Mujie Lin
MiniMax-M1: Scaling Test-Time Compute Efficiently with Lightning Attention
Jun 16, 2025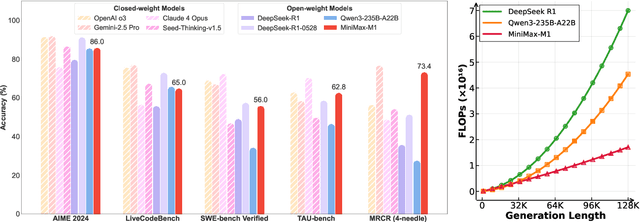
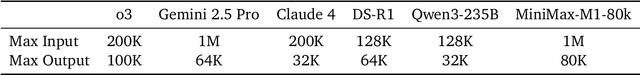
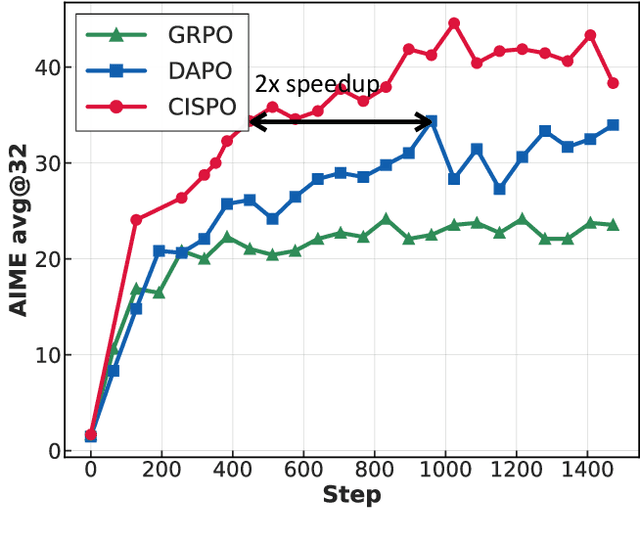
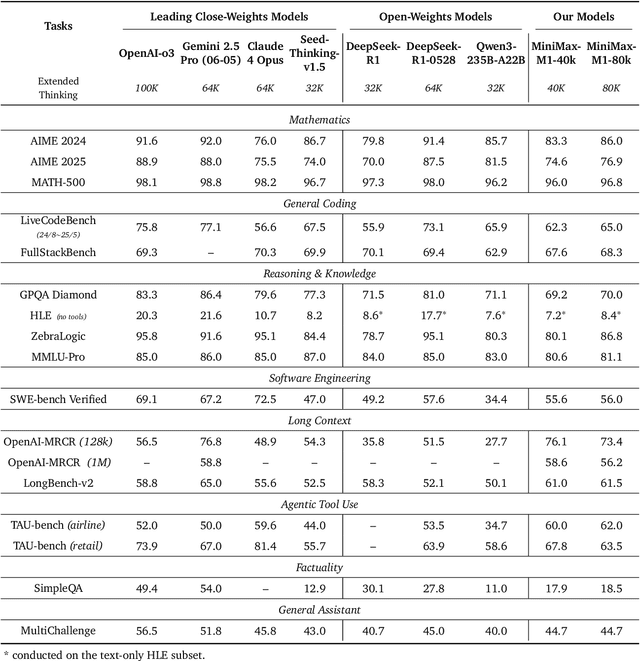
Abstract:We introduce MiniMax-M1, the world's first open-weight, large-scale hybrid-attention reasoning model. MiniMax-M1 is powered by a hybrid Mixture-of-Experts (MoE) architecture combined with a lightning attention mechanism. The model is developed based on our previous MiniMax-Text-01 model, which contains a total of 456 billion parameters with 45.9 billion parameters activated per token. The M1 model natively supports a context length of 1 million tokens, 8x the context size of DeepSeek R1. Furthermore, the lightning attention mechanism in MiniMax-M1 enables efficient scaling of test-time compute. These properties make M1 particularly suitable for complex tasks that require processing long inputs and thinking extensively. MiniMax-M1 is trained using large-scale reinforcement learning (RL) on diverse problems including sandbox-based, real-world software engineering environments. In addition to M1's inherent efficiency advantage for RL training, we propose CISPO, a novel RL algorithm to further enhance RL efficiency. CISPO clips importance sampling weights rather than token updates, outperforming other competitive RL variants. Combining hybrid-attention and CISPO enables MiniMax-M1's full RL training on 512 H800 GPUs to complete in only three weeks, with a rental cost of just $534,700. We release two versions of MiniMax-M1 models with 40K and 80K thinking budgets respectively, where the 40K model represents an intermediate phase of the 80K training. Experiments on standard benchmarks show that our models are comparable or superior to strong open-weight models such as the original DeepSeek-R1 and Qwen3-235B, with particular strengths in complex software engineering, tool utilization, and long-context tasks. We publicly release MiniMax-M1 at https://github.com/MiniMax-AI/MiniMax-M1.
Uni-SMART: Universal Science Multimodal Analysis and Research Transformer
Mar 15, 2024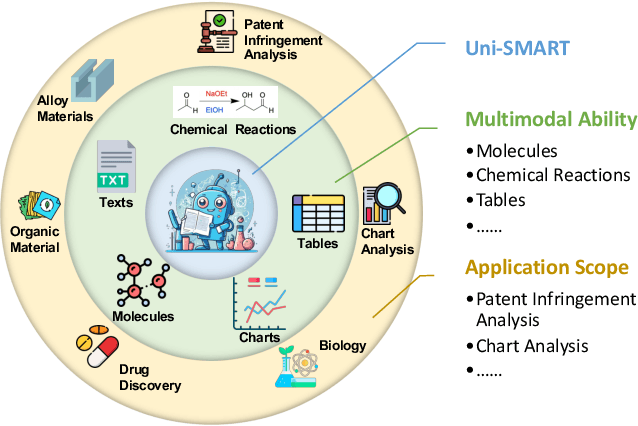
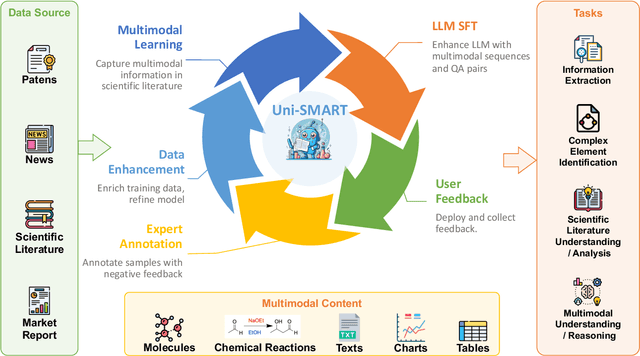
Abstract:In scientific research and its application, scientific literature analysis is crucial as it allows researchers to build on the work of others. However, the fast growth of scientific knowledge has led to a massive increase in scholarly articles, making in-depth literature analysis increasingly challenging and time-consuming. The emergence of Large Language Models (LLMs) has offered a new way to address this challenge. Known for their strong abilities in summarizing texts, LLMs are seen as a potential tool to improve the analysis of scientific literature. However, existing LLMs have their own limits. Scientific literature often includes a wide range of multimodal elements, such as molecular structure, tables, and charts, which are hard for text-focused LLMs to understand and analyze. This issue points to the urgent need for new solutions that can fully understand and analyze multimodal content in scientific literature. To answer this demand, we present Uni-SMART (Universal Science Multimodal Analysis and Research Transformer), an innovative model designed for in-depth understanding of multimodal scientific literature. Through rigorous quantitative evaluation across several domains, Uni-SMART demonstrates superior performance over leading text-focused LLMs. Furthermore, our exploration extends to practical applications, including patent infringement detection and nuanced analysis of charts. These applications not only highlight Uni-SMART's adaptability but also its potential to revolutionize how we interact with scientific literature.
SciAssess: Benchmarking LLM Proficiency in Scientific Literature Analysis
Mar 15, 2024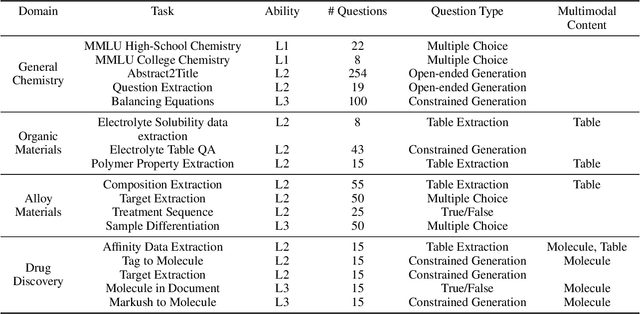
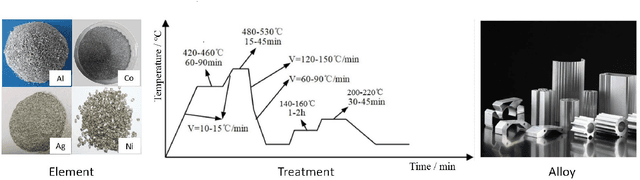
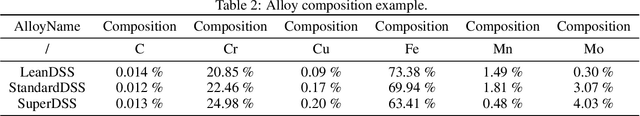
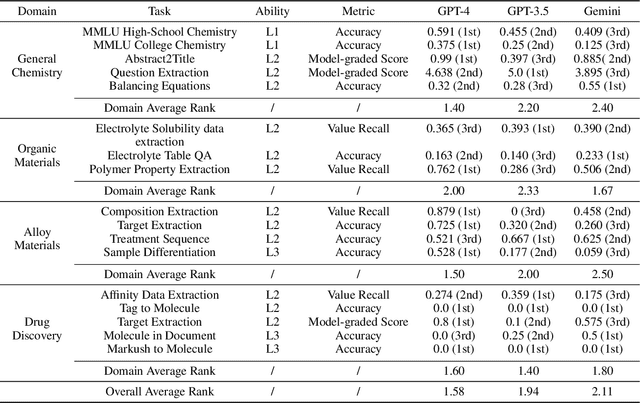
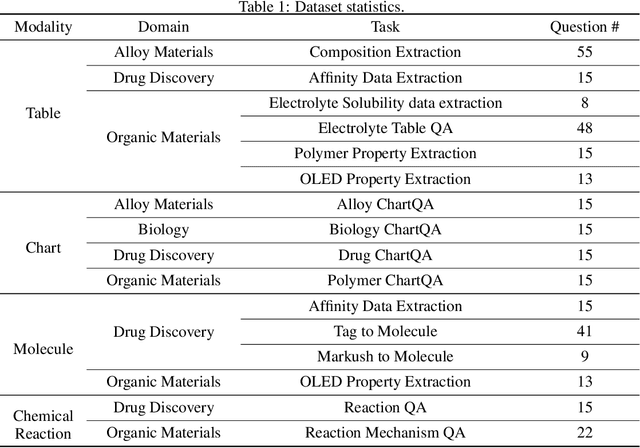
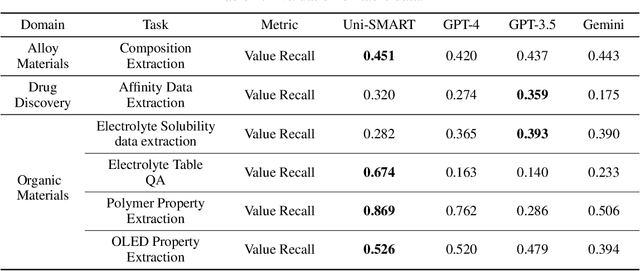
Abstract:Recent breakthroughs in Large Language Models (LLMs) have revolutionized natural language understanding and generation, igniting a surge of interest in leveraging these technologies in the field of scientific literature analysis. Existing benchmarks, however, inadequately evaluate the proficiency of LLMs in scientific literature analysis, especially in scenarios involving complex comprehension and multimodal data. In response, we introduced SciAssess, a benchmark tailored for the in-depth analysis of scientific literature, crafted to provide a thorough assessment of LLMs' efficacy. SciAssess focuses on evaluating LLMs' abilities in memorization, comprehension, and analysis within the context of scientific literature analysis. It includes representative tasks from diverse scientific fields, such as general chemistry, organic materials, and alloy materials. And rigorous quality control measures ensure its reliability in terms of correctness, anonymization, and copyright compliance. SciAssess evaluates leading LLMs, including GPT-4, GPT-3.5, and Gemini, identifying their strengths and aspects for improvement and supporting the ongoing development of LLM applications in scientific literature analysis. SciAssess and its resources are made available at https://sci-assess.github.io, offering a valuable tool for advancing LLM capabilities in scientific literature analysis.
ADCNet: a unified framework for predicting the activity of antibody-drug conjugates
Jan 17, 2024



Abstract:Antibody-drug conjugate (ADC) has revolutionized the field of cancer treatment in the era of precision medicine due to their ability to precisely target cancer cells and release highly effective drug. Nevertheless, the realization of rational design of ADC is very difficult because the relationship between their structures and activities is difficult to understand. In the present study, we introduce a unified deep learning framework called ADCNet to help design potential ADCs. The ADCNet highly integrates the protein representation learning language model ESM-2 and small-molecule representation learning language model FG-BERT models to achieve activity prediction through learning meaningful features from antigen and antibody protein sequences of ADC, SMILES strings of linker and payload, and drug-antibody ratio (DAR) value. Based on a carefully designed and manually tailored ADC data set, extensive evaluation results reveal that ADCNet performs best on the test set compared to baseline machine learning models across all evaluation metrics. For example, it achieves an average prediction accuracy of 87.12%, a balanced accuracy of 0.8689, and an area under receiver operating characteristic curve of 0.9293 on the test set. In addition, cross-validation, ablation experiments, and external independent testing results further prove the stability, advancement, and robustness of the ADCNet architecture. For the convenience of the community, we develop the first online platform (https://ADCNet.idruglab.cn) for the prediction of ADCs activity based on the optimal ADCNet model, and the source code is publicly available at https://github.com/idrugLab/ADCNet.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge