Murat Bilgel
from the iSTAGING consortium, for the ADNI
HACA3: A Unified Approach for Multi-site MR Image Harmonization
Dec 12, 2022Abstract:The lack of standardization is a prominent issue in magnetic resonance (MR) imaging. This often causes undesired contrast variations due to differences in hardware and acquisition parameters. In recent years, MR harmonization using image synthesis with disentanglement has been proposed to compensate for the undesired contrast variations. Despite the success of existing methods, we argue that three major improvements can be made. First, most existing methods are built upon the assumption that multi-contrast MR images of the same subject share the same anatomy. This assumption is questionable since different MR contrasts are specialized to highlight different anatomical features. Second, these methods often require a fixed set of MR contrasts for training (e.g., both Tw-weighted and T2-weighted images must be available), which limits their applicability. Third, existing methods generally are sensitive to imaging artifacts. In this paper, we present a novel approach, Harmonization with Attention-based Contrast, Anatomy, and Artifact Awareness (HACA3), to address these three issues. We first propose an anatomy fusion module that enables HACA3 to respect the anatomical differences between MR contrasts. HACA3 is also robust to imaging artifacts and can be trained and applied to any set of MR contrasts. Experiments show that HACA3 achieves state-of-the-art performance under multiple image quality metrics. We also demonstrate the applicability of HACA3 on downstream tasks with diverse MR datasets acquired from 21 sites with different field strengths, scanner platforms, and acquisition protocols.
Disentangling A Single MR Modality
May 10, 2022



Abstract:Disentangling anatomical and contrast information from medical images has gained attention recently, demonstrating benefits for various image analysis tasks. Current methods learn disentangled representations using either paired multi-modal images with the same underlying anatomy or auxiliary labels (e.g., manual delineations) to provide inductive bias for disentanglement. However, these requirements could significantly increase the time and cost in data collection and limit the applicability of these methods when such data are not available. Moreover, these methods generally do not guarantee disentanglement. In this paper, we present a novel framework that learns theoretically and practically superior disentanglement from single modality magnetic resonance images. Moreover, we propose a new information-based metric to quantitatively evaluate disentanglement. Comparisons over existing disentangling methods demonstrate that the proposed method achieves superior performance in both disentanglement and cross-domain image-to-image translation tasks.
Disentangling Alzheimer's disease neurodegeneration from typical brain aging using machine learning
Sep 08, 2021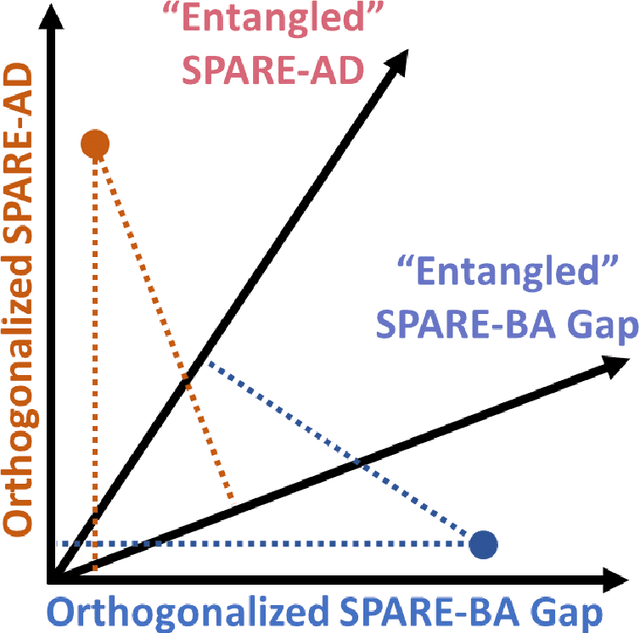
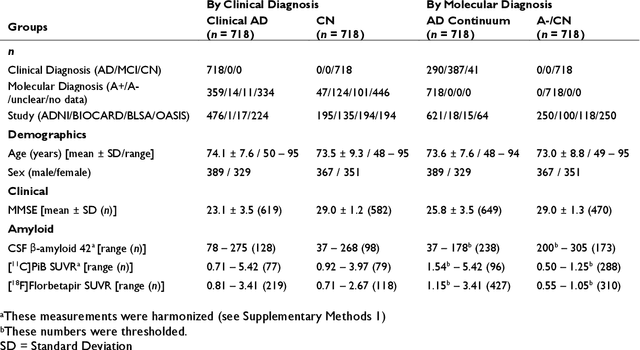
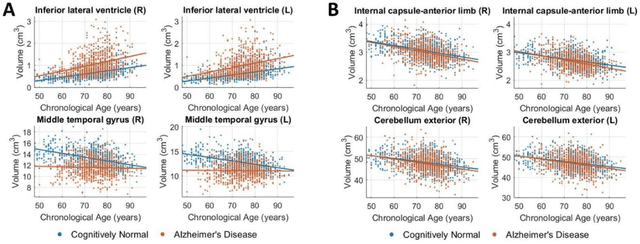
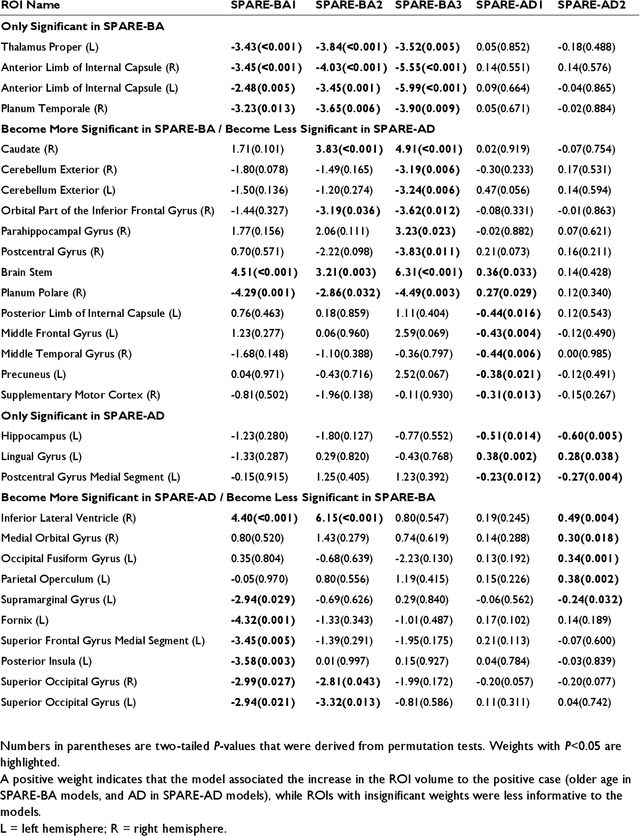
Abstract:Neuroimaging biomarkers that distinguish between typical brain aging and Alzheimer's disease (AD) are valuable for determining how much each contributes to cognitive decline. Machine learning models can derive multi-variate brain change patterns related to the two processes, including the SPARE-AD (Spatial Patterns of Atrophy for Recognition of Alzheimer's Disease) and SPARE-BA (of Brain Aging) investigated herein. However, substantial overlap between brain regions affected in the two processes confounds measuring them independently. We present a methodology toward disentangling the two. T1-weighted MRI images of 4,054 participants (48-95 years) with AD, mild cognitive impairment (MCI), or cognitively normal (CN) diagnoses from the iSTAGING (Imaging-based coordinate SysTem for AGIng and NeurodeGenerative diseases) consortium were analyzed. First, a subset of AD patients and CN adults were selected based purely on clinical diagnoses to train SPARE-BA1 (regression of age using CN individuals) and SPARE-AD1 (classification of CN versus AD). Second, analogous groups were selected based on clinical and molecular markers to train SPARE-BA2 and SPARE-AD2: amyloid-positive (A+) AD continuum group (consisting of A+AD, A+MCI, and A+ and tau-positive CN individuals) and amyloid-negative (A-) CN group. Finally, the combined group of the AD continuum and A-/CN individuals was used to train SPARE-BA3, with the intention to estimate brain age regardless of AD-related brain changes. Disentangled SPARE models derived brain patterns that were more specific to the two types of the brain changes. Correlation between the SPARE-BA and SPARE-AD was significantly reduced. Correlation of disentangled SPARE-AD was non-inferior to the molecular measurements and to the number of APOE4 alleles, but was less to AD-related psychometric test scores, suggesting contribution of advanced brain aging to these scores.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge