Parul Chopra
Scaling Laws for Multilingual Language Models
Oct 15, 2024



Abstract:We propose a novel scaling law for general-purpose decoder-only language models (LMs) trained on multilingual data, addressing the problem of balancing languages during multilingual pretraining. A primary challenge in studying multilingual scaling is the difficulty of analyzing individual language performance due to cross-lingual transfer. To address this, we shift the focus from individual languages to language families. We introduce and validate a hypothesis that the test cross-entropy loss for each language family is determined solely by its own sampling ratio, independent of other languages in the mixture. This insight simplifies the complexity of multilingual scaling and make the analysis scalable to an arbitrary number of languages. Building on this hypothesis, we derive a power-law relationship that links performance with dataset size, model size and sampling ratios. This relationship enables us to predict performance across various combinations of the above three quantities, and derive the optimal sampling ratios at different model scales. To demonstrate the effectiveness and accuracy of our proposed scaling law, we perform a large-scale empirical study, training more than 100 models on 23 languages spanning 5 language families. Our experiments show that the optimal sampling ratios derived from small models (85M parameters) generalize effectively to models that are several orders of magnitude larger (1.2B parameters), offering a resource-efficient approach for multilingual LM training at scale.
Phi-3 Technical Report: A Highly Capable Language Model Locally on Your Phone
Apr 23, 2024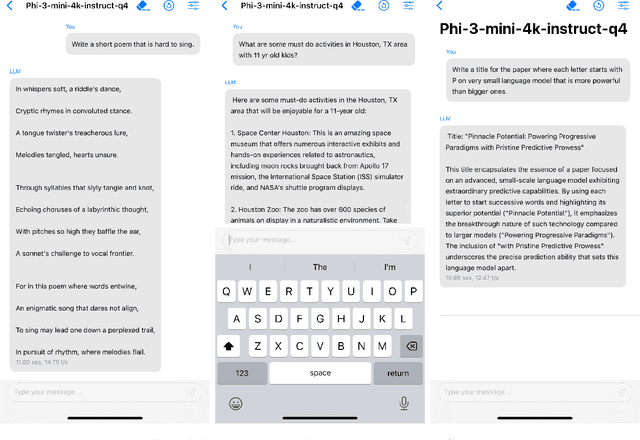
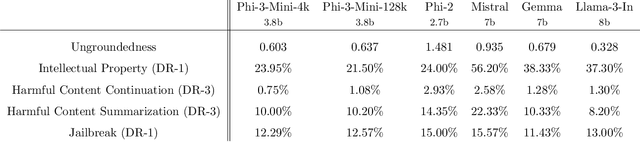
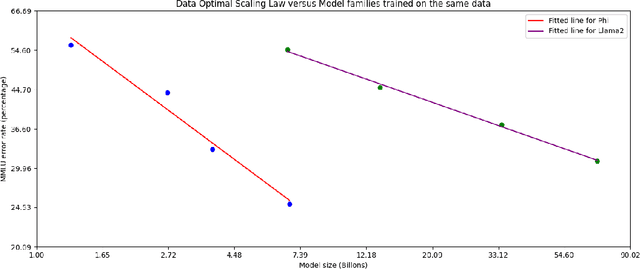
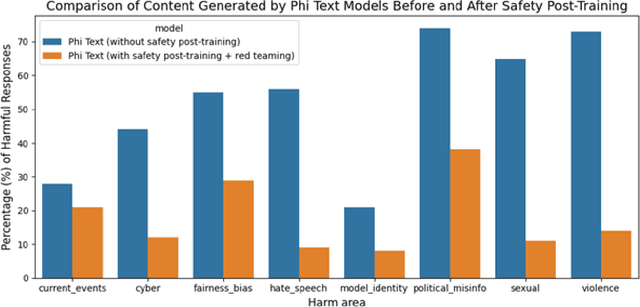
Abstract:We introduce phi-3-mini, a 3.8 billion parameter language model trained on 3.3 trillion tokens, whose overall performance, as measured by both academic benchmarks and internal testing, rivals that of models such as Mixtral 8x7B and GPT-3.5 (e.g., phi-3-mini achieves 69% on MMLU and 8.38 on MT-bench), despite being small enough to be deployed on a phone. The innovation lies entirely in our dataset for training, a scaled-up version of the one used for phi-2, composed of heavily filtered web data and synthetic data. The model is also further aligned for robustness, safety, and chat format. We also provide some initial parameter-scaling results with a 7B and 14B models trained for 4.8T tokens, called phi-3-small and phi-3-medium, both significantly more capable than phi-3-mini (e.g., respectively 75% and 78% on MMLU, and 8.7 and 8.9 on MT-bench).
Switch Point biased Self-Training: Re-purposing Pretrained Models for Code-Switching
Nov 01, 2021



Abstract:Code-switching (CS), a ubiquitous phenomenon due to the ease of communication it offers in multilingual communities still remains an understudied problem in language processing. The primary reasons behind this are: (1) minimal efforts in leveraging large pretrained multilingual models, and (2) the lack of annotated data. The distinguishing case of low performance of multilingual models in CS is the intra-sentence mixing of languages leading to switch points. We first benchmark two sequence labeling tasks -- POS and NER on 4 different language pairs with a suite of pretrained models to identify the problems and select the best performing model, char-BERT, among them (addressing (1)). We then propose a self training method to repurpose the existing pretrained models using a switch-point bias by leveraging unannotated data (addressing (2)). We finally demonstrate that our approach performs well on both tasks by reducing the gap between the switch point performance while retaining the overall performance on two distinct language pairs in both the tasks. Our code is available here: https://github.com/PC09/EMNLP2021-Switch-Point-biased-Self-Training.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge