Piyush K. Sharma
Emergent Behaviors in Multi-Agent Target Acquisition
Dec 15, 2022Abstract:Only limited studies and superficial evaluations are available on agents' behaviors and roles within a Multi-Agent System (MAS). We simulate a MAS using Reinforcement Learning (RL) in a pursuit-evasion (a.k.a predator-prey pursuit) game, which shares task goals with target acquisition, and we create different adversarial scenarios by replacing RL-trained pursuers' policies with two distinct (non-RL) analytical strategies. Using heatmaps of agents' positions (state-space variable) over time, we are able to categorize an RL-trained evader's behaviors. The novelty of our approach entails the creation of an influential feature set that reveals underlying data regularities, which allow us to classify an agent's behavior. This classification may aid in catching the (enemy) targets by enabling us to identify and predict their behaviors, and when extended to pursuers, this approach towards identifying teammates' behavior may allow agents to coordinate more effectively.
* This article appeared in the news at: https://www.army.mil/article/258408/u_s_army_scientists_invent_a_method_to_characterize_ai_behavior
Strategic Maneuver and Disruption with Reinforcement Learning Approaches for Multi-Agent Coordination
Mar 17, 2022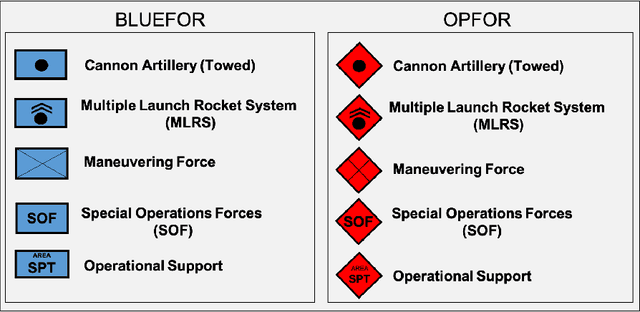
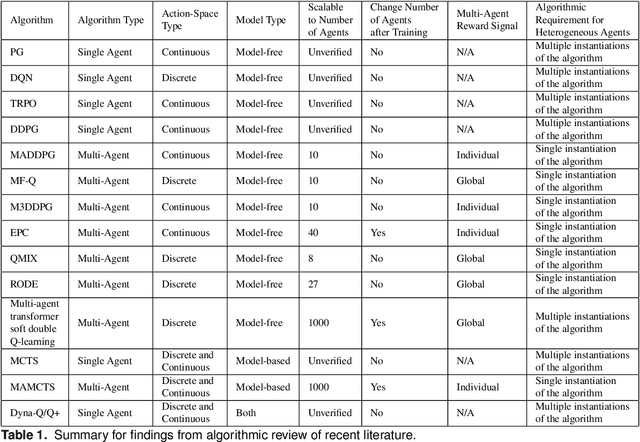
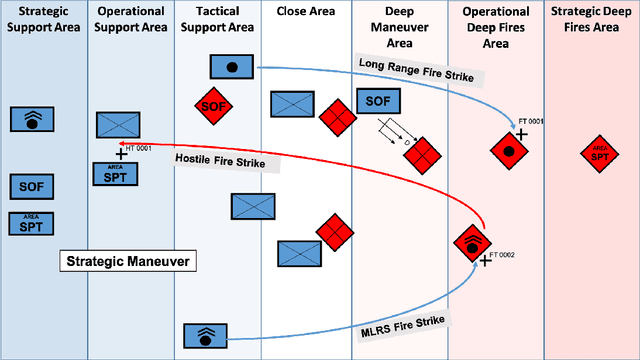
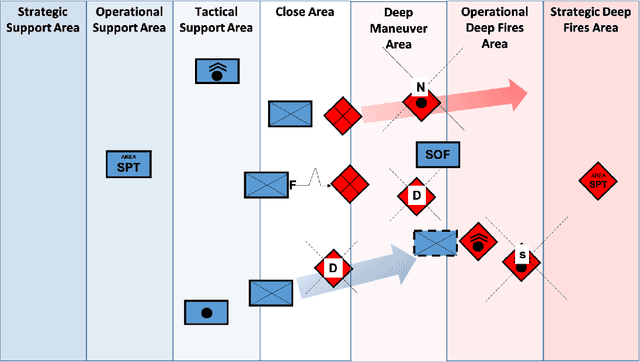
Abstract:Reinforcement learning (RL) approaches can illuminate emergent behaviors that facilitate coordination across teams of agents as part of a multi-agent system (MAS), which can provide windows of opportunity in various military tasks. Technologically advancing adversaries pose substantial risks to a friendly nation's interests and resources. Superior resources alone are not enough to defeat adversaries in modern complex environments because adversaries create standoff in multiple domains against predictable military doctrine-based maneuvers. Therefore, as part of a defense strategy, friendly forces must use strategic maneuvers and disruption to gain superiority in complex multi-faceted domains such as multi-domain operations (MDO). One promising avenue for implementing strategic maneuver and disruption to gain superiority over adversaries is through coordination of MAS in future military operations. In this paper, we present overviews of prominent works in the RL domain with their strengths and weaknesses for overcoming the challenges associated with performing autonomous strategic maneuver and disruption in military contexts.
A Scalable Graph-Theoretic Distributed Framework for Cooperative Multi-Agent Reinforcement Learning
Mar 01, 2022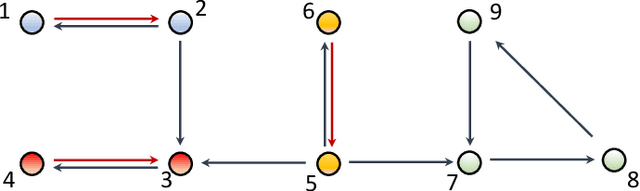
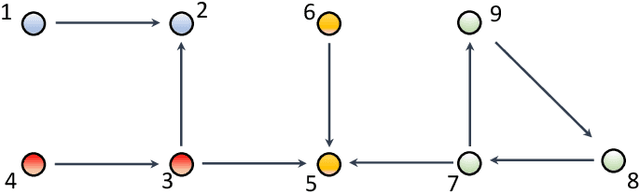
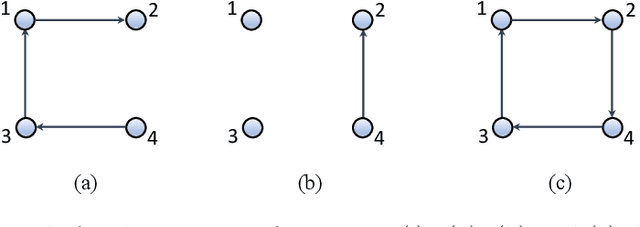
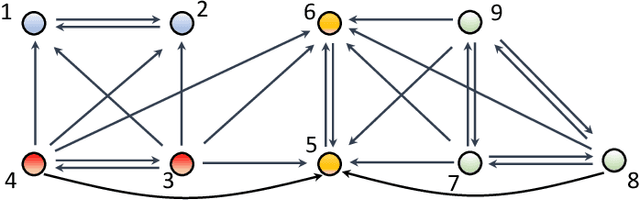
Abstract:The main challenge of large-scale cooperative multi-agent reinforcement learning (MARL) is two-fold: (i) the RL algorithm is desired to be distributed due to limited resource for each individual agent; (ii) issues on convergence or computational complexity emerge due to the curse of dimensionality. Unfortunately, most of existing distributed RL references only focus on ensuring that the individual policy-seeking process of each agent is based on local information, but fail to solve the scalability issue induced by high dimensions of the state and action spaces when facing large-scale networks. In this paper, we propose a general distributed framework for cooperative MARL by utilizing the structures of graphs involved in this problem. We introduce three graphs in MARL, namely, the coordination graph, the observation graph and the reward graph. Based on these three graphs, and a given communication graph, we propose two distributed RL approaches. The first approach utilizes the inherent decomposability property of the problem itself, whose efficiency depends on the structures of the aforementioned four graphs, and is able to produce a high performance under specific graphical conditions. The second approach provides an approximate solution and is applicable for any graphs. Here the approximation error depends on an artificially designed index. The choice of this index is a trade-off between minimizing the approximation error and reducing the computational complexity. Simulations show that our RL algorithms have a significantly improved scalability to large-scale MASs compared with centralized and consensus-based distributed RL algorithms.
Survey of Recent Multi-Agent Reinforcement Learning Algorithms Utilizing Centralized Training
Jul 29, 2021Abstract:Much work has been dedicated to the exploration of Multi-Agent Reinforcement Learning (MARL) paradigms implementing a centralized learning with decentralized execution (CLDE) approach to achieve human-like collaboration in cooperative tasks. Here, we discuss variations of centralized training and describe a recent survey of algorithmic approaches. The goal is to explore how different implementations of information sharing mechanism in centralized learning may give rise to distinct group coordinated behaviors in multi-agent systems performing cooperative tasks.
* This article appeared in the news at: https://www.army.mil/article/247261/army_researchers_develop_innovative_framework_for_training_ai
Asynchronous Distributed Reinforcement Learning for LQR Control via Zeroth-Order Block Coordinate Descent
Jul 28, 2021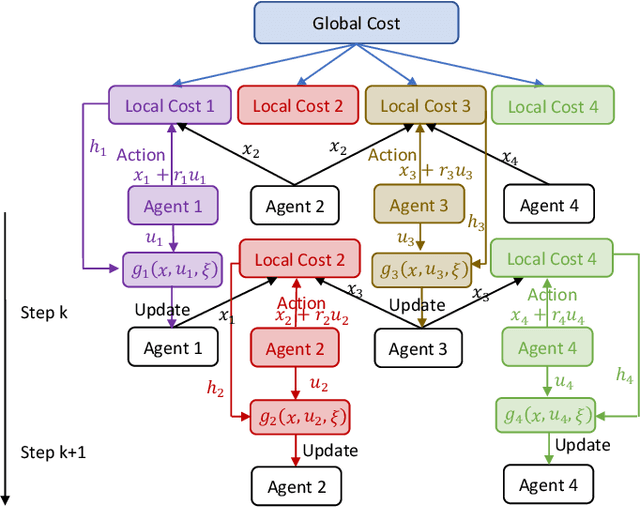
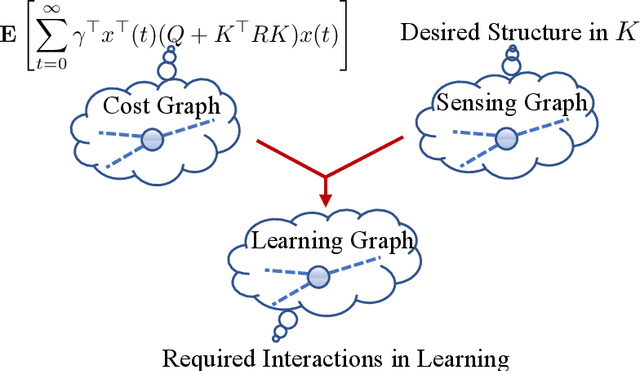
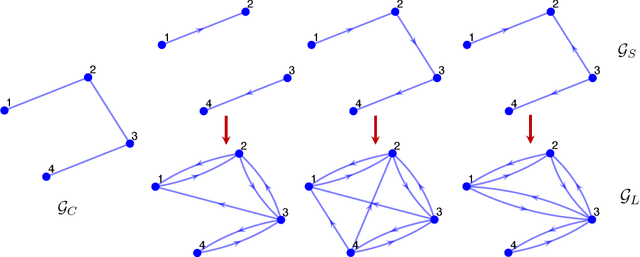
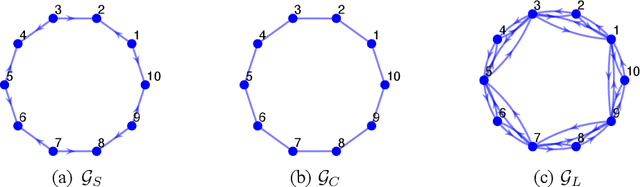
Abstract:Recently introduced distributed zeroth-order optimization (ZOO) algorithms have shown their utility in distributed reinforcement learning (RL). Unfortunately, in the gradient estimation process, almost all of them require random samples with the same dimension as the global variable and/or require evaluation of the global cost function, which may induce high estimation variance for large-scale networks. In this paper, we propose a novel distributed zeroth-order algorithm by leveraging the network structure inherent in the optimization objective, which allows each agent to estimate its local gradient by local cost evaluation independently, without use of any consensus protocol. The proposed algorithm exhibits an asynchronous update scheme, and is designed for stochastic non-convex optimization with a possibly non-convex feasible domain based on the block coordinate descent method. The algorithm is later employed as a distributed model-free RL algorithm for distributed linear quadratic regulator design, where a learning graph is designed to describe the required interaction relationship among agents in distributed learning. We provide an empirical validation of the proposed algorithm to benchmark its performance on convergence rate and variance against a centralized ZOO algorithm.
Image-Audio Encoding to Improve C2 Decision-Making in Multi-Domain Environment
Jun 03, 2021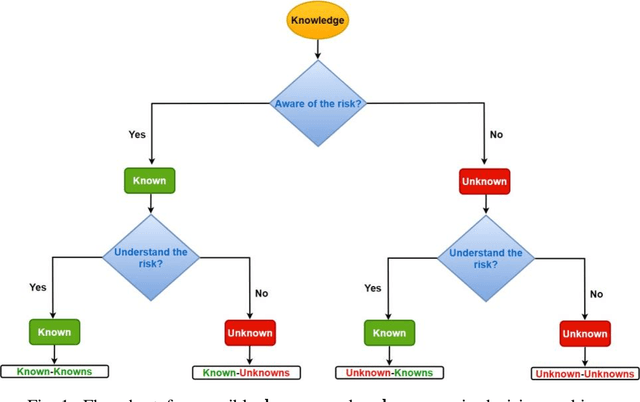
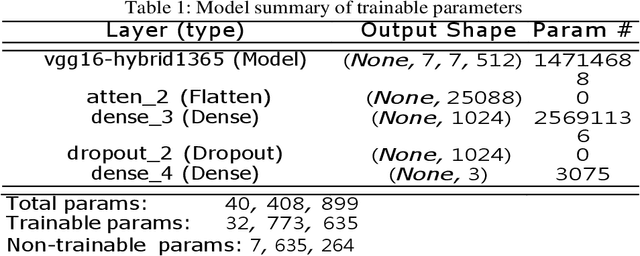
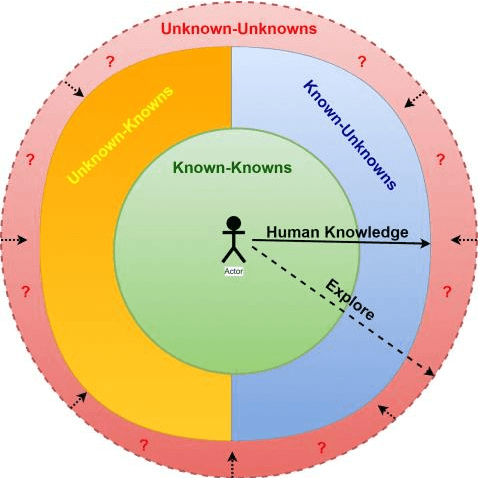
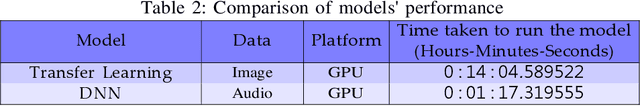
Abstract:The military is investigating methods to improve communication and agility in its multi-domain operations (MDO). Nascent popularity of Internet of Things (IoT) has gained traction in public and government domains. Its usage in MDO may revolutionize future battlefields and may enable strategic advantage. While this technology offers leverage to military capabilities, it comes with challenges where one is the uncertainty and associated risk. A key question is how can these uncertainties be addressed. Recently published studies proposed information camouflage to transform information from one data domain to another. As this is comparatively a new approach, we investigate challenges of such transformations and how these associated uncertainties can be detected and addressed, specifically unknown-unknowns to improve decision-making.
* Published in: The 25th International Command and Control Research and Technology Symposium (ICCRTS - 2020)
Heterogeneous Noisy Short Signal Camouflage in Multi-Domain Environment Decision-Making
Jun 02, 2021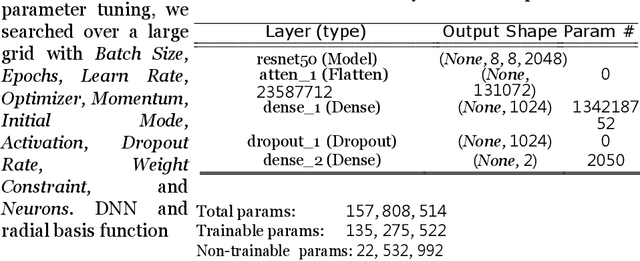
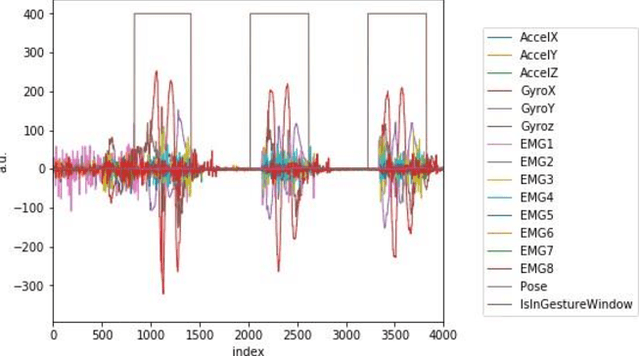
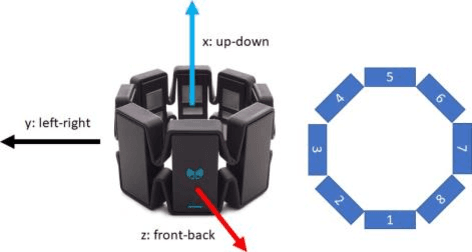
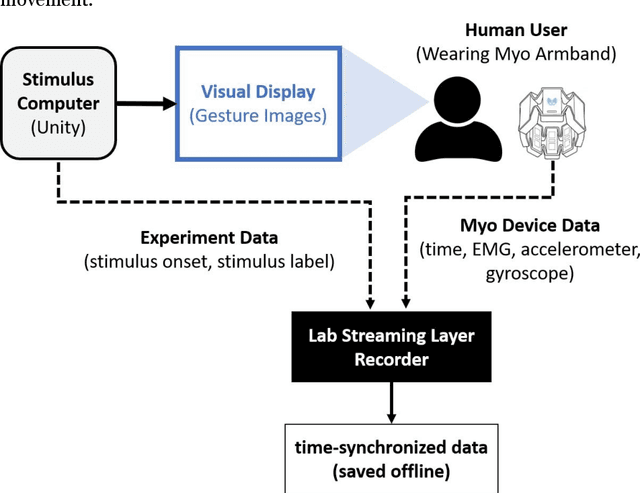
Abstract:Data transmission between two or more digital devices in industry and government demands secure and agile technology. Digital information distribution often requires deployment of Internet of Things (IoT) devices and Data Fusion techniques which have also gained popularity in both, civilian and military environments, such as, emergence of Smart Cities and Internet of Battlefield Things (IoBT). This usually requires capturing and consolidating data from multiple sources. Because datasets do not necessarily originate from identical sensors, fused data typically results in a complex Big Data problem. Due to potentially sensitive nature of IoT datasets, Blockchain technology is used to facilitate secure sharing of IoT datasets, which allows digital information to be distributed, but not copied. However, blockchain has several limitations related to complexity, scalability, and excessive energy consumption. We propose an approach to hide information (sensor signal) by transforming it to an image or an audio signal. In one of the latest attempts to the military modernization, we investigate sensor fusion approach by investigating the challenges of enabling an intelligent identification and detection operation and demonstrates the feasibility of the proposed Deep Learning and Anomaly Detection models that can support future application for specific hand gesture alert system from wearable devices.
* Published at: http://www.ibai-publishing.org/journal/issue_massdata/2020_september/massdata_11_1_3_26.php. arXiv admin note: substantial text overlap with arXiv:2106.01497
IoT Solutions with Multi-Sensor Fusion and Signal-Image Encoding for Secure Data Transfer and Decision Making
Jun 02, 2021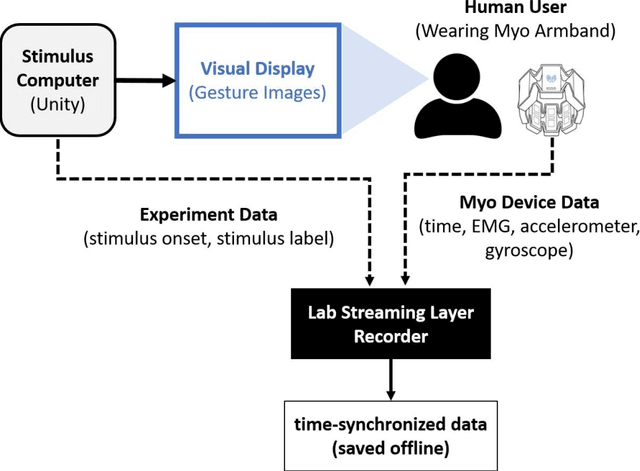
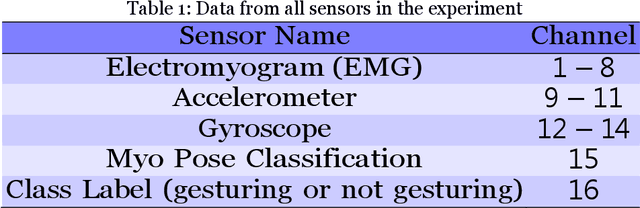
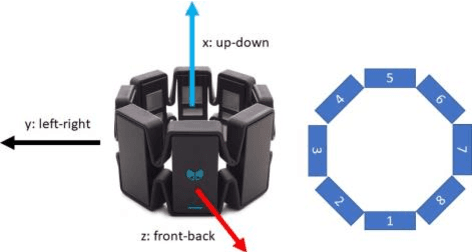
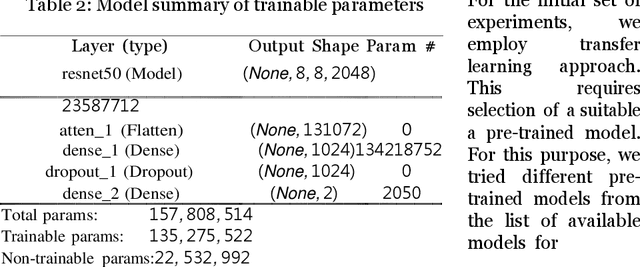
Abstract:Deployment of Internet of Things (IoT) devices and Data Fusion techniques have gained popularity in public and government domains. This usually requires capturing and consolidating data from multiple sources. As datasets do not necessarily originate from identical sensors, fused data typically results in a complex data problem. Because military is investigating how heterogeneous IoT devices can aid processes and tasks, we investigate a multi-sensor approach. Moreover, we propose a signal to image encoding approach to transform information (signal) to integrate (fuse) data from IoT wearable devices to an image which is invertible and easier to visualize supporting decision making. Furthermore, we investigate the challenge of enabling an intelligent identification and detection operation and demonstrate the feasibility of the proposed Deep Learning and Anomaly Detection models that can support future application that utilizes hand gesture data from wearable devices.
Investigating Manifold Neighborhood size for Nonlinear Analysis of LIBS Amino Acid Spectra
May 25, 2021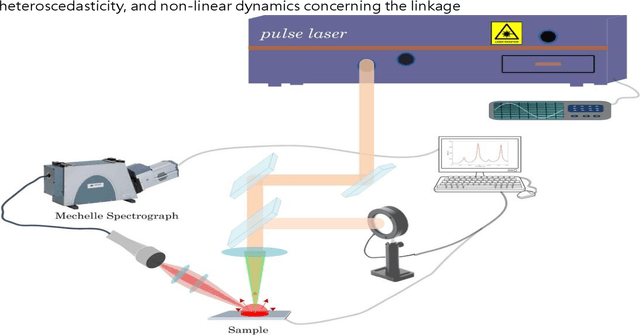
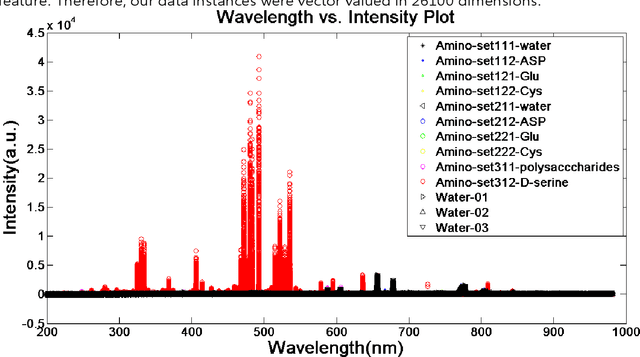
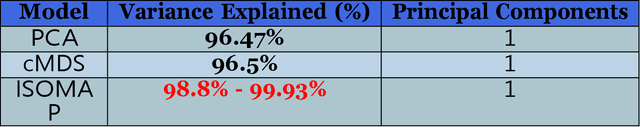
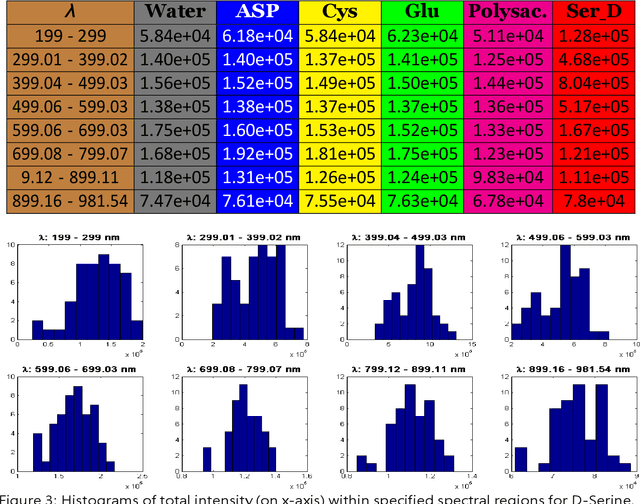
Abstract:Classification and identification of amino acids in aqueous solutions is important in the study of biomacromolecules. Laser Induced Breakdown Spectroscopy (LIBS) uses high energy laser-pulses for ablation of chemical compounds whose radiated spectra are captured and recorded to reveal molecular structure. Spectral peaks and noise from LIBS are impacted by experimental protocols. Current methods for LIBS spectral analysis achieves promising results using PCA, a linear method. It is well-known that the underlying physical processes behind LIBS are highly nonlinear. Our work set out to understand the impact of LIBS spectra on suitable neighborhood size over which to consider pattern phenomena, if nonlinear methods capture pattern phenomena with increased efficacy, and how they improve classification and identification of compounds. We analyzed four amino acids, polysaccharide, and a control group, water. We developed an information theoretic method for measurement of LIBS energy spectra, implemented manifold methods for nonlinear dimensionality reduction, and found while clustering results were not statistically significantly different, nonlinear methods lead to increased classification accuracy. Moreover, our approach uncovered the contribution of micro-wells (experimental protocol) in LIBS spectra. To the best of our knowledge, ours is the first application of Manifold methods to LIBS amino-acid analysis in the research literature.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge