Mohammed Javed
ETLNet: An Efficient TCN-BiLSTM Network for Road Anomaly Detection Using Smartphone Sensors
Dec 06, 2024Abstract:Road anomalies can be defined as irregularities on the road surface or in the surface itself. Some may be intentional (such as speedbumps), accidental (such as materials falling off a truck), or the result of roads' excessive use or low or no maintenance, such as potholes. Despite their varying origins, these irregularities often harm vehicles substantially. Speed bumps are intentionally placed for safety but are dangerous due to their non-standard shape, size, and lack of proper markings. Potholes are unintentional and can also cause severe damage. To address the detection of these anomalies, we need an automated road monitoring system. Today, various systems exist that use visual information to track these anomalies. Still, due to poor lighting conditions and improper or missing markings, they may go undetected and have severe consequences for public transport, automated vehicles, etc. In this paper, the Enhanced Temporal-BiLSTM Network (ETLNet) is introduced as a novel approach that integrates two Temporal Convolutional Network (TCN) layers with a Bidirectional Long Short-Term Memory (BiLSTM) layer. This combination is tailored to detect anomalies effectively irrespective of lighting conditions, as it depends not on visuals but smartphone inertial sensor data. Our methodology employs accelerometer and gyroscope sensors, typically in smartphones, to gather data on road conditions. Empirical evaluations demonstrate that the ETLNet model maintains an F1-score for detecting speed bumps of 99.3%. The ETLNet model's robustness and efficiency significantly advance automated road surface monitoring technologies.
Point-GR: Graph Residual Point Cloud Network for 3D Object Classification and Segmentation
Dec 04, 2024Abstract:In recent years, the challenge of 3D shape analysis within point cloud data has gathered significant attention in computer vision. Addressing the complexities of effective 3D information representation and meaningful feature extraction for classification tasks remains crucial. This paper presents Point-GR, a novel deep learning architecture designed explicitly to transform unordered raw point clouds into higher dimensions while preserving local geometric features. It introduces residual-based learning within the network to mitigate the point permutation issues in point cloud data. The proposed Point-GR network significantly reduced the number of network parameters in Classification and Part-Segmentation compared to baseline graph-based networks. Notably, the Point-GR model achieves a state-of-the-art scene segmentation mean IoU of 73.47% on the S3DIS benchmark dataset, showcasing its effectiveness. Furthermore, the model shows competitive results in Classification and Part-Segmentation tasks.
Alt4Blind: A User Interface to Simplify Charts Alt-Text Creation
May 29, 2024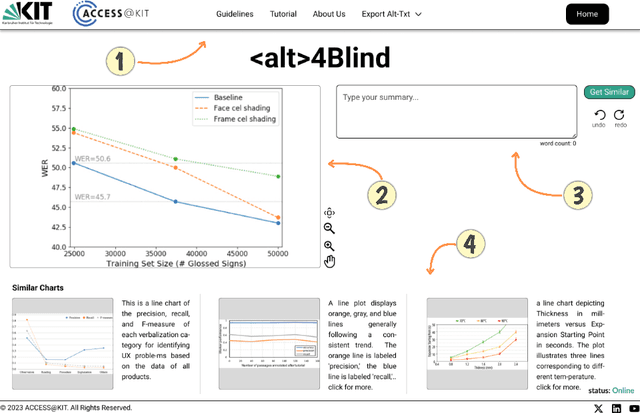
Abstract:Alternative Texts (Alt-Text) for chart images are essential for making graphics accessible to people with blindness and visual impairments. Traditionally, Alt-Text is manually written by authors but often encounters issues such as oversimplification or complication. Recent trends have seen the use of AI for Alt-Text generation. However, existing models are susceptible to producing inaccurate or misleading information. We address this challenge by retrieving high-quality alt-texts from similar chart images, serving as a reference for the user when creating alt-texts. Our three contributions are as follows: (1) we introduce a new benchmark comprising 5,000 real images with semantically labeled high-quality Alt-Texts, collected from Human Computer Interaction venues. (2) We developed a deep learning-based model to rank and retrieve similar chart images that share the same visual and textual semantics. (3) We designed a user interface (UI) to facilitate the alt-text creation process. Our preliminary interviews and investigations highlight the usability of our UI. For the dataset and further details, please refer to our project page: https://moured.github.io/alt4blind/.
CompTLL-UNet: Compressed Domain Text-Line Localization in Challenging Handwritten Documents using Deep Feature Learning from JPEG Coefficients
Aug 11, 2023


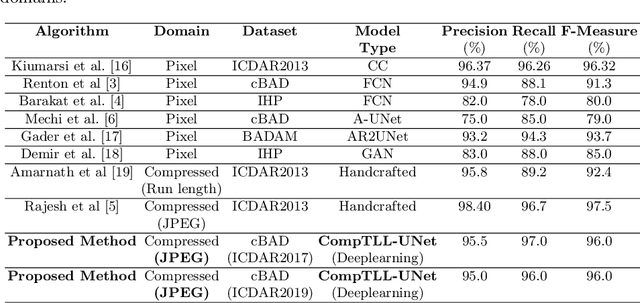
Abstract:Automatic localization of text-lines in handwritten documents is still an open and challenging research problem. Various writing issues such as uneven spacing between the lines, oscillating and touching text, and the presence of skew become much more challenging when the case of complex handwritten document images are considered for segmentation directly in their respective compressed representation. This is because, the conventional way of processing compressed documents is through decompression, but here in this paper, we propose an idea that employs deep feature learning directly from the JPEG compressed coefficients without full decompression to accomplish text-line localization in the JPEG compressed domain. A modified U-Net architecture known as Compressed Text-Line Localization Network (CompTLL-UNet) is designed to accomplish it. The model is trained and tested with JPEG compressed version of benchmark datasets including ICDAR2017 (cBAD) and ICDAR2019 (cBAD), reporting the state-of-the-art performance with reduced storage and computational costs in the JPEG compressed domain.
A Survey on Change Detection Techniques in Document Images
Jul 15, 2023

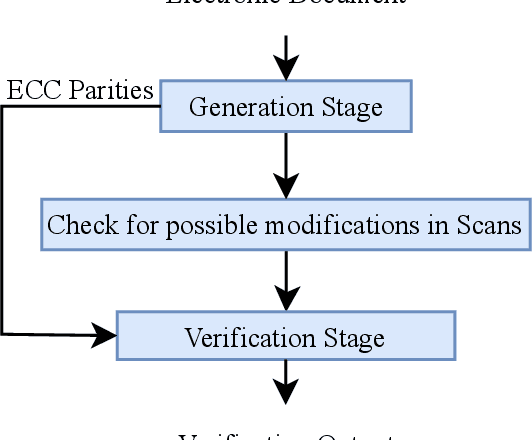
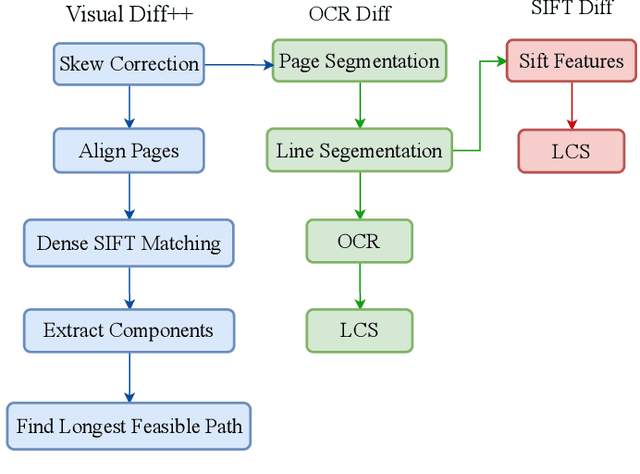
Abstract:The problem of change detection in images finds application in different domains like diagnosis of diseases in the medical field, detecting growth patterns of cities through remote sensing, and finding changes in legal documents and contracts. However, this paper presents a survey on core techniques and rules to detect changes in different versions of a document image. Our discussions on change detection focus on two categories -- content-based and layout-based. The content-based techniques intelligently extract and analyze the image contents (text or non-text) to show the possible differences, whereas the layout-based techniques use structural information to predict document changes. We also summarize the existing datasets and evaluation metrics used in change detection experiments. The shortcomings and challenges the existing methods face are reported, along with some pointers for future research work.
A Survey on Figure Classification Techniques in Scientific Documents
Jul 09, 2023Abstract:Figures visually represent an essential piece of information and provide an effective means to communicate scientific facts. Recently there have been many efforts toward extracting data directly from figures, specifically from tables, diagrams, and plots, using different Artificial Intelligence and Machine Learning techniques. This is because removing information from figures could lead to deeper insights into the concepts highlighted in the scientific documents. In this survey paper, we systematically categorize figures into five classes - tables, photos, diagrams, maps, and plots, and subsequently present a critical review of the existing methodologies and data sets that address the problem of figure classification. Finally, we identify the current research gaps and provide possible directions for further research on figure classification.
A Survey and Approach to Chart Classification
Jul 09, 2023Abstract:Charts represent an essential source of visual information in documents and facilitate a deep understanding and interpretation of information typically conveyed numerically. In the scientific literature, there are many charts, each with its stylistic differences. Recently the document understanding community has begun to address the problem of automatic chart understanding, which begins with chart classification. In this paper, we present a survey of the current state-of-the-art techniques for chart classification and discuss the available datasets and their supported chart types. We broadly classify these contributions as traditional approaches based on ML, CNN, and Transformers. Furthermore, we carry out an extensive comparative performance analysis of CNN-based and transformer-based approaches on the recently published CHARTINFO UB-UNITECH PMC dataset for the CHART-Infographics competition at ICPR 2022. The data set includes 15 different chart categories, including 22,923 training images and 13,260 test images. We have implemented a vision-based transformer model that produces state-of-the-art results in chart classification.
DWT-CompCNN: Deep Image Classification Network for High Throughput JPEG 2000 Compressed Documents
Jun 02, 2023Abstract:For any digital application with document images such as retrieval, the classification of document images becomes an essential stage. Conventionally for the purpose, the full versions of the documents, that is the uncompressed document images make the input dataset, which poses a threat due to the big volume required to accommodate the full versions of the documents. Therefore, it would be novel, if the same classification task could be accomplished directly (with some partial decompression) with the compressed representation of documents in order to make the whole process computationally more efficient. In this research work, a novel deep learning model, DWT CompCNN is proposed for classification of documents that are compressed using High Throughput JPEG 2000 (HTJ2K) algorithm. The proposed DWT-CompCNN comprises of five convolutional layers with filter sizes of 16, 32, 64, 128, and 256 consecutively for each increasing layer to improve learning from the wavelet coefficients extracted from the compressed images. Experiments are performed on two benchmark datasets- Tobacco-3482 and RVL-CDIP, which demonstrate that the proposed model is time and space efficient, and also achieves a better classification accuracy in compressed domain.
T2CI-GAN: Text to Compressed Image generation using Generative Adversarial Network
Oct 01, 2022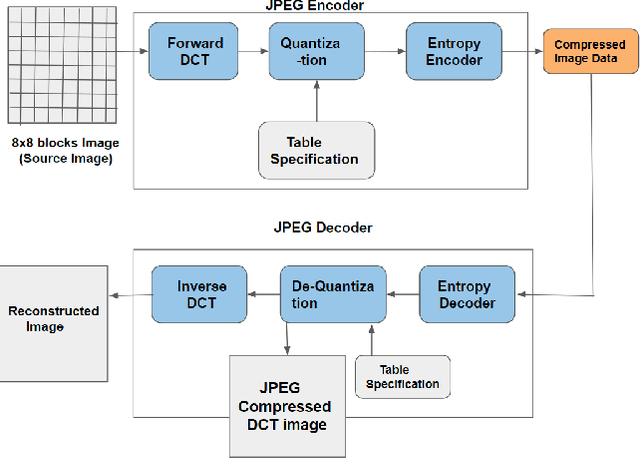

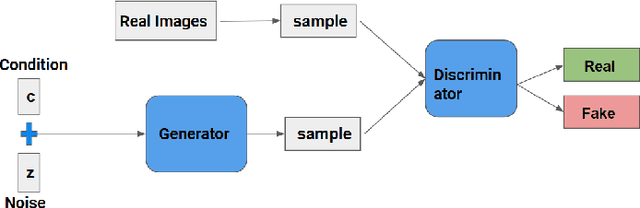

Abstract:The problem of generating textual descriptions for the visual data has gained research attention in the recent years. In contrast to that the problem of generating visual data from textual descriptions is still very challenging, because it requires the combination of both Natural Language Processing (NLP) and Computer Vision techniques. The existing methods utilize the Generative Adversarial Networks (GANs) and generate the uncompressed images from textual description. However, in practice, most of the visual data are processed and transmitted in the compressed representation. Hence, the proposed work attempts to generate the visual data directly in the compressed representation form using Deep Convolutional GANs (DCGANs) to achieve the storage and computational efficiency. We propose GAN models for compressed image generation from text. The first model is directly trained with JPEG compressed DCT images (compressed domain) to generate the compressed images from text descriptions. The second model is trained with RGB images (pixel domain) to generate JPEG compressed DCT representation from text descriptions. The proposed models are tested on an open source benchmark dataset Oxford-102 Flower images using both RGB and JPEG compressed versions, and accomplished the state-of-the-art performance in the JPEG compressed domain. The code will be publicly released at GitHub after acceptance of paper.
Document Image Binarization in JPEG Compressed Domain using Dual Discriminator Generative Adversarial Networks
Sep 13, 2022



Abstract:Image binarization techniques are being popularly used in enhancement of noisy and/or degraded images catering different Document Image Anlaysis (DIA) applications like word spotting, document retrieval, and OCR. Most of the existing techniques focus on feeding pixel images into the Convolution Neural Networks to accomplish document binarization, which may not produce effective results when working with compressed images that need to be processed without full decompression. Therefore in this research paper, the idea of document image binarization directly using JPEG compressed stream of document images is proposed by employing Dual Discriminator Generative Adversarial Networks (DD-GANs). Here the two discriminator networks - Global and Local work on different image ratios and use focal loss as generator loss. The proposed model has been thoroughly tested with different versions of DIBCO dataset having challenges like holes, erased or smudged ink, dust, and misplaced fibres. The model proved to be highly robust, efficient both in terms of time and space complexities, and also resulted in state-of-the-art performance in JPEG compressed domain.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge