Nour Aburaed
University of Strathclyde, University of Dubai
Modeling Beyond MOS: Quality Assessment Models Must Integrate Context, Reasoning, and Multimodality
May 26, 2025Abstract:This position paper argues that Mean Opinion Score (MOS), while historically foundational, is no longer sufficient as the sole supervisory signal for multimedia quality assessment models. MOS reduces rich, context-sensitive human judgments to a single scalar, obscuring semantic failures, user intent, and the rationale behind quality decisions. We contend that modern quality assessment models must integrate three interdependent capabilities: (1) context-awareness, to adapt evaluations to task-specific goals and viewing conditions; (2) reasoning, to produce interpretable, evidence-grounded justifications for quality judgments; and (3) multimodality, to align perceptual and semantic cues using vision-language models. We critique the limitations of current MOS-centric benchmarks and propose a roadmap for reform: richer datasets with contextual metadata and expert rationales, and new evaluation metrics that assess semantic alignment, reasoning fidelity, and contextual sensitivity. By reframing quality assessment as a contextual, explainable, and multimodal modeling task, we aim to catalyze a shift toward more robust, human-aligned, and trustworthy evaluation systems.
Applications of Knowledge Distillation in Remote Sensing: A Survey
Sep 18, 2024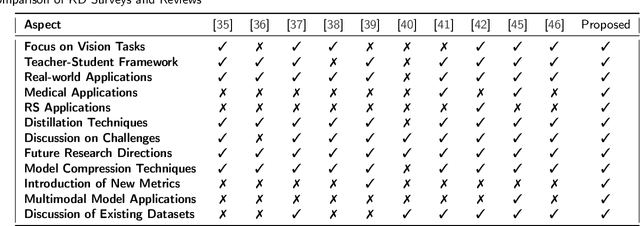
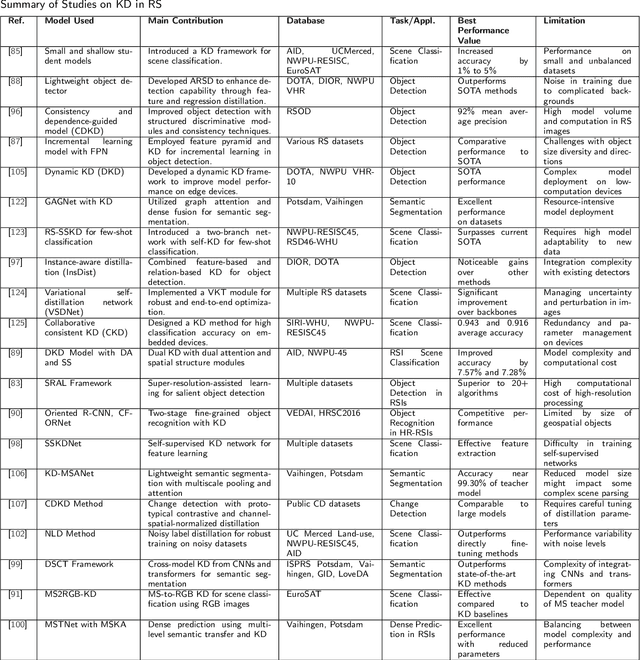
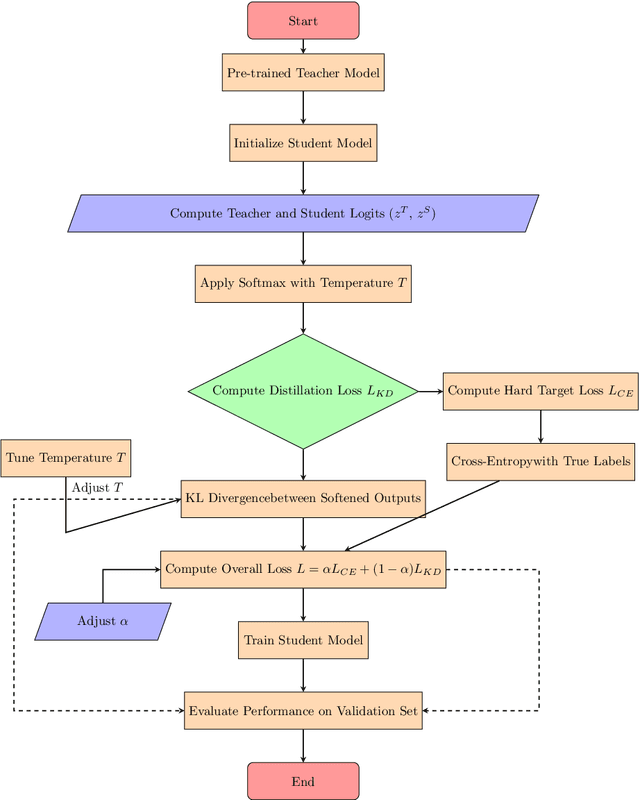
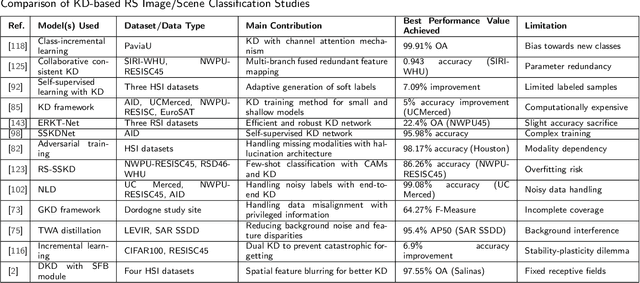
Abstract:With the ever-growing complexity of models in the field of remote sensing (RS), there is an increasing demand for solutions that balance model accuracy with computational efficiency. Knowledge distillation (KD) has emerged as a powerful tool to meet this need, enabling the transfer of knowledge from large, complex models to smaller, more efficient ones without significant loss in performance. This review article provides an extensive examination of KD and its innovative applications in RS. KD, a technique developed to transfer knowledge from a complex, often cumbersome model (teacher) to a more compact and efficient model (student), has seen significant evolution and application across various domains. Initially, we introduce the fundamental concepts and historical progression of KD methods. The advantages of employing KD are highlighted, particularly in terms of model compression, enhanced computational efficiency, and improved performance, which are pivotal for practical deployments in RS scenarios. The article provides a comprehensive taxonomy of KD techniques, where each category is critically analyzed to demonstrate the breadth and depth of the alternative options, and illustrates specific case studies that showcase the practical implementation of KD methods in RS tasks, such as instance segmentation and object detection. Further, the review discusses the challenges and limitations of KD in RS, including practical constraints and prospective future directions, providing a comprehensive overview for researchers and practitioners in the field of RS. Through this organization, the paper not only elucidates the current state of research in KD but also sets the stage for future research opportunities, thereby contributing significantly to both academic research and real-world applications.
SDF2Net: Shallow to Deep Feature Fusion Network for PolSAR Image Classification
Feb 27, 2024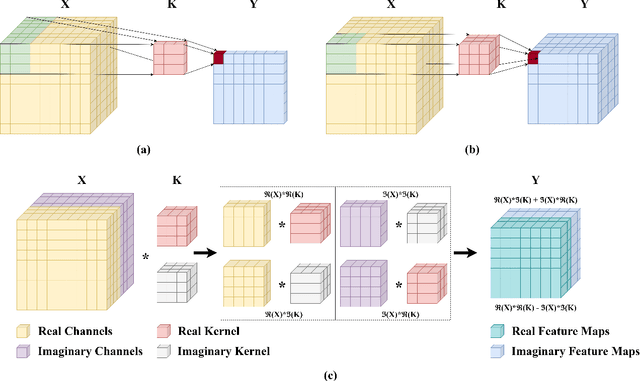
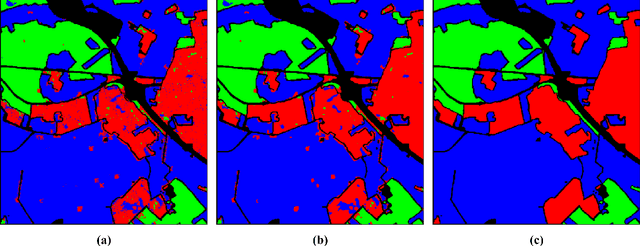
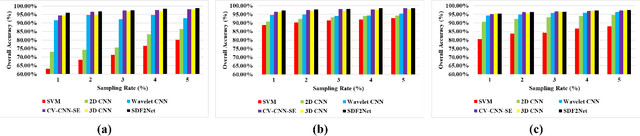
Abstract:Polarimetric synthetic aperture radar (PolSAR) images encompass valuable information that can facilitate extensive land cover interpretation and generate diverse output products. Extracting meaningful features from PolSAR data poses challenges distinct from those encountered in optical imagery. Deep learning (DL) methods offer effective solutions for overcoming these challenges in PolSAR feature extraction. Convolutional neural networks (CNNs) play a crucial role in capturing PolSAR image characteristics by leveraging kernel capabilities to consider local information and the complex-valued nature of PolSAR data. In this study, a novel three-branch fusion of complex-valued CNN, named the Shallow to Deep Feature Fusion Network (SDF2Net), is proposed for PolSAR image classification. To validate the performance of the proposed method, classification results are compared against multiple state-of-the-art approaches using the airborne synthetic aperture radar (AIRSAR) datasets of Flevoland and San Francisco, as well as the ESAR Oberpfaffenhofen dataset. The results indicate that the proposed approach demonstrates improvements in overallaccuracy, with a 1.3% and 0.8% enhancement for the AIRSAR datasets and a 0.5% improvement for the ESAR dataset. Analyses conducted on the Flevoland data underscore the effectiveness of the SDF2Net model, revealing a promising overall accuracy of 96.01% even with only a 1% sampling ratio.
Attention based Dual-Branch Complex Feature Fusion Network for Hyperspectral Image Classification
Nov 02, 2023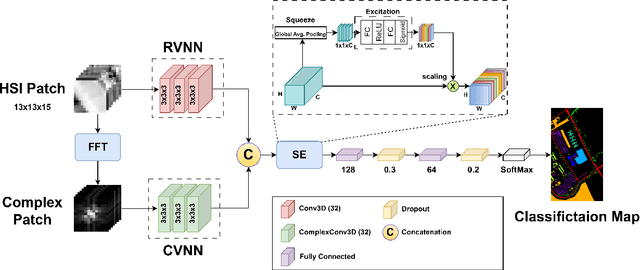
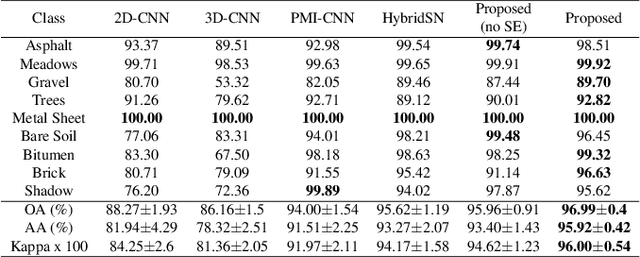
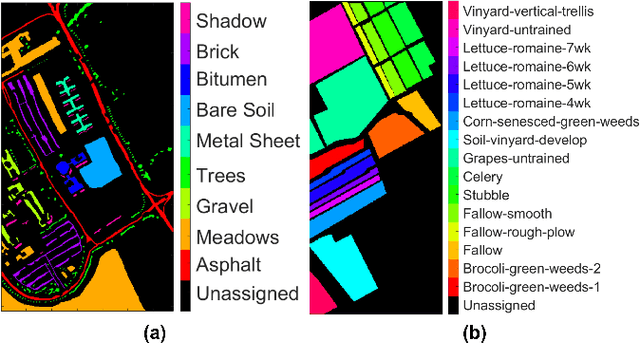
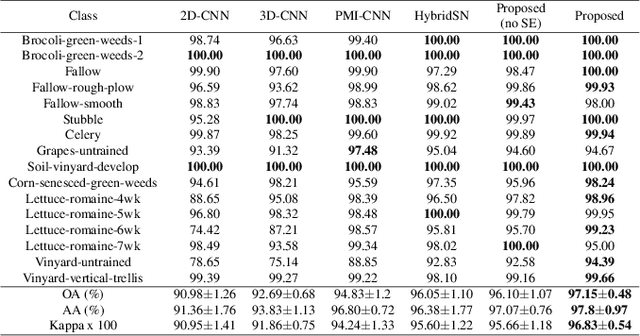
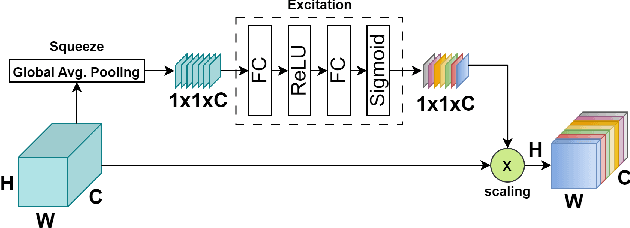
Abstract:This research work presents a novel dual-branch model for hyperspectral image classification that combines two streams: one for processing standard hyperspectral patches using Real-Valued Neural Network (RVNN) and the other for processing their corresponding Fourier transforms using Complex-Valued Neural Network (CVNN). The proposed model is evaluated on the Pavia University and Salinas datasets. Results show that the proposed model outperforms state-of-the-art methods in terms of overall accuracy, average accuracy, and Kappa. Through the incorporation of Fourier transforms in the second stream, the model is able to extract frequency information, which complements the spatial information extracted by the first stream. The combination of these two streams improves the overall performance of the model. Furthermore, to enhance the model performance, the Squeeze and Excitation (SE) mechanism has been utilized. Experimental evidence show that SE block improves the models overall accuracy by almost 1\%.
Operational Neural Networks for Efficient Hyperspectral Single-Image Super-Resolution
Mar 29, 2023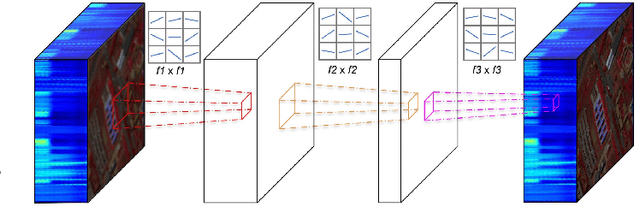
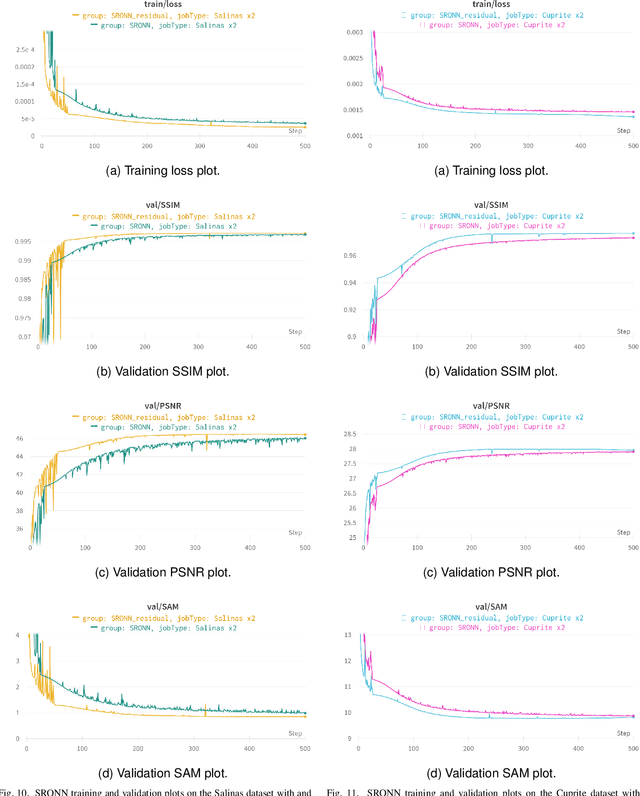
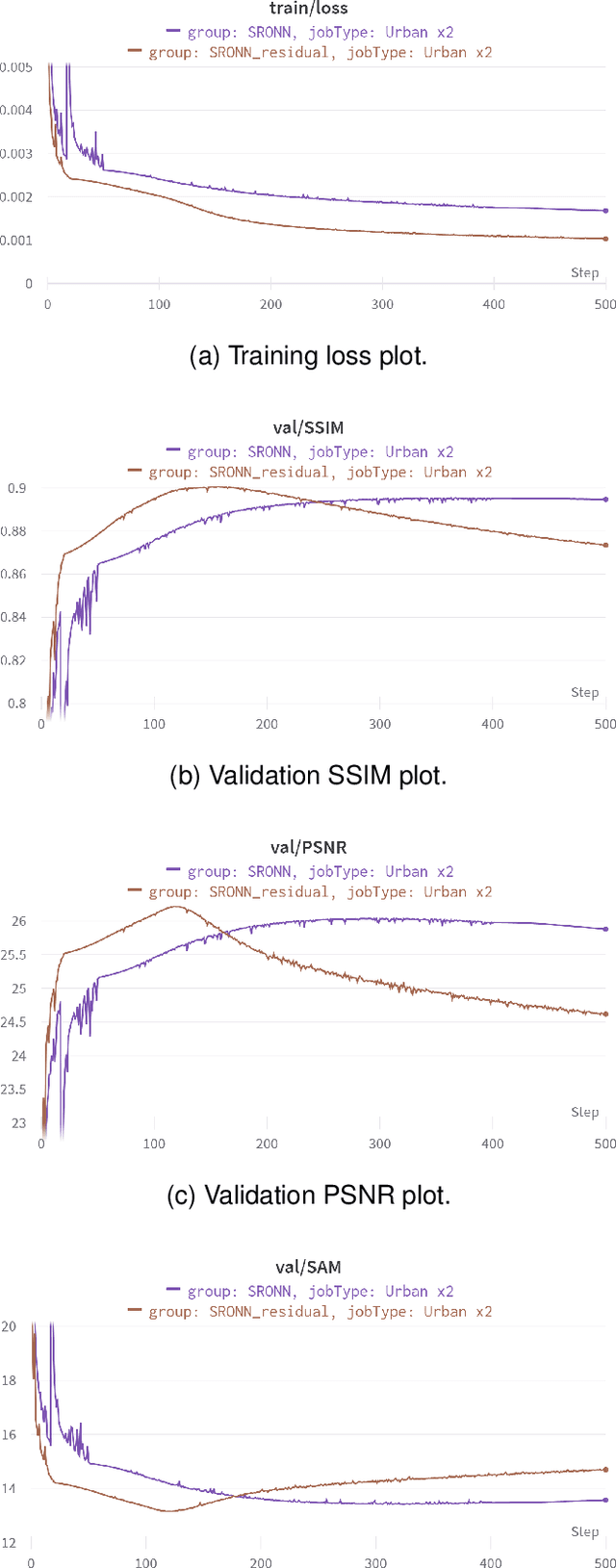
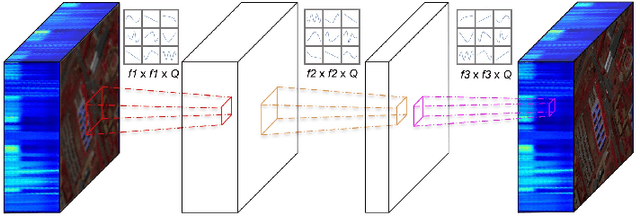
Abstract:Hyperspectral Imaging is a crucial tool in remote sensing which captures far more spectral information than standard color images. However, the increase in spectral information comes at the cost of spatial resolution. Super-resolution is a popular technique where the goal is to generate a high-resolution version of a given low-resolution input. The majority of modern super-resolution approaches use convolutional neural networks. However, convolution itself is a linear operation and the networks rely on the non-linear activation functions after each layer to provide the necessary non-linearity to learn the complex underlying function. This means that convolutional neural networks tend to be very deep to achieve the desired results. Recently, self-organized operational neural networks have been proposed that aim to overcome this limitation by replacing the convolutional filters with learnable non-linear functions through the use of MacLaurin series expansions. This work focuses on extending the convolutional filters of a popular super-resolution model to more powerful operational filters to enhance the model performance on hyperspectral images. We also investigate the effects that residual connections and different normalization types have on this type of enhanced network. Despite having fewer parameters than their convolutional network equivalents, our results show that operational neural networks achieve superior super-resolution performance on small hyperspectral image datasets.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge