections, such as Greek vase paintings. Unfortunately, existing HPE methods do not generalise well across domains resulting in poorly recognized poses. Therefore, we propose a two step approach: (1) adapting a dataset of natural images of known person and pose annotations to the style of Greek vase paintings by means of image style-transfer. We introduce a perceptually-grounded style transfer training to enforce perceptual consistency. Then, we fine-tune the base model with this newly created dataset. We show that using style-transfer learning significantly improves the SOTA performance on unlabelled data by more than 6% mean average precision (mAP) as well as mean average recall (mAR). (2) To improve the already strong results further, we created a small dataset (ClassArch) consisting of ancient Greek vase paintings from the 6-5th century BCE with person and pose annotations. We show that fine-tuning on this data with a style-transferred model improves the performance further. In a thorough ablation study, we give a targeted analysis of the influence of style intensities, revealing that the model learns generic domain styles. Additionally, we provide a pose-based image retrieval to demonstrate the effectiveness of our method.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge