Mourad Gridach
Agentic AI for Scientific Discovery: A Survey of Progress, Challenges, and Future Directions
Mar 12, 2025Abstract:The integration of Agentic AI into scientific discovery marks a new frontier in research automation. These AI systems, capable of reasoning, planning, and autonomous decision-making, are transforming how scientists perform literature review, generate hypotheses, conduct experiments, and analyze results. This survey provides a comprehensive overview of Agentic AI for scientific discovery, categorizing existing systems and tools, and highlighting recent progress across fields such as chemistry, biology, and materials science. We discuss key evaluation metrics, implementation frameworks, and commonly used datasets to offer a detailed understanding of the current state of the field. Finally, we address critical challenges, such as literature review automation, system reliability, and ethical concerns, while outlining future research directions that emphasize human-AI collaboration and enhanced system calibration.
A translational pathway of deep learning methods in GastroIntestinal Endoscopy
Oct 12, 2020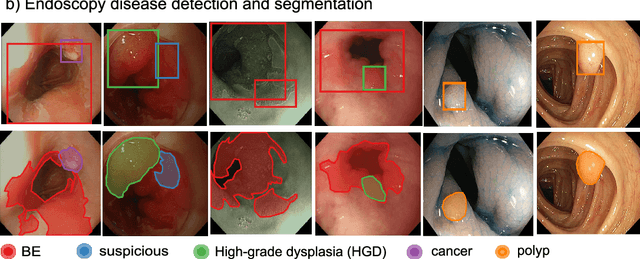
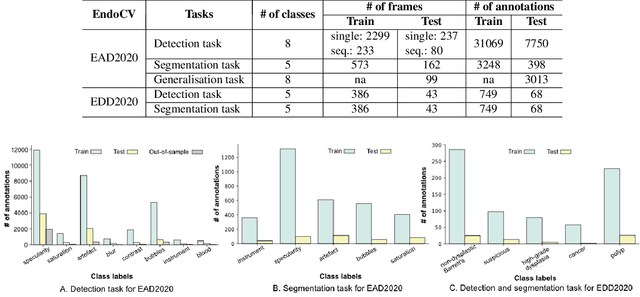
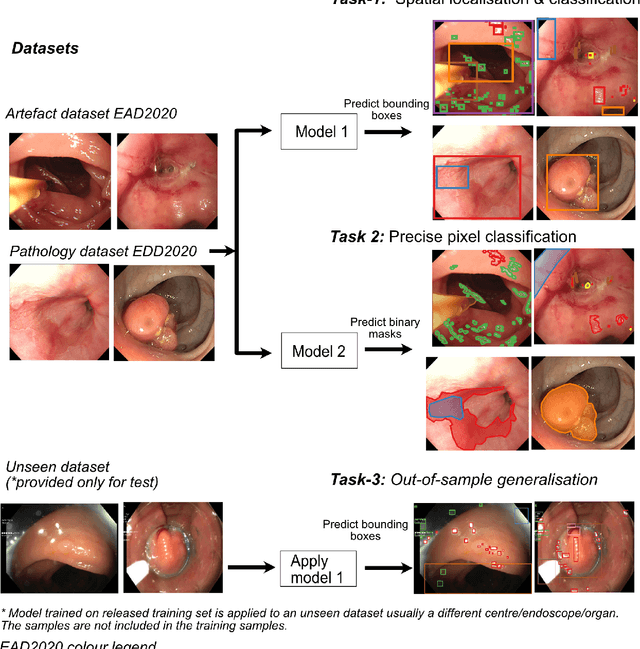
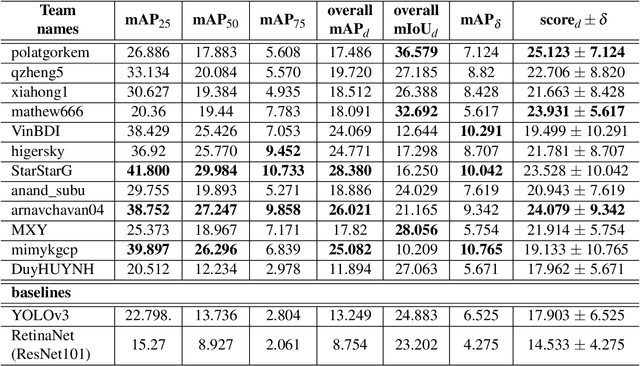
Abstract:The Endoscopy Computer Vision Challenge (EndoCV) is a crowd-sourcing initiative to address eminent problems in developing reliable computer aided detection and diagnosis endoscopy systems and suggest a pathway for clinical translation of technologies. Whilst endoscopy is a widely used diagnostic and treatment tool for hollow-organs, there are several core challenges often faced by endoscopists, mainly: 1) presence of multi-class artefacts that hinder their visual interpretation, and 2) difficulty in identifying subtle precancerous precursors and cancer abnormalities. Artefacts often affect the robustness of deep learning methods applied to the gastrointestinal tract organs as they can be confused with tissue of interest. EndoCV2020 challenges are designed to address research questions in these remits. In this paper, we present a summary of methods developed by the top 17 teams and provide an objective comparison of state-of-the-art methods and methods designed by the participants for two sub-challenges: i) artefact detection and segmentation (EAD2020), and ii) disease detection and segmentation (EDD2020). Multi-center, multi-organ, multi-class, and multi-modal clinical endoscopy datasets were compiled for both EAD2020 and EDD2020 sub-challenges. An out-of-sample generalisation ability of detection algorithms was also evaluated. Whilst most teams focused on accuracy improvements, only a few methods hold credibility for clinical usability. The best performing teams provided solutions to tackle class imbalance, and variabilities in size, origin, modality and occurrences by exploring data augmentation, data fusion, and optimal class thresholding techniques.
Empirical Evaluation of Leveraging Named Entities for Arabic Sentiment Analysis
Apr 23, 2019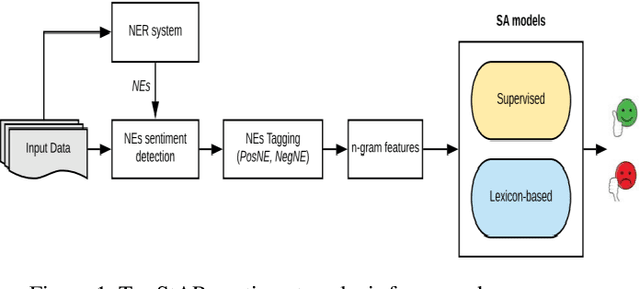
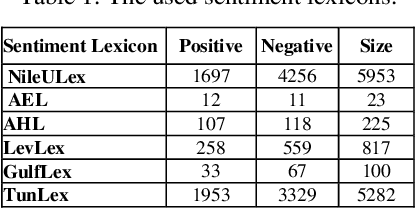
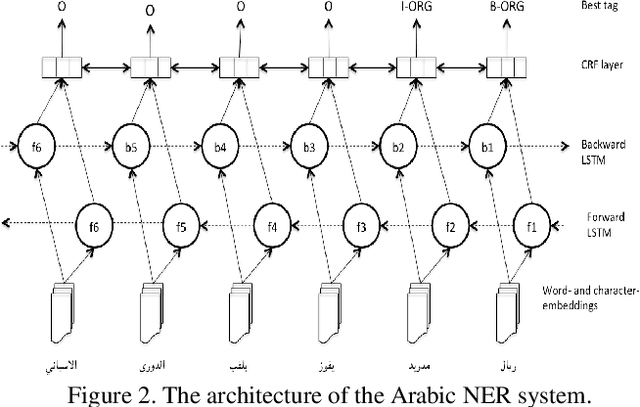
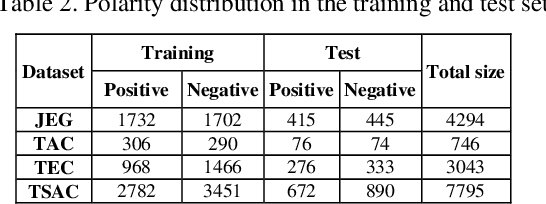
Abstract:Social media reflects the public attitudes towards specific events. Events are often related to persons, locations or organizations, the so-called Named Entities. This can define Named Entities as sentiment-bearing components. In this paper, we dive beyond Named Entities recognition to the exploitation of sentiment-annotated Named Entities in Arabic sentiment analysis. Therefore, we develop an algorithm to detect the sentiment of Named Entities based on the majority of attitudes towards them. This enabled tagging Named Entities with proper tags and, thus, including them in a sentiment analysis framework of two models: supervised and lexicon-based. Both models were applied on datasets of multi-dialectal content. The results revealed that Named Entities have no considerable impact on the supervised model, while employing them in the lexicon-based model improved the classification performance and outperformed most of the baseline systems.
Developing a New Approach for Arabic Morphological Analysis and Generation
Jan 28, 2011



Abstract:Arabic morphological analysis is one of the essential stages in Arabic Natural Language Processing. In this paper we present an approach for Arabic morphological analysis. This approach is based on Arabic morphological automaton (AMAUT). The proposed technique uses a morphological database realized using XMODEL language. Arabic morphology represents a special type of morphological systems because it is based on the concept of scheme to represent Arabic words. We use this concept to develop the Arabic morphological automata. The proposed approach has development standardization aspect. It can be exploited by NLP applications such as syntactic and semantic analysis, information retrieval, machine translation and orthographical correction. The proposed approach is compared with Xerox Arabic Analyzer and Smrz Arabic Analyzer.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge