Alptekin Temizel
TopoBDA: Towards Bezier Deformable Attention for Road Topology Understanding
Dec 25, 2024



Abstract:Understanding road topology is crucial for autonomous driving. This paper introduces TopoBDA (Topology with Bezier Deformable Attention), a novel approach that enhances road topology understanding by leveraging Bezier Deformable Attention (BDA). BDA utilizes Bezier control points to drive the deformable attention mechanism, significantly improving the detection and representation of elongated and thin polyline structures, such as lane centerlines. TopoBDA processes multi-camera 360-degree imagery to generate Bird's Eye View (BEV) features, which are refined through a transformer decoder employing BDA. This method enhances computational efficiency while maintaining high accuracy in centerline prediction. Additionally, TopoBDA incorporates an instance mask formulation and an auxiliary one-to-many set prediction loss strategy to further refine centerline detection and improve road topology understanding. Experimental evaluations on the OpenLane-V2 dataset demonstrate that TopoBDA outperforms existing methods, achieving state-of-the-art results in centerline detection and topology reasoning. The integration of multi-modal data, including lidar and radar, specifically for road topology understanding, further enhances the model's performance, underscoring its importance in autonomous driving applications.
Augmentation Policy Generation for Image Classification Using Large Language Models
Oct 17, 2024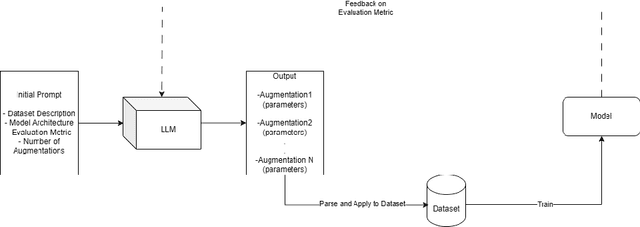
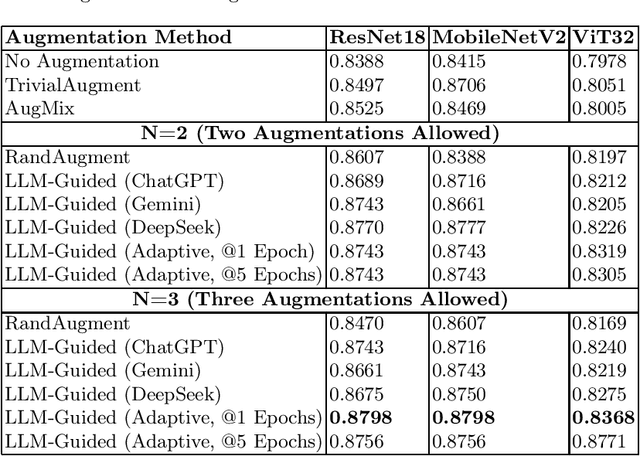
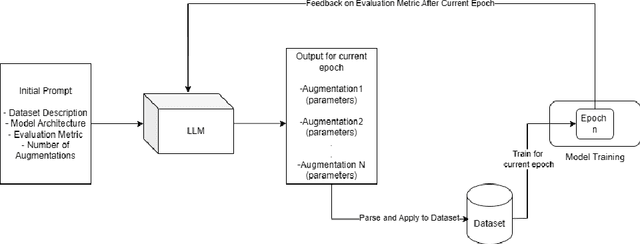
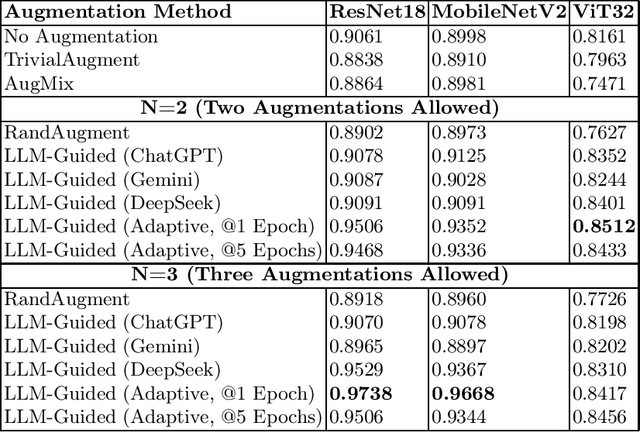
Abstract:Automated data augmentation methods have significantly improved the performance and generalization capability of deep learning models in image classification. Yet, most state-of-the-art methods are optimized on common benchmark datasets, limiting their applicability to more diverse or domain-specific data, such as medical datasets. In this paper, we propose a strategy that uses large language models to automatically generate efficient augmentation policies, customized to fit the specific characteristics of any dataset and model architecture. The proposed method iteratively interacts with an LLM to obtain and refine the augmentation policies on model performance feedback, creating a dataset-agnostic data augmentation pipeline. The proposed method was evaluated on medical imaging datasets, showing a clear improvement over state-of-the-art methods. The proposed approach offers an adaptive and scalable solution. Although it increases computational cost, it significantly boosts model robustness, automates the process, and minimizes the need for human involvement during model development.
TopoMaskV2: Enhanced Instance-Mask-Based Formulation for the Road Topology Problem
Sep 17, 2024



Abstract:Recently, the centerline has become a popular representation of lanes due to its advantages in solving the road topology problem. To enhance centerline prediction, we have developed a new approach called TopoMask. Unlike previous methods that rely on keypoints or parametric methods, TopoMask utilizes an instance-mask-based formulation coupled with a masked-attention-based transformer architecture. We introduce a quad-direction label representation to enrich the mask instances with flow information and design a corresponding post-processing technique for mask-to-centerline conversion. Additionally, we demonstrate that the instance-mask formulation provides complementary information to parametric Bezier regressions, and fusing both outputs leads to improved detection and topology performance. Moreover, we analyze the shortcomings of the pillar assumption in the Lift Splat technique and adapt a multi-height bin configuration. Experimental results show that TopoMask achieves state-of-the-art performance in the OpenLane-V2 dataset, increasing from 44.1 to 49.4 for Subset-A and 44.7 to 51.8 for Subset-B in the V1.1 OLS baseline.
State-of-the-Art in Nudity Classification: A Comparative Analysis
Dec 26, 2023


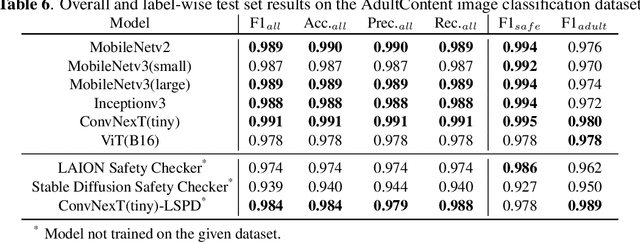
Abstract:This paper presents a comparative analysis of existing nudity classification techniques for classifying images based on the presence of nudity, with a focus on their application in content moderation. The evaluation focuses on CNN-based models, vision transformer, and popular open-source safety checkers from Stable Diffusion and Large-scale Artificial Intelligence Open Network (LAION). The study identifies the limitations of current evaluation datasets and highlights the need for more diverse and challenging datasets. The paper discusses the potential implications of these findings for developing more accurate and effective image classification systems on online platforms. Overall, the study emphasizes the importance of continually improving image classification models to ensure the safety and well-being of platform users. The project page, including the demonstrations and results is publicly available at https://github.com/fcakyon/content-moderation-deep-learning.
Ulcerative Colitis Mayo Endoscopic Scoring Classification with Active Learning and Generative Data Augmentation
Nov 10, 2023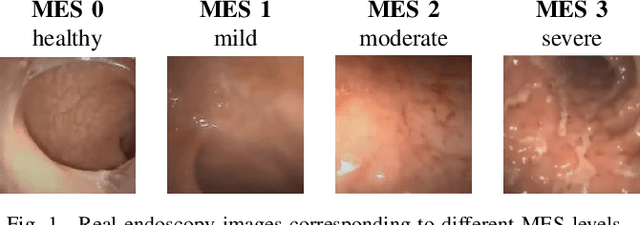
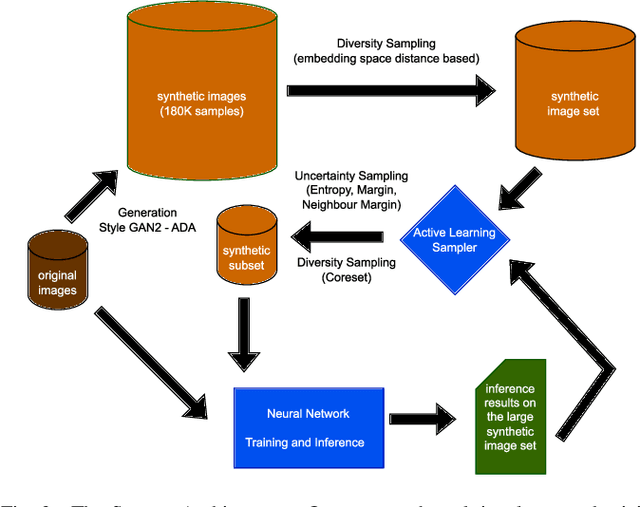
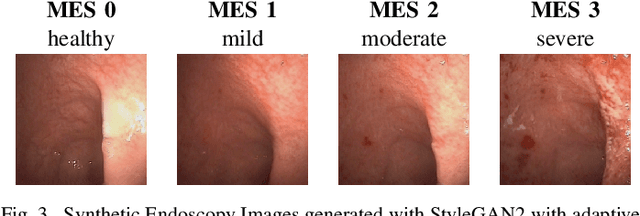
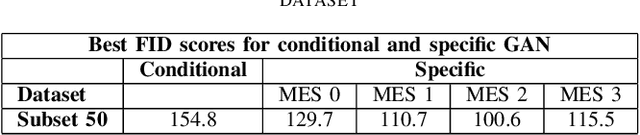
Abstract:Endoscopic imaging is commonly used to diagnose Ulcerative Colitis (UC) and classify its severity. It has been shown that deep learning based methods are effective in automated analysis of these images and can potentially be used to aid medical doctors. Unleashing the full potential of these methods depends on the availability of large amount of labeled images; however, obtaining and labeling these images are quite challenging. In this paper, we propose a active learning based generative augmentation method. The method involves generating a large number of synthetic samples by training using a small dataset consisting of real endoscopic images. The resulting data pool is narrowed down by using active learning methods to select the most informative samples, which are then used to train a classifier. We demonstrate the effectiveness of our method through experiments on a publicly available endoscopic image dataset. The results show that using synthesized samples in conjunction with active learning leads to improved classification performance compared to using only the original labeled examples and the baseline classification performance of 68.1% increases to 74.5% in terms of Quadratic Weighted Kappa (QWK) Score. Another observation is that, attaining equivalent performance using only real data necessitated three times higher number of images.
Adversarial Image Generation by Spatial Transformation in Perceptual Colorspaces
Oct 21, 2023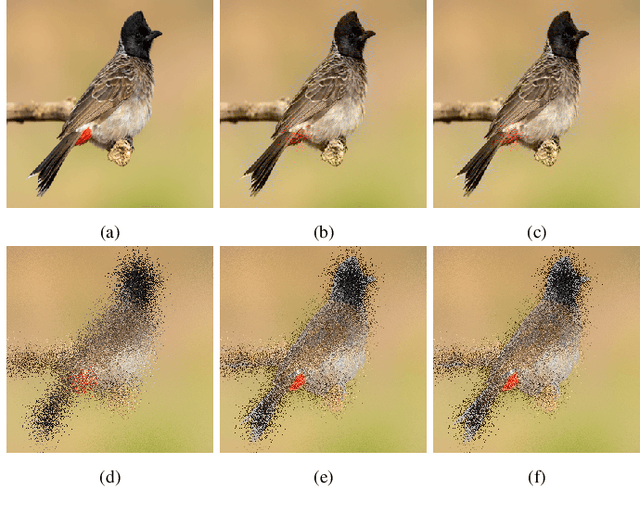
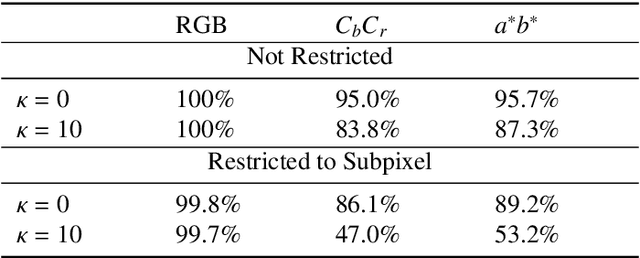
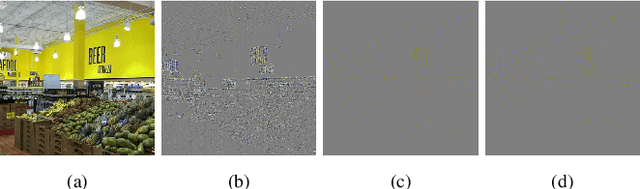
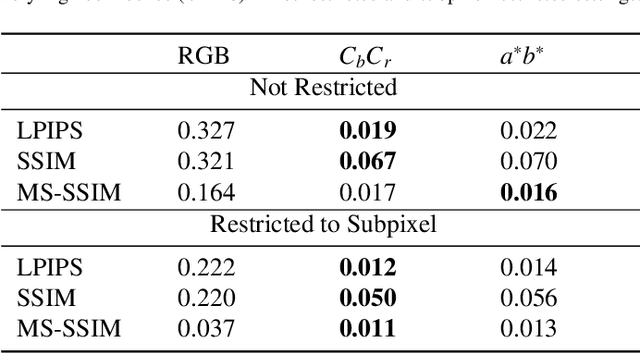
Abstract:Deep neural networks are known to be vulnerable to adversarial perturbations. The amount of these perturbations are generally quantified using $L_p$ metrics, such as $L_0$, $L_2$ and $L_\infty$. However, even when the measured perturbations are small, they tend to be noticeable by human observers since $L_p$ distance metrics are not representative of human perception. On the other hand, humans are less sensitive to changes in colorspace. In addition, pixel shifts in a constrained neighborhood are hard to notice. Motivated by these observations, we propose a method that creates adversarial examples by applying spatial transformations, which creates adversarial examples by changing the pixel locations independently to chrominance channels of perceptual colorspaces such as $YC_{b}C_{r}$ and $CIELAB$, instead of making an additive perturbation or manipulating pixel values directly. In a targeted white-box attack setting, the proposed method is able to obtain competitive fooling rates with very high confidence. The experimental evaluations show that the proposed method has favorable results in terms of approximate perceptual distance between benign and adversarially generated images. The source code is publicly available at https://github.com/ayberkydn/stadv-torch
TopoMask: Instance-Mask-Based Formulation for the Road Topology Problem via Transformer-Based Architecture
Jun 08, 2023



Abstract:Driving scene understanding task involves detecting static elements such as lanes, traffic signs, and traffic lights, and their relationships with each other. To facilitate the development of comprehensive scene understanding solutions using multiple camera views, a new dataset called Road Genome (OpenLane-V2) has been released. This dataset allows for the exploration of complex road connections and situations where lane markings may be absent. Instead of using traditional lane markings, the lanes in this dataset are represented by centerlines, which offer a more suitable representation of lanes and their connections. In this study, we have introduced a new approach called TopoMask for predicting centerlines in road topology. Unlike existing approaches in the literature that rely on keypoints or parametric methods, TopoMask utilizes an instance-mask based formulation with a transformer-based architecture and, in order to enrich the mask instances with flow information, a direction label representation is proposed. TopoMask have ranked 4th in the OpenLane-V2 Score (OLS) and ranked 2nd in the F1 score of centerline prediction in OpenLane Topology Challenge 2023. In comparison to the current state-of-the-art method, TopoNet, the proposed method has achieved similar performance in Frechet-based lane detection and outperformed TopoNet in Chamfer-based lane detection without utilizing its scene graph neural network.
Deep Architectures for Content Moderation and Movie Content Rating
Dec 12, 2022Abstract:Rating a video based on its content is an important step for classifying video age categories. Movie content rating and TV show rating are the two most common rating systems established by professional committees. However, manually reviewing and evaluating scene/film content by a committee is a tedious work and it becomes increasingly difficult with the ever-growing amount of online video content. As such, a desirable solution is to use computer vision based video content analysis techniques to automate the evaluation process. In this paper, related works are summarized for action recognition, multi-modal learning, movie genre classification, and sensitive content detection in the context of content moderation and movie content rating. The project page is available at https://github.com/fcakyon/content-moderation-deep-learning.
Sequence Models for Drone vs Bird Classification
Jul 21, 2022
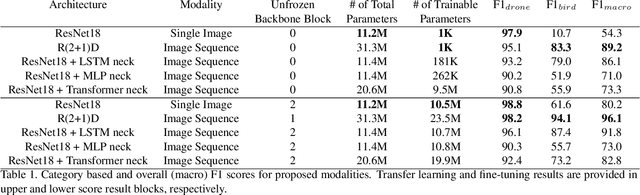
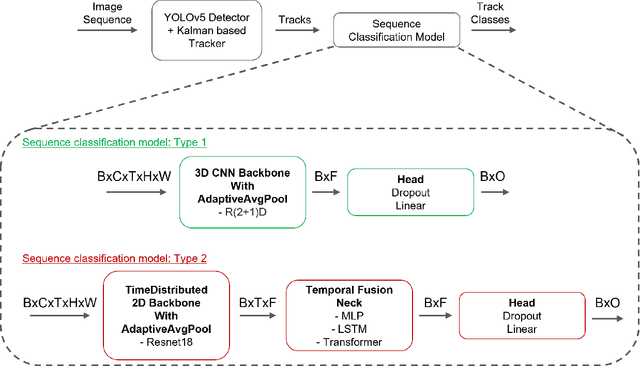
Abstract:Drone detection has become an essential task in object detection as drone costs have decreased and drone technology has improved. It is, however, difficult to detect distant drones when there is weak contrast, long range, and low visibility. In this work, we propose several sequence classification architectures to reduce the detected false-positive ratio of drone tracks. Moreover, we propose a new drone vs. bird sequence classification dataset to train and evaluate the proposed architectures. 3D CNN, LSTM, and Transformer based sequence classification architectures have been trained on the proposed dataset to show the effectiveness of the proposed idea. As experiments show, using sequence information, bird classification and overall F1 scores can be increased by up to 73% and 35%, respectively. Among all sequence classification models, R(2+1)D-based fully convolutional model yields the best transfer learning and fine-tuning results.
Evaluation and Analysis of Different Aggregation and Hyperparameter Selection Methods for Federated Brain Tumor Segmentation
Feb 16, 2022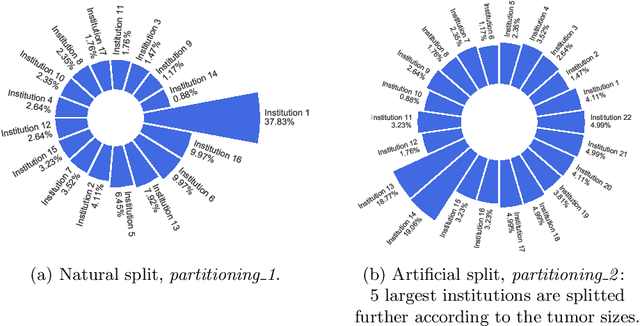
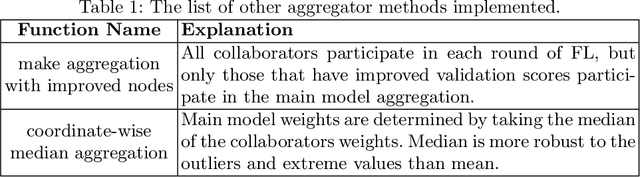

Abstract:Availability of large, diverse, and multi-national datasets is crucial for the development of effective and clinically applicable AI systems in the medical imaging domain. However, forming a global model by bringing these datasets together at a central location, comes along with various data privacy and ownership problems. To alleviate these problems, several recent studies focus on the federated learning paradigm, a distributed learning approach for decentralized data. Federated learning leverages all the available data without any need for sharing collaborators' data with each other or collecting them on a central server. Studies show that federated learning can provide competitive performance with conventional central training, while having a good generalization capability. In this work, we have investigated several federated learning approaches on the brain tumor segmentation problem. We explore different strategies for faster convergence and better performance which can also work on strong Non-IID cases.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge