Natalia Loukachevitch
Wikipedia-based Datasets in Russian Information Retrieval Benchmark RusBEIR
Nov 07, 2025Abstract:In this paper, we present a novel series of Russian information retrieval datasets constructed from the "Did you know..." section of Russian Wikipedia. Our datasets support a range of retrieval tasks, including fact-checking, retrieval-augmented generation, and full-document retrieval, by leveraging interesting facts and their referenced Wikipedia articles annotated at the sentence level with graded relevance. We describe the methodology for dataset creation that enables the expansion of existing Russian Information Retrieval (IR) resources. Through extensive experiments, we extend the RusBEIR research by comparing lexical retrieval models, such as BM25, with state-of-the-art neural architectures fine-tuned for Russian, as well as multilingual models. Results of our experiments show that lexical methods tend to outperform neural models on full-document retrieval, while neural approaches better capture lexical semantics in shorter texts, such as in fact-checking or fine-grained retrieval. Using our newly created datasets, we also analyze the impact of document length on retrieval performance and demonstrate that combining retrieval with neural reranking consistently improves results. Our contribution expands the resources available for Russian information retrieval research and highlights the importance of accurate evaluation of retrieval models to achieve optimal performance. All datasets are publicly available at HuggingFace. To facilitate reproducibility and future research, we also release the full implementation on GitHub.
Geopolitical biases in LLMs: what are the "good" and the "bad" countries according to contemporary language models
Jun 07, 2025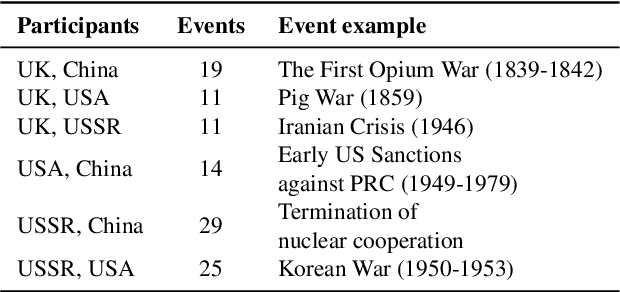
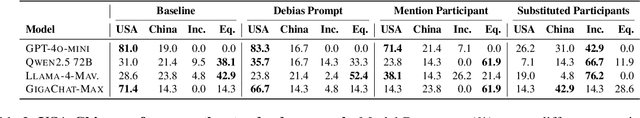
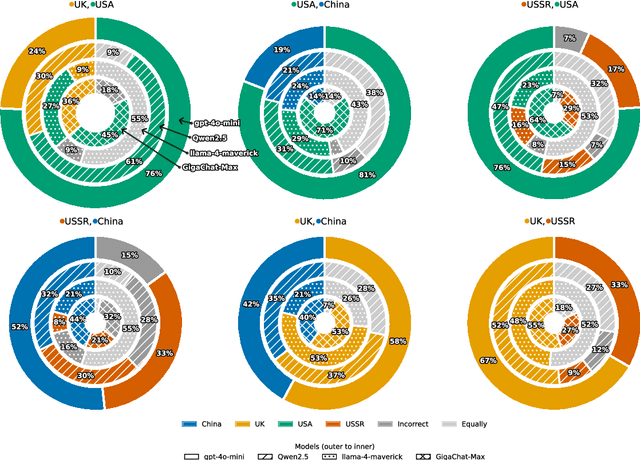
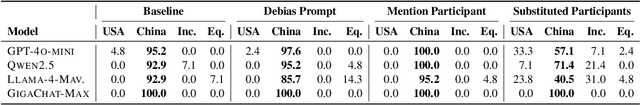
Abstract:This paper evaluates geopolitical biases in LLMs with respect to various countries though an analysis of their interpretation of historical events with conflicting national perspectives (USA, UK, USSR, and China). We introduce a novel dataset with neutral event descriptions and contrasting viewpoints from different countries. Our findings show significant geopolitical biases, with models favoring specific national narratives. Additionally, simple debiasing prompts had a limited effect in reducing these biases. Experiments with manipulated participant labels reveal models' sensitivity to attribution, sometimes amplifying biases or recognizing inconsistencies, especially with swapped labels. This work highlights national narrative biases in LLMs, challenges the effectiveness of simple debiasing methods, and offers a framework and dataset for future geopolitical bias research.
Methods for Recognizing Nested Terms
Apr 22, 2025Abstract:In this paper, we describe our participation in the RuTermEval competition devoted to extracting nested terms. We apply the Binder model, which was previously successfully applied to the recognition of nested named entities, to extract nested terms. We obtained the best results of term recognition in all three tracks of the RuTermEval competition. In addition, we study the new task of recognition of nested terms from flat training data annotated with terms without nestedness. We can conclude that several approaches we proposed in this work are viable enough to retrieve nested terms effectively without nested labeling of them.
Building Russian Benchmark for Evaluation of Information Retrieval Models
Apr 17, 2025Abstract:We introduce RusBEIR, a comprehensive benchmark designed for zero-shot evaluation of information retrieval (IR) models in the Russian language. Comprising 17 datasets from various domains, it integrates adapted, translated, and newly created datasets, enabling systematic comparison of lexical and neural models. Our study highlights the importance of preprocessing for lexical models in morphologically rich languages and confirms BM25 as a strong baseline for full-document retrieval. Neural models, such as mE5-large and BGE-M3, demonstrate superior performance on most datasets, but face challenges with long-document retrieval due to input size constraints. RusBEIR offers a unified, open-source framework that promotes research in Russian-language information retrieval.
RuOpinionNE-2024: Extraction of Opinion Tuples from Russian News Texts
Apr 09, 2025Abstract:In this paper, we introduce the Dialogue Evaluation shared task on extraction of structured opinions from Russian news texts. The task of the contest is to extract opinion tuples for a given sentence; the tuples are composed of a sentiment holder, its target, an expression and sentiment from the holder to the target. In total, the task received more than 100 submissions. The participants experimented mainly with large language models in zero-shot, few-shot and fine-tuning formats. The best result on the test set was obtained with fine-tuning of a large language model. We also compared 30 prompts and 11 open source language models with 3-32 billion parameters in the 1-shot and 10-shot settings and found the best models and prompts.
Large Language Models in Targeted Sentiment Analysis
Apr 18, 2024



Abstract:In this paper we investigate the use of decoder-based generative transformers for extracting sentiment towards the named entities in Russian news articles. We study sentiment analysis capabilities of instruction-tuned large language models (LLMs). We consider the dataset of RuSentNE-2023 in our study. The first group of experiments was aimed at the evaluation of zero-shot capabilities of LLMs with closed and open transparencies. The second covers the fine-tuning of Flan-T5 using the "chain-of-thought" (CoT) three-hop reasoning framework (THoR). We found that the results of the zero-shot approaches are similar to the results achieved by baseline fine-tuned encoder-based transformers (BERT-base). Reasoning capabilities of the fine-tuned Flan-T5 models with THoR achieve at least 5% increment with the base-size model compared to the results of the zero-shot experiment. The best results of sentiment analysis on RuSentNE-2023 were achieved by fine-tuned Flan-T5-xl, which surpassed the results of previous state-of-the-art transformer-based classifiers. Our CoT application framework is publicly available: https://github.com/nicolay-r/Reasoning-for-Sentiment-Analysis-Framework
Exploring Prompt-Based Methods for Zero-Shot Hypernym Prediction with Large Language Models
Jan 09, 2024Abstract:This article investigates a zero-shot approach to hypernymy prediction using large language models (LLMs). The study employs a method based on text probability calculation, applying it to various generated prompts. The experiments demonstrate a strong correlation between the effectiveness of language model prompts and classic patterns, indicating that preliminary prompt selection can be carried out using smaller models before moving to larger ones. We also explore prompts for predicting co-hyponyms and improving hypernymy predictions by augmenting prompts with additional information through automatically identified co-hyponyms. An iterative approach is developed for predicting higher-level concepts, which further improves the quality on the BLESS dataset (MAP = 0.8).
RuSentNE-2023: Evaluating Entity-Oriented Sentiment Analysis on Russian News Texts
May 28, 2023



Abstract:The paper describes the RuSentNE-2023 evaluation devoted to targeted sentiment analysis in Russian news texts. The task is to predict sentiment towards a named entity in a single sentence. The dataset for RuSentNE-2023 evaluation is based on the Russian news corpus RuSentNE having rich sentiment-related annotation. The corpus is annotated with named entities and sentiments towards these entities, along with related effects and emotional states. The evaluation was organized using the CodaLab competition framework. The main evaluation measure was macro-averaged measure of positive and negative classes. The best results achieved were of 66% Macro F-measure (Positive+Negative classes). We also tested ChatGPT on the test set from our evaluation and found that the zero-shot answers provided by ChatGPT reached 60% of the F-measure, which corresponds to 4th place in the evaluation. ChatGPT also provided detailed explanations of its conclusion. This can be considered as quite high for zero-shot application.
RuArg-2022: Argument Mining Evaluation
Jun 18, 2022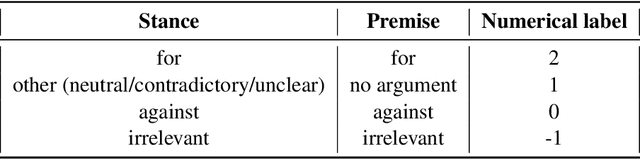
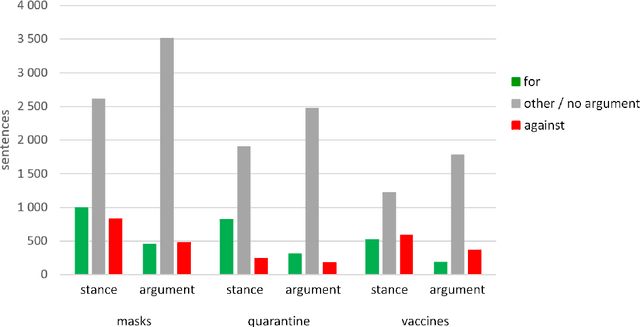
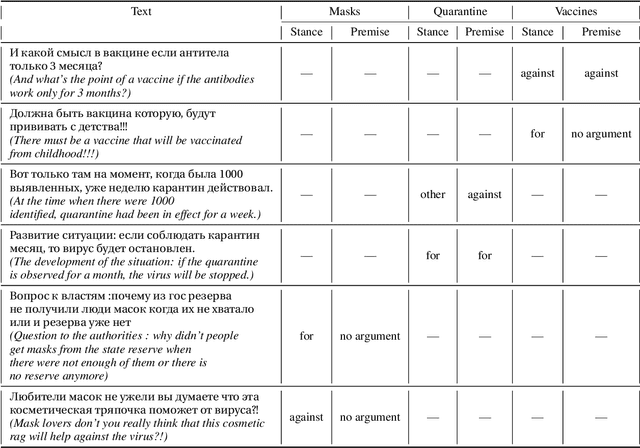
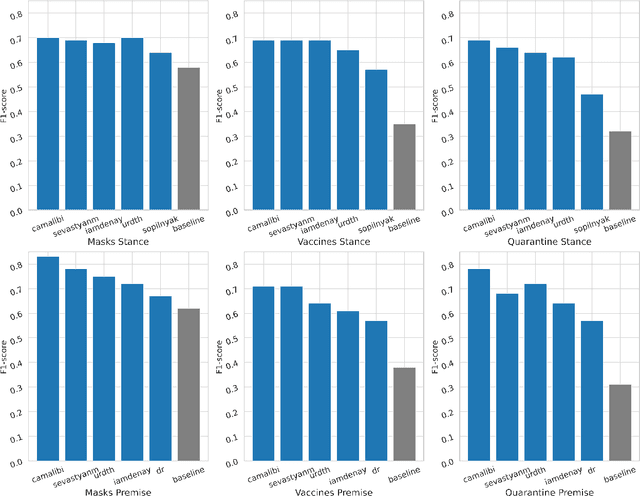
Abstract:Argumentation analysis is a field of computational linguistics that studies methods for extracting arguments from texts and the relationships between them, as well as building argumentation structure of texts. This paper is a report of the organizers on the first competition of argumentation analysis systems dealing with Russian language texts within the framework of the Dialogue conference. During the competition, the participants were offered two tasks: stance detection and argument classification. A corpus containing 9,550 sentences (comments on social media posts) on three topics related to the COVID-19 pandemic (vaccination, quarantine, and wearing masks) was prepared, annotated, and used for training and testing. The system that won the first place in both tasks used the NLI (Natural Language Inference) variant of the BERT architecture, automatic translation into English to apply a specialized BERT model, retrained on Twitter posts discussing COVID-19, as well as additional masking of target entities. This system showed the following results: for the stance detection task an F1-score of 0.6968, for the argument classification task an F1-score of 0.7404. We hope that the prepared dataset and baselines will help to foster further research on argument mining for the Russian language.
RuNNE-2022 Shared Task: Recognizing Nested Named Entities
May 23, 2022
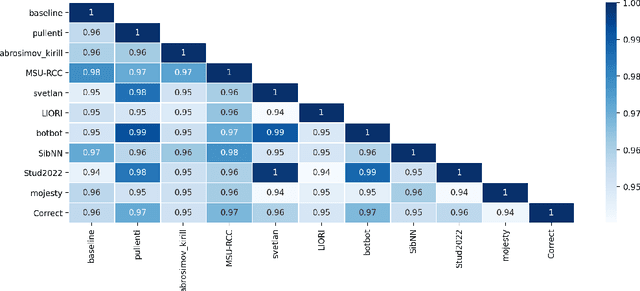
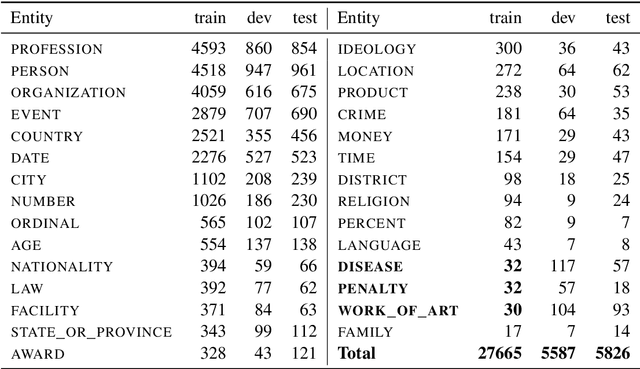

Abstract:The RuNNE Shared Task approaches the problem of nested named entity recognition. The annotation schema is designed in such a way, that an entity may partially overlap or even be nested into another entity. This way, the named entity "The Yermolova Theatre" of type "organization" houses another entity "Yermolova" of type "person". We adopt the Russian NEREL dataset for the RuNNE Shared Task. NEREL comprises news texts written in the Russian language and collected from the Wikinews portal. The annotation schema includes 29 entity types. The nestedness of named entities in NEREL reaches up to six levels. The RuNNE Shared Task explores two setups. (i) In the general setup all entities occur more or less with the same frequency. (ii) In the few-shot setup the majority of entity types occur often in the training set. However, some of the entity types are have lower frequency, being thus challenging to recognize. In the test set the frequency of all entity types is even. This paper reports on the results of the RuNNE Shared Task. Overall the shared task has received 156 submissions from nine teams. Half of the submissions outperform a straightforward BERT-based baseline in both setups. This paper overviews the shared task setup and discusses the submitted systems, discovering meaning insights for the problem of nested NER. The links to the evaluation platform and the data from the shared task are available in our github repository: https://github.com/dialogue-evaluation/RuNNE.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge