Tatiana Batura
Automatic Aspect Extraction from Scientific Texts
Oct 06, 2023



Abstract:Being able to extract from scientific papers their main points, key insights, and other important information, referred to here as aspects, might facilitate the process of conducting a scientific literature review. Therefore, the aim of our research is to create a tool for automatic aspect extraction from Russian-language scientific texts of any domain. In this paper, we present a cross-domain dataset of scientific texts in Russian, annotated with such aspects as Task, Contribution, Method, and Conclusion, as well as a baseline algorithm for aspect extraction, based on the multilingual BERT model fine-tuned on our data. We show that there are some differences in aspect representation in different domains, but even though our model was trained on a limited number of scientific domains, it is still able to generalize to new domains, as was proved by cross-domain experiments. The code and the dataset are available at \url{https://github.com/anna-marshalova/automatic-aspect-extraction-from-scientific-texts}.
Named Entity Inclusion in Abstractive Text Summarization
Jul 05, 2023Abstract:We address the named entity omission - the drawback of many current abstractive text summarizers. We suggest a custom pretraining objective to enhance the model's attention on the named entities in a text. At first, the named entity recognition model RoBERTa is trained to determine named entities in the text. After that, this model is used to mask named entities in the text and the BART model is trained to reconstruct them. Next, the BART model is fine-tuned on the summarization task. Our experiments showed that this pretraining approach improves named entity inclusion precision and recall metrics.
* https://aclanthology.org/2022.sdp-1.17/
TERMinator: A system for scientific texts processing
Sep 29, 2022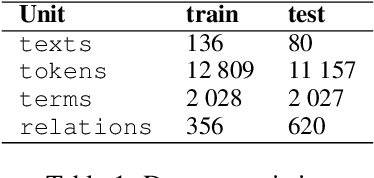

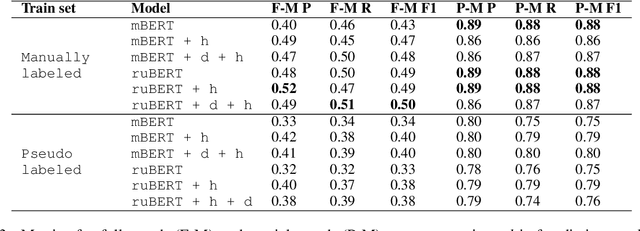

Abstract:This paper is devoted to the extraction of entities and semantic relations between them from scientific texts, where we consider scientific terms as entities. In this paper, we present a dataset that includes annotations for two tasks and develop a system called TERMinator for the study of the influence of language models on term recognition and comparison of different approaches for relation extraction. Experiments show that language models pre-trained on the target language are not always show the best performance. Also adding some heuristic approaches may improve the overall quality of the particular task. The developed tool and the annotated corpus are publicly available at https://github.com/iis-research-team/terminator and may be useful for other researchers.
RuNNE-2022 Shared Task: Recognizing Nested Named Entities
May 23, 2022
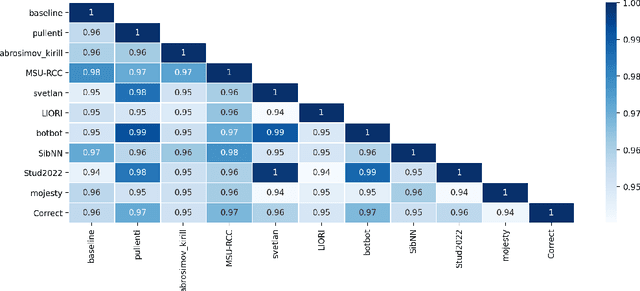
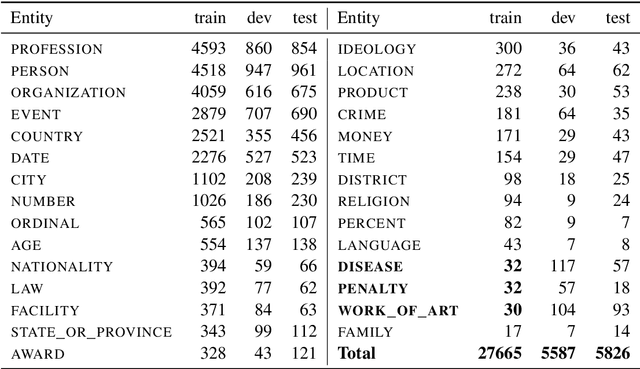

Abstract:The RuNNE Shared Task approaches the problem of nested named entity recognition. The annotation schema is designed in such a way, that an entity may partially overlap or even be nested into another entity. This way, the named entity "The Yermolova Theatre" of type "organization" houses another entity "Yermolova" of type "person". We adopt the Russian NEREL dataset for the RuNNE Shared Task. NEREL comprises news texts written in the Russian language and collected from the Wikinews portal. The annotation schema includes 29 entity types. The nestedness of named entities in NEREL reaches up to six levels. The RuNNE Shared Task explores two setups. (i) In the general setup all entities occur more or less with the same frequency. (ii) In the few-shot setup the majority of entity types occur often in the training set. However, some of the entity types are have lower frequency, being thus challenging to recognize. In the test set the frequency of all entity types is even. This paper reports on the results of the RuNNE Shared Task. Overall the shared task has received 156 submissions from nine teams. Half of the submissions outperform a straightforward BERT-based baseline in both setups. This paper overviews the shared task setup and discusses the submitted systems, discovering meaning insights for the problem of nested NER. The links to the evaluation platform and the data from the shared task are available in our github repository: https://github.com/dialogue-evaluation/RuNNE.
A system for information extraction from scientific texts in Russian
Sep 14, 2021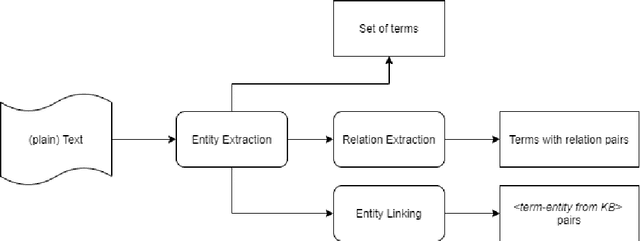
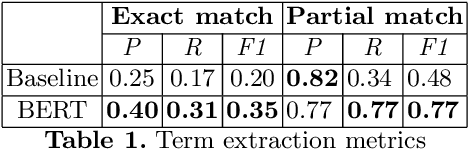
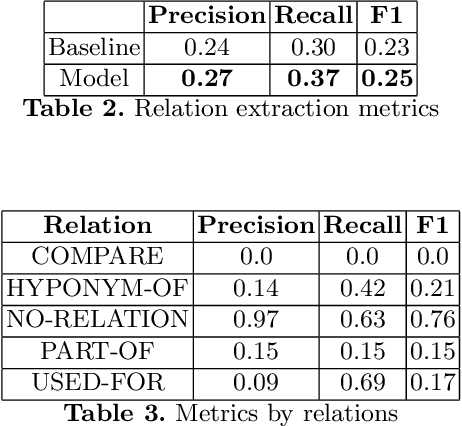

Abstract:In this paper, we present a system for information extraction from scientific texts in the Russian language. The system performs several tasks in an end-to-end manner: term recognition, extraction of relations between terms, and term linking with entities from the knowledge base. These tasks are extremely important for information retrieval, recommendation systems, and classification. The advantage of the implemented methods is that the system does not require a large amount of labeled data, which saves time and effort for data labeling and therefore can be applied in low- and mid-resource settings. The source code is publicly available and can be used for different research purposes.
NEREL: A Russian Dataset with Nested Named Entities, Relations and Events
Sep 03, 2021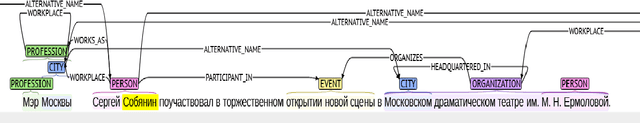
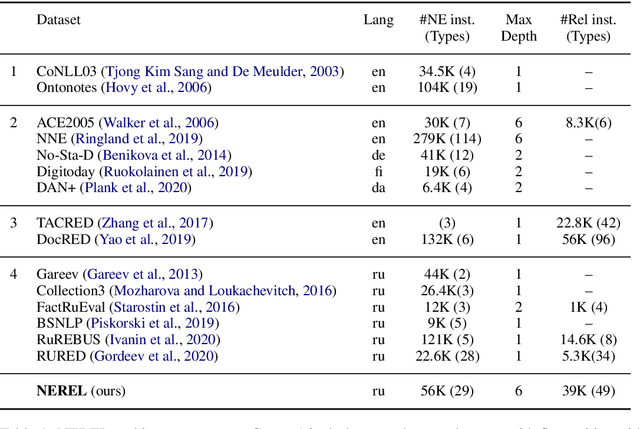
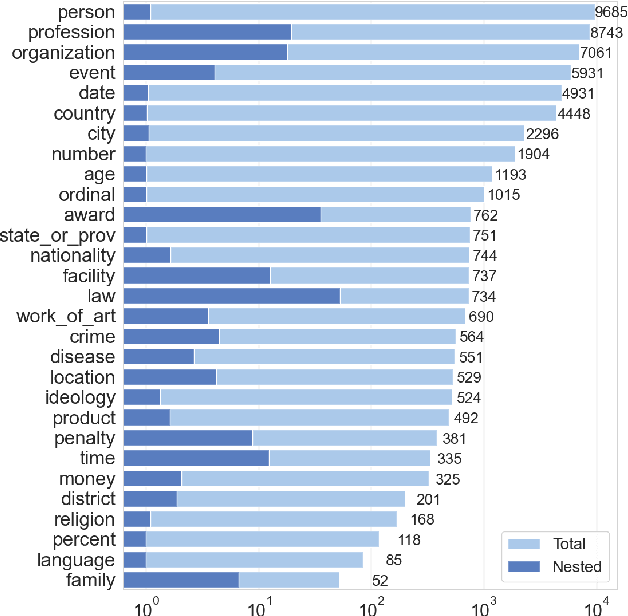
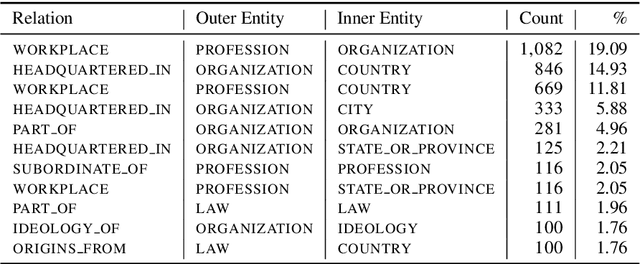
Abstract:In this paper, we present NEREL, a Russian dataset for named entity recognition and relation extraction. NEREL is significantly larger than existing Russian datasets: to date it contains 56K annotated named entities and 39K annotated relations. Its important difference from previous datasets is annotation of nested named entities, as well as relations within nested entities and at the discourse level. NEREL can facilitate development of novel models that can extract relations between nested named entities, as well as relations on both sentence and document levels. NEREL also contains the annotation of events involving named entities and their roles in the events. The NEREL collection is available via https://github.com/nerel-ds/NEREL.
Entity Recognition and Relation Extraction from Scientific and Technical Texts in Russian
Dec 14, 2020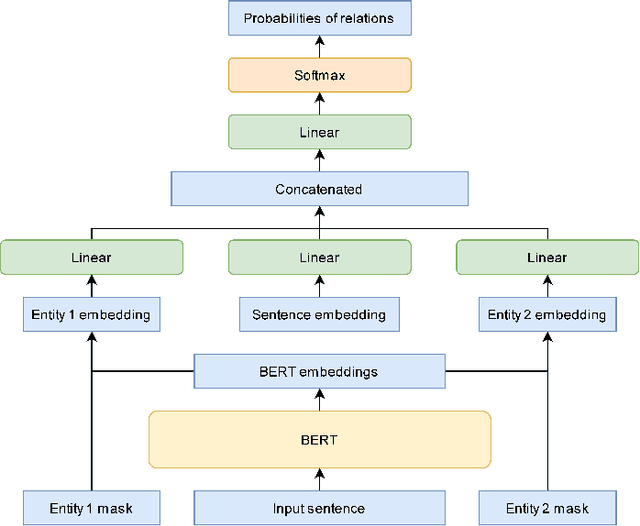
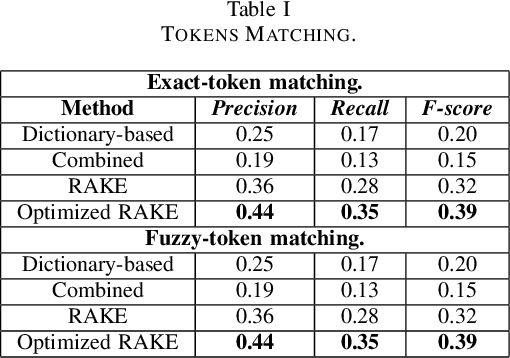
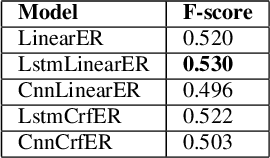
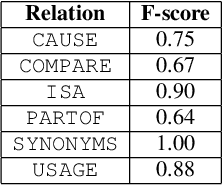
Abstract:This paper is devoted to the study of methods for information extraction (entity recognition and relation classification) from scientific texts on information technology. Scientific publications provide valuable information into cutting-edge scientific advances, but efficient processing of increasing amounts of data is a time-consuming task. In this paper, several modifications of methods for the Russian language are proposed. It also includes the results of experiments comparing a keyword extraction method, vocabulary method, and some methods based on neural networks. Text collections for these tasks exist for the English language and are actively used by the scientific community, but at present, such datasets in Russian are not publicly available. In this paper, we present a corpus of scientific texts in Russian, RuSERRC. This dataset consists of 1600 unlabeled documents and 80 labeled with entities and semantic relations (6 relation types were considered). The dataset and models are available at https://github.com/iis-research-team. We hope they can be useful for research purposes and development of information extraction systems.
RuREBus: a Case Study of Joint Named Entity Recognition and Relation Extraction from e-Government Domain
Oct 29, 2020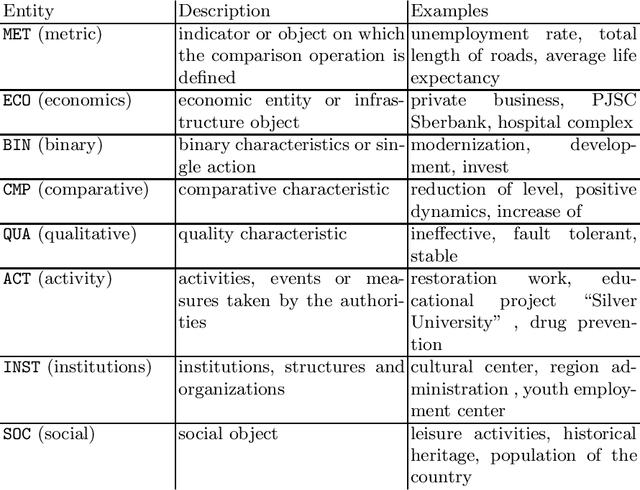

Abstract:We show-case an application of information extraction methods, such as named entity recognition (NER) and relation extraction (RE) to a novel corpus, consisting of documents, issued by a state agency. The main challenges of this corpus are: 1) the annotation scheme differs greatly from the one used for the general domain corpora, and 2) the documents are written in a language other than English. Unlike expectations, the state-of-the-art transformer-based models show modest performance for both tasks, either when approached sequentially, or in an end-to-end fashion. Our experiments have demonstrated that fine-tuning on a large unlabeled corpora does not automatically yield significant improvement and thus we may conclude that more sophisticated strategies of leveraging unlabelled texts are demanded. In this paper, we describe the whole developed pipeline, starting from text annotation, baseline development, and designing a shared task in hopes of improving the baseline. Eventually, we realize that the current NER and RE technologies are far from being mature and do not overcome so far challenges like ours.
So What's the Plan? Mining Strategic Planning Documents
Jul 07, 2020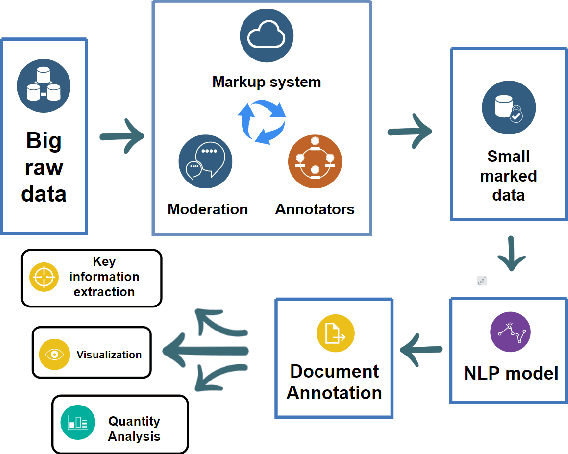
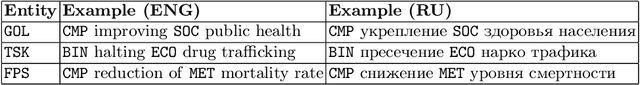
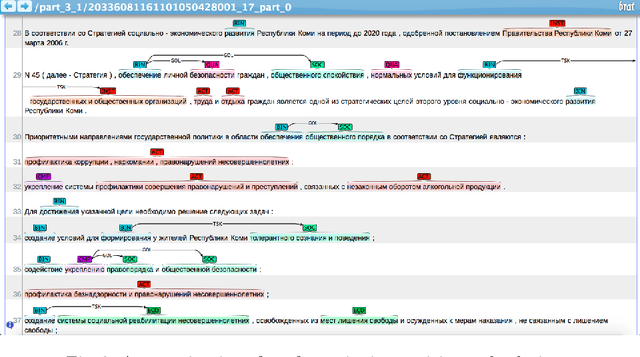
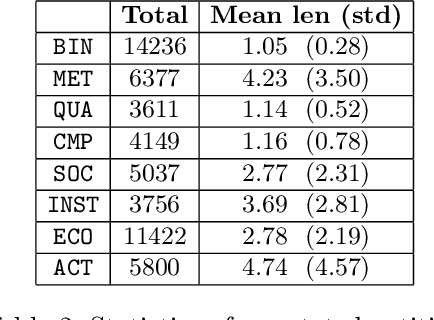
Abstract:In this paper we present a corpus of Russian strategic planning documents, RuREBus. This project is grounded both from language technology and e-government perspectives. Not only new language sources and tools are being developed, but also their applications to e-goverment research. We demonstrate the pipeline for creating a text corpus from scratch. First, the annotation schema is designed. Next texts are marked up using human-in-the-loop strategy, so that preliminary annotations are derived from a machine learning model and are manually corrected. The amount of annotated texts is large enough to showcase what insights can be gained from RuREBus.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge