Olivier Jeunen
Behavioural Effects of Agentic Messaging: A Case Study on a Financial Service Application
Dec 19, 2025

Abstract:Marketing and product personalisation provide a prominent and visible use-case for the application of Information Retrieval methods across several business domains. Recently, agentic approaches to these problems have been gaining traction. This work evaluates the behavioural and retention effects of agentic personalisation on a financial service application's customer communication system during a 2025 national tax filing period. Through a two month-long randomised controlled trial, we compare an agentic messaging approach against a business-as-usual (BAU) rule-based campaign system, focusing on two primary outcomes: unsubscribe behaviour and conversion timing. Empirical results show that agent-led messaging reduced unsubscribe events by 21\% ($\pm 0.01$) relative to BAU and increased early filing behaviour in the weeks preceding the national deadline. These findings demonstrate how adaptive, user-level decision-making systems can modulate engagement intensity whilst improving long-term retention indicators.
Meta Off-Policy Estimation
Aug 11, 2025Abstract:Off-policy estimation (OPE) methods enable unbiased offline evaluation of recommender systems, directly estimating the online reward some target policy would have obtained, from offline data and with statistical guarantees. The theoretical elegance of the framework combined with practical successes have led to a surge of interest, with many competing estimators now available to practitioners and researchers. Among these, Doubly Robust methods provide a prominent strategy to combine value- and policy-based estimators. In this work, we take an alternative perspective to combine a set of OPE estimators and their associated confidence intervals into a single, more accurate estimate. Our approach leverages a correlated fixed-effects meta-analysis framework, explicitly accounting for dependencies among estimators that arise due to shared data. This yields a best linear unbiased estimate (BLUE) of the target policy's value, along with an appropriately conservative confidence interval that reflects inter-estimator correlation. We validate our method on both simulated and real-world data, demonstrating improved statistical efficiency over existing individual estimators.
Procedural Memory Is Not All You Need: Bridging Cognitive Gaps in LLM-Based Agents
May 06, 2025Abstract:Large Language Models (LLMs) represent a landmark achievement in Artificial Intelligence (AI), demonstrating unprecedented proficiency in procedural tasks such as text generation, code completion, and conversational coherence. These capabilities stem from their architecture, which mirrors human procedural memory -- the brain's ability to automate repetitive, pattern-driven tasks through practice. However, as LLMs are increasingly deployed in real-world applications, it becomes impossible to ignore their limitations operating in complex, unpredictable environments. This paper argues that LLMs, while transformative, are fundamentally constrained by their reliance on procedural memory. To create agents capable of navigating ``wicked'' learning environments -- where rules shift, feedback is ambiguous, and novelty is the norm -- we must augment LLMs with semantic memory and associative learning systems. By adopting a modular architecture that decouples these cognitive functions, we can bridge the gap between narrow procedural expertise and the adaptive intelligence required for real-world problem-solving.
$t$-Testing the Waters: Empirically Validating Assumptions for Reliable A/B-Testing
Feb 07, 2025


Abstract:A/B-tests are a cornerstone of experimental design on the web, with wide-ranging applications and use-cases. The statistical $t$-test comparing differences in means is the most commonly used method for assessing treatment effects, often justified through the Central Limit Theorem (CLT). The CLT ascertains that, as the sample size grows, the sampling distribution of the Average Treatment Effect converges to normality, making the $t$-test valid for sufficiently large sample sizes. When outcome measures are skewed or non-normal, quantifying what "sufficiently large" entails is not straightforward. To ensure that confidence intervals maintain proper coverage and that $p$-values accurately reflect the false positive rate, it is critical to validate this normality assumption. We propose a practical method to test this, by analysing repeatedly resampled A/A-tests. When the normality assumption holds, the resulting $p$-value distribution should be uniform, and this property can be tested using the Kolmogorov-Smirnov test. This provides an efficient and effective way to empirically assess whether the $t$-test's assumptions are met, and the A/B-test is valid. We demonstrate our methodology and highlight how it helps to identify scenarios prone to inflated Type-I errors. Our approach provides a practical framework to ensure and improve the reliability and robustness of A/B-testing practices.
Powerful A/B-Testing Metrics and Where to Find Them
Jul 30, 2024Abstract:Online controlled experiments, colloquially known as A/B-tests, are the bread and butter of real-world recommender system evaluation. Typically, end-users are randomly assigned some system variant, and a plethora of metrics are then tracked, collected, and aggregated throughout the experiment. A North Star metric (e.g. long-term growth or revenue) is used to assess which system variant should be deemed superior. As a result, most collected metrics are supporting in nature, and serve to either (i) provide an understanding of how the experiment impacts user experience, or (ii) allow for confident decision-making when the North Star metric moves insignificantly (i.e. a false negative or type-II error). The latter is not straightforward: suppose a treatment variant leads to fewer but longer sessions, with more views but fewer engagements; should this be considered a positive or negative outcome? The question then becomes: how do we assess a supporting metric's utility when it comes to decision-making using A/B-testing? Online platforms typically run dozens of experiments at any given time. This provides a wealth of information about interventions and treatment effects that can be used to evaluate metrics' utility for online evaluation. We propose to collect this information and leverage it to quantify type-I, type-II, and type-III errors for the metrics of interest, alongside a distribution of measurements of their statistical power (e.g. $z$-scores and $p$-values). We present results and insights from building this pipeline at scale for two large-scale short-video platforms: ShareChat and Moj; leveraging hundreds of past experiments to find online metrics with high statistical power.
$Δ\text{-}{\rm OPE}$: Off-Policy Estimation with Pairs of Policies
May 16, 2024Abstract:The off-policy paradigm casts recommendation as a counterfactual decision-making task, allowing practitioners to unbiasedly estimate online metrics using offline data. This leads to effective evaluation metrics, as well as learning procedures that directly optimise online success. Nevertheless, the high variance that comes with unbiasedness is typically the crux that complicates practical applications. An important insight is that the difference between policy values can often be estimated with significantly reduced variance, if said policies have positive covariance. This allows us to formulate a pairwise off-policy estimation task: $\Delta\text{-}{\rm OPE}$. $\Delta\text{-}{\rm OPE}$ subsumes the common use-case of estimating improvements of a learnt policy over a production policy, using data collected by a stochastic logging policy. We introduce $\Delta\text{-}{\rm OPE}$ methods based on the widely used Inverse Propensity Scoring estimator and its extensions. Moreover, we characterise a variance-optimal additive control variate that further enhances efficiency. Simulated, offline, and online experiments show that our methods significantly improve performance for both evaluation and learning tasks.
Optimal Baseline Corrections for Off-Policy Contextual Bandits
May 09, 2024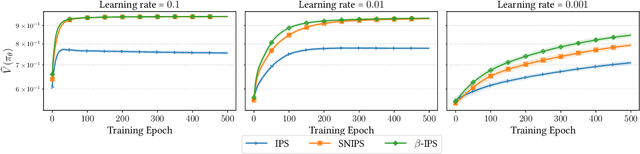
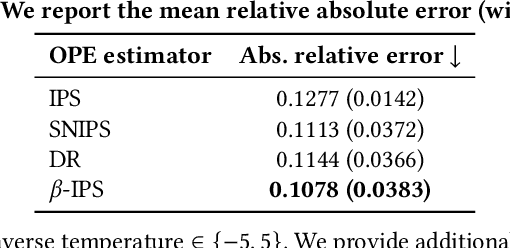
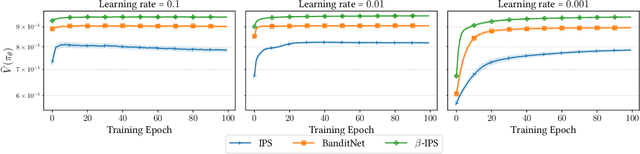
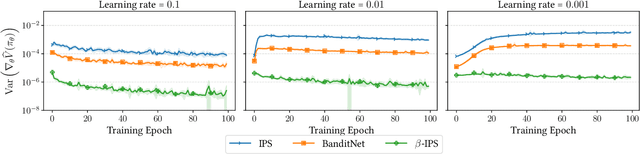
Abstract:The off-policy learning paradigm allows for recommender systems and general ranking applications to be framed as decision-making problems, where we aim to learn decision policies that optimize an unbiased offline estimate of an online reward metric. With unbiasedness comes potentially high variance, and prevalent methods exist to reduce estimation variance. These methods typically make use of control variates, either additive (i.e., baseline corrections or doubly robust methods) or multiplicative (i.e., self-normalisation). Our work unifies these approaches by proposing a single framework built on their equivalence in learning scenarios. The foundation of our framework is the derivation of an equivalent baseline correction for all of the existing control variates. Consequently, our framework enables us to characterize the variance-optimal unbiased estimator and provide a closed-form solution for it. This optimal estimator brings significantly improved performance in both evaluation and learning, and minimizes data requirements. Empirical observations corroborate our theoretical findings.
Multi-Objective Recommendation via Multivariate Policy Learning
May 03, 2024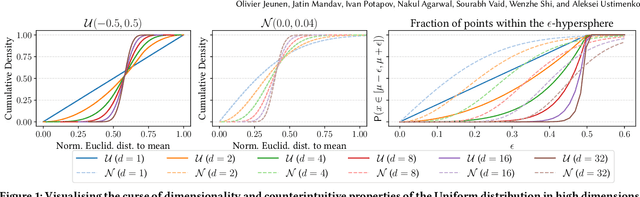

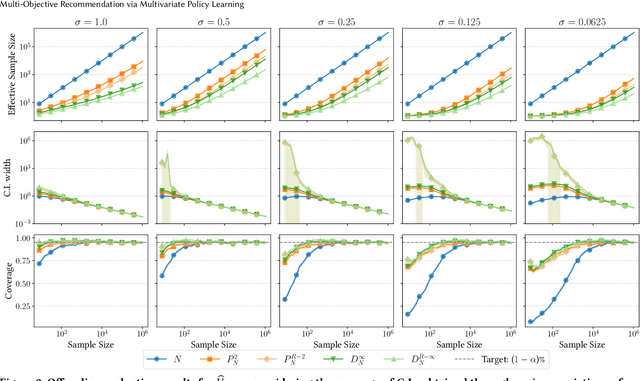
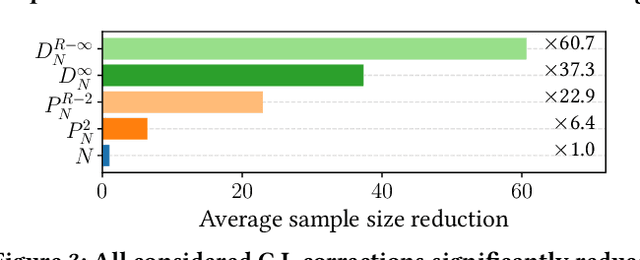
Abstract:Real-world recommender systems often need to balance multiple objectives when deciding which recommendations to present to users. These include behavioural signals (e.g. clicks, shares, dwell time), as well as broader objectives (e.g. diversity, fairness). Scalarisation methods are commonly used to handle this balancing task, where a weighted average of per-objective reward signals determines the final score used for ranking. Naturally, how these weights are computed exactly, is key to success for any online platform. We frame this as a decision-making task, where the scalarisation weights are actions taken to maximise an overall North Star reward (e.g. long-term user retention or growth). We extend existing policy learning methods to the continuous multivariate action domain, proposing to maximise a pessimistic lower bound on the North Star reward that the learnt policy will yield. Typical lower bounds based on normal approximations suffer from insufficient coverage, and we propose an efficient and effective policy-dependent correction for this. We provide guidance to design stochastic data collection policies, as well as highly sensitive reward signals. Empirical observations from simulations, offline and online experiments highlight the efficacy of our deployed approach.
Learning Metrics that Maximise Power for Accelerated A/B-Tests
Feb 06, 2024Abstract:Online controlled experiments are a crucial tool to allow for confident decision-making in technology companies. A North Star metric is defined (such as long-term revenue or user retention), and system variants that statistically significantly improve on this metric in an A/B-test can be considered superior. North Star metrics are typically delayed and insensitive. As a result, the cost of experimentation is high: experiments need to run for a long time, and even then, type-II errors (i.e. false negatives) are prevalent. We propose to tackle this by learning metrics from short-term signals that directly maximise the statistical power they harness with respect to the North Star. We show that existing approaches are prone to overfitting, in that higher average metric sensitivity does not imply improved type-II errors, and propose to instead minimise the $p$-values a metric would have produced on a log of past experiments. We collect such datasets from two social media applications with over 160 million Monthly Active Users each, totalling over 153 A/B-pairs. Empirical results show that we are able to increase statistical power by up to 78% when using our learnt metrics stand-alone, and by up to 210% when used in tandem with the North Star. Alternatively, we can obtain constant statistical power at a sample size that is down to 12% of what the North Star requires, significantly reducing the cost of experimentation.
Variance Reduction in Ratio Metrics for Efficient Online Experiments
Jan 08, 2024
Abstract:Online controlled experiments, such as A/B-tests, are commonly used by modern tech companies to enable continuous system improvements. Despite their paramount importance, A/B-tests are expensive: by their very definition, a percentage of traffic is assigned an inferior system variant. To ensure statistical significance on top-level metrics, online experiments typically run for several weeks. Even then, a considerable amount of experiments will lead to inconclusive results (i.e. false negatives, or type-II error). The main culprit for this inefficiency is the variance of the online metrics. Variance reduction techniques have been proposed in the literature, but their direct applicability to commonly used ratio metrics (e.g. click-through rate or user retention) is limited. In this work, we successfully apply variance reduction techniques to ratio metrics on a large-scale short-video platform: ShareChat. Our empirical results show that we can either improve A/B-test confidence in 77% of cases, or can retain the same level of confidence with 30% fewer data points. Importantly, we show that the common approach of including as many covariates as possible in regression is counter-productive, highlighting that control variates based on Gradient-Boosted Decision Tree predictors are most effective. We discuss the practicalities of implementing these methods at scale and showcase the cost reduction they beget.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge