Pingping Lin
STAND-Guard: A Small Task-Adaptive Content Moderation Model
Nov 07, 2024

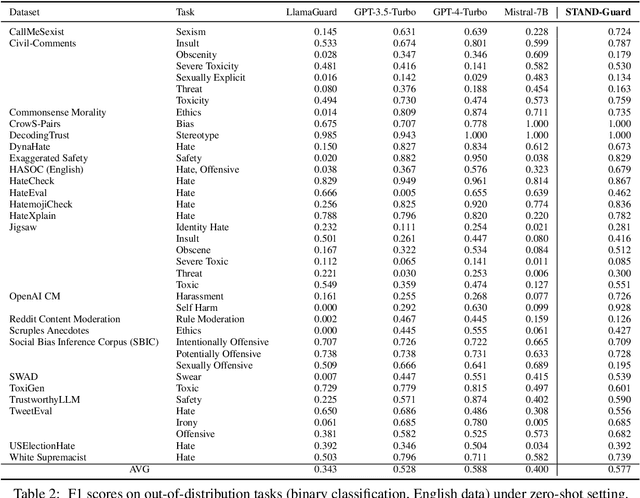

Abstract:Content moderation, the process of reviewing and monitoring the safety of generated content, is important for development of welcoming online platforms and responsible large language models. Content moderation contains various tasks, each with its unique requirements tailored to specific scenarios. Therefore, it is crucial to develop a model that can be easily adapted to novel or customized content moderation tasks accurately without extensive model tuning. This paper presents STAND-GUARD, a Small Task-Adaptive coNtent moDeration model. The basic motivation is: by performing instruct tuning on various content moderation tasks, we can unleash the power of small language models (SLMs) on unseen (out-of-distribution) content moderation tasks. We also carefully study the effects of training tasks and model size on the efficacy of cross-task fine-tuning mechanism. Experiments demonstrate STAND-Guard is comparable to GPT-3.5-Turbo across over 40 public datasets, as well as proprietary datasets derived from real-world business scenarios. Remarkably, STAND-Guard achieved nearly equivalent results to GPT-4-Turbo on unseen English binary classification tasks
Neural Storyboard Artist: Visualizing Stories with Coherent Image Sequences
Nov 24, 2019


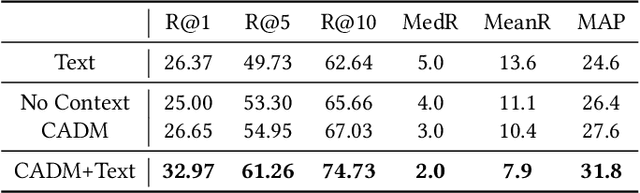
Abstract:A storyboard is a sequence of images to illustrate a story containing multiple sentences, which has been a key process to create different story products. In this paper, we tackle a new multimedia task of automatic storyboard creation to facilitate this process and inspire human artists. Inspired by the fact that our understanding of languages is based on our past experience, we propose a novel inspire-and-create framework with a story-to-image retriever that selects relevant cinematic images for inspiration and a storyboard creator that further refines and renders images to improve the relevancy and visual consistency. The proposed retriever dynamically employs contextual information in the story with hierarchical attentions and applies dense visual-semantic matching to accurately retrieve and ground images. The creator then employs three rendering steps to increase the flexibility of retrieved images, which include erasing irrelevant regions, unifying styles of images and substituting consistent characters. We carry out extensive experiments on both in-domain and out-of-domain visual story datasets. The proposed model achieves better quantitative performance than the state-of-the-art baselines for storyboard creation. Qualitative visualizations and user studies further verify that our approach can create high-quality storyboards even for stories in the wild.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge