Muyu Li
DSReg: Using Distant Supervision as a Regularizer
May 30, 2019
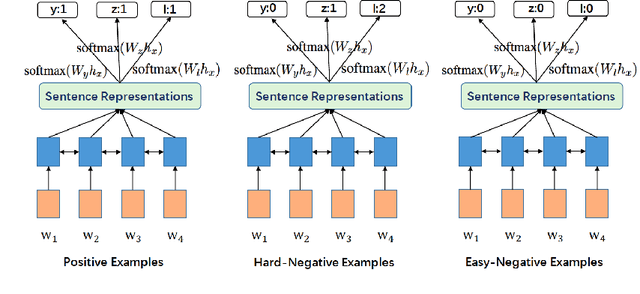
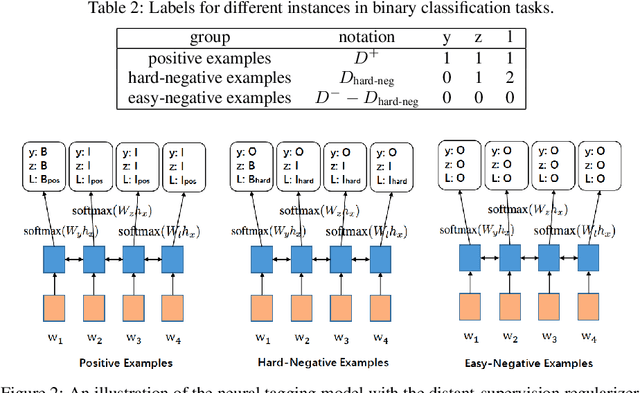
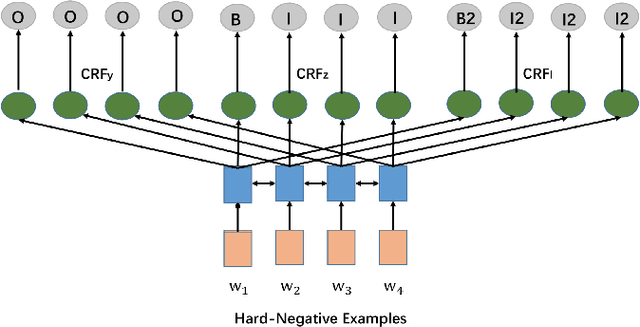
Abstract:In this paper, we aim at tackling a general issue in NLP tasks where some of the negative examples are highly similar to the positive examples, i.e., hard-negative examples. We propose the distant supervision as a regularizer (DSReg) approach to tackle this issue. The original task is converted to a multi-task learning problem, in which distant supervision is used to retrieve hard-negative examples. The obtained hard-negative examples are then used as a regularizer. The original target objective of distinguishing positive examples from negative examples is jointly optimized with the auxiliary task objective of distinguishing softened positive (i.e., hard-negative examples plus positive examples) from easy-negative examples. In the neural context, this can be done by outputting the same representation from the last neural layer to different $softmax$ functions. Using this strategy, we can improve the performance of baseline models in a range of different NLP tasks, including text classification, sequence labeling and reading comprehension.
Glyce: Glyph-vectors for Chinese Character Representations
Jan 29, 2019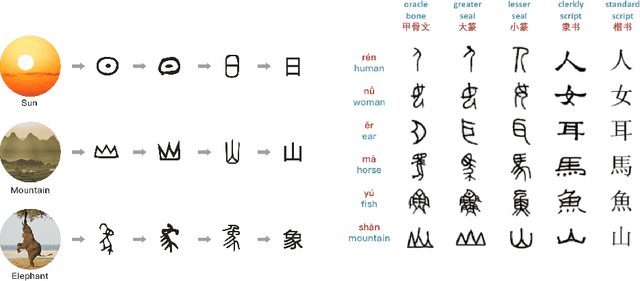
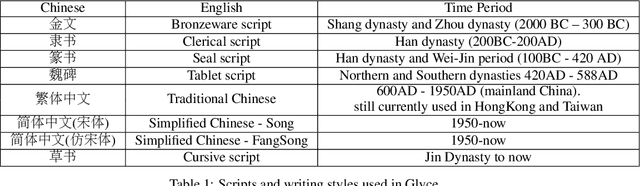
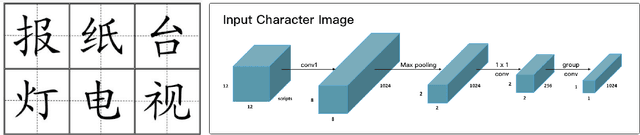
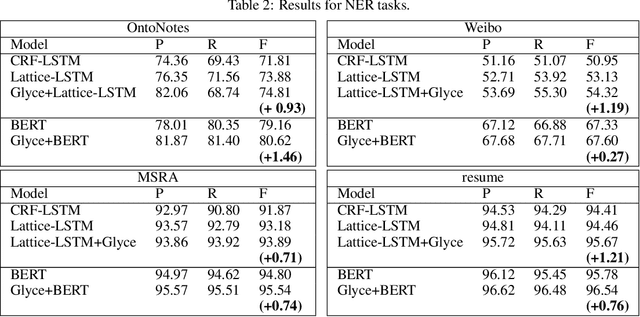
Abstract:It is intuitive that NLP tasks for logographic languages like Chinese should benefit from the use of the glyph information in those languages. However, due to the lack of rich pictographic evidence in glyphs and the weak generalization ability of standard computer vision models on character data, an effective way to utilize the glyph information remains to be found. In this paper, we address this gap by presenting the Glyce, the glyph-vectors for Chinese character representations. We make three major innovations: (1) We use historical Chinese scripts (e.g., bronzeware script, seal script, traditional Chinese, etc) to enrich the pictographic evidence in characters; (2) We design CNN structures tailored to Chinese character image processing; and (3) We use image-classification as an auxiliary task in a multi-task learning setup to increase the model's ability to generalize. For the first time, we show that glyph-based models are able to consistently outperform word/char ID-based models in a wide range of Chinese NLP tasks. Using Glyce, we are able to achieve the state-of-the-art performances on 13 (almost all) Chinese NLP tasks, including (1) character-Level language modeling, (2) word-Level language modeling, (3) Chinese word segmentation, (4) name entity recognition, (5) part-of-speech tagging, (6) dependency parsing, (7) semantic role labeling, (8) sentence semantic similarity, (9) sentence intention identification, (10) Chinese-English machine translation, (11) sentiment analysis, (12) document classification and (13) discourse parsing
Learning When to Concentrate or Divert Attention: Self-Adaptive Attention Temperature for Neural Machine Translation
Aug 26, 2018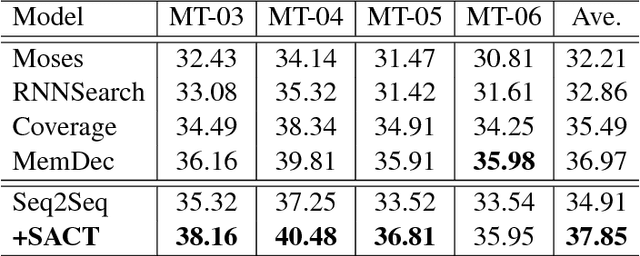
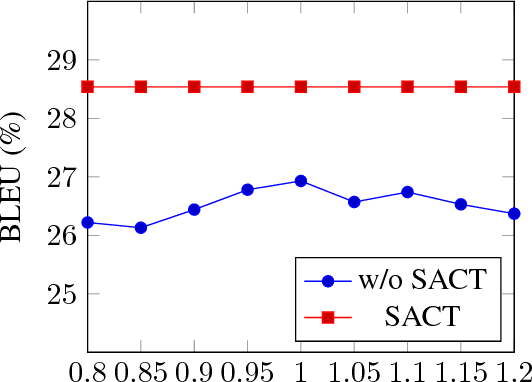
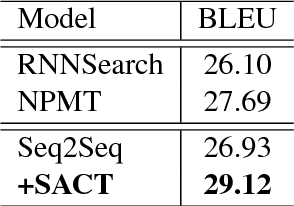
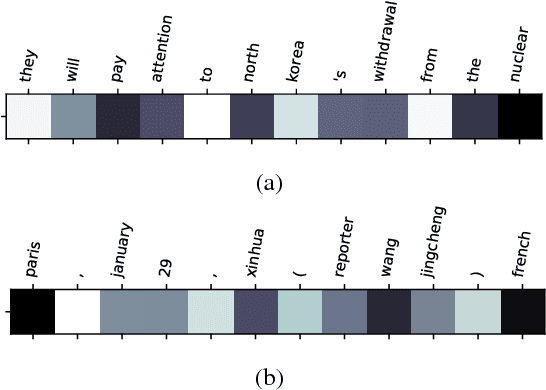
Abstract:Most of the Neural Machine Translation (NMT) models are based on the sequence-to-sequence (Seq2Seq) model with an encoder-decoder framework equipped with the attention mechanism. However, the conventional attention mechanism treats the decoding at each time step equally with the same matrix, which is problematic since the softness of the attention for different types of words (e.g. content words and function words) should differ. Therefore, we propose a new model with a mechanism called Self-Adaptive Control of Temperature (SACT) to control the softness of attention by means of an attention temperature. Experimental results on the Chinese-English translation and English-Vietnamese translation demonstrate that our model outperforms the baseline models, and the analysis and the case study show that our model can attend to the most relevant elements in the source-side contexts and generate the translation of high quality.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge