Mohammad Taghi Saffar
StoryBench: A Multifaceted Benchmark for Continuous Story Visualization
Aug 22, 2023



Abstract:Generating video stories from text prompts is a complex task. In addition to having high visual quality, videos need to realistically adhere to a sequence of text prompts whilst being consistent throughout the frames. Creating a benchmark for video generation requires data annotated over time, which contrasts with the single caption used often in video datasets. To fill this gap, we collect comprehensive human annotations on three existing datasets, and introduce StoryBench: a new, challenging multi-task benchmark to reliably evaluate forthcoming text-to-video models. Our benchmark includes three video generation tasks of increasing difficulty: action execution, where the next action must be generated starting from a conditioning video; story continuation, where a sequence of actions must be executed starting from a conditioning video; and story generation, where a video must be generated from only text prompts. We evaluate small yet strong text-to-video baselines, and show the benefits of training on story-like data algorithmically generated from existing video captions. Finally, we establish guidelines for human evaluation of video stories, and reaffirm the need of better automatic metrics for video generation. StoryBench aims at encouraging future research efforts in this exciting new area.
Phenaki: Variable Length Video Generation From Open Domain Textual Description
Oct 05, 2022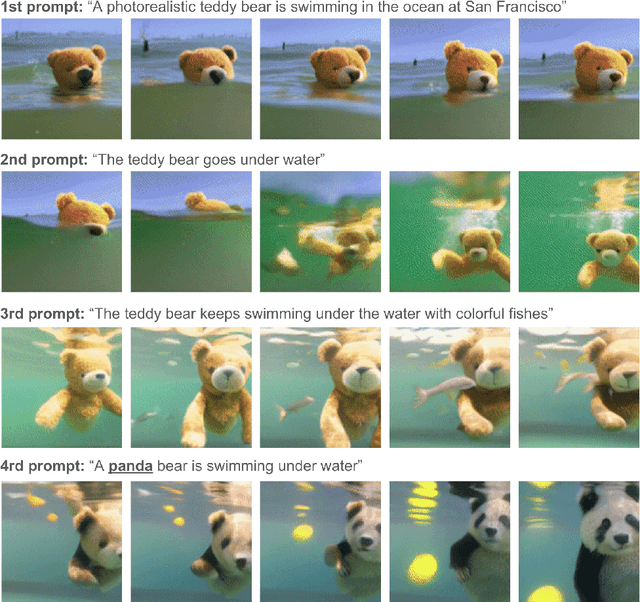
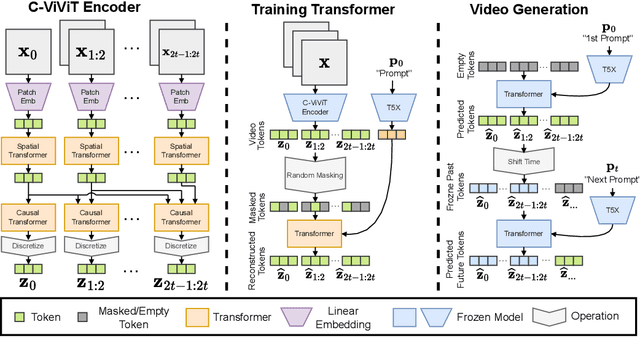


Abstract:We present Phenaki, a model capable of realistic video synthesis, given a sequence of textual prompts. Generating videos from text is particularly challenging due to the computational cost, limited quantities of high quality text-video data and variable length of videos. To address these issues, we introduce a new model for learning video representation which compresses the video to a small representation of discrete tokens. This tokenizer uses causal attention in time, which allows it to work with variable-length videos. To generate video tokens from text we are using a bidirectional masked transformer conditioned on pre-computed text tokens. The generated video tokens are subsequently de-tokenized to create the actual video. To address data issues, we demonstrate how joint training on a large corpus of image-text pairs as well as a smaller number of video-text examples can result in generalization beyond what is available in the video datasets. Compared to the previous video generation methods, Phenaki can generate arbitrary long videos conditioned on a sequence of prompts (i.e. time variable text or a story) in open domain. To the best of our knowledge, this is the first time a paper studies generating videos from time variable prompts. In addition, compared to the per-frame baselines, the proposed video encoder-decoder computes fewer tokens per video but results in better spatio-temporal consistency.
FitVid: Overfitting in Pixel-Level Video Prediction
Jun 24, 2021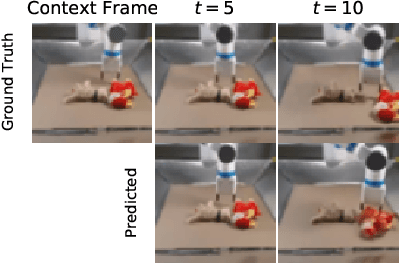

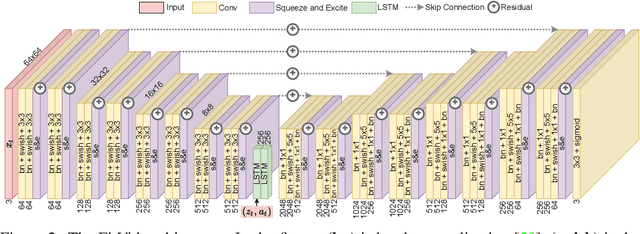
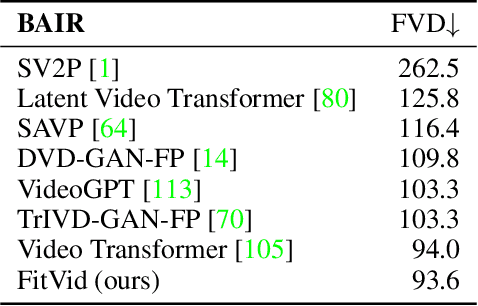
Abstract:An agent that is capable of predicting what happens next can perform a variety of tasks through planning with no additional training. Furthermore, such an agent can internally represent the complex dynamics of the real-world and therefore can acquire a representation useful for a variety of visual perception tasks. This makes predicting the future frames of a video, conditioned on the observed past and potentially future actions, an interesting task which remains exceptionally challenging despite many recent advances. Existing video prediction models have shown promising results on simple narrow benchmarks but they generate low quality predictions on real-life datasets with more complicated dynamics or broader domain. There is a growing body of evidence that underfitting on the training data is one of the primary causes for the low quality predictions. In this paper, we argue that the inefficient use of parameters in the current video models is the main reason for underfitting. Therefore, we introduce a new architecture, named FitVid, which is capable of severe overfitting on the common benchmarks while having similar parameter count as the current state-of-the-art models. We analyze the consequences of overfitting, illustrating how it can produce unexpected outcomes such as generating high quality output by repeating the training data, and how it can be mitigated using existing image augmentation techniques. As a result, FitVid outperforms the current state-of-the-art models across four different video prediction benchmarks on four different metrics.
Models, Pixels, and Rewards: Evaluating Design Trade-offs in Visual Model-Based Reinforcement Learning
Dec 08, 2020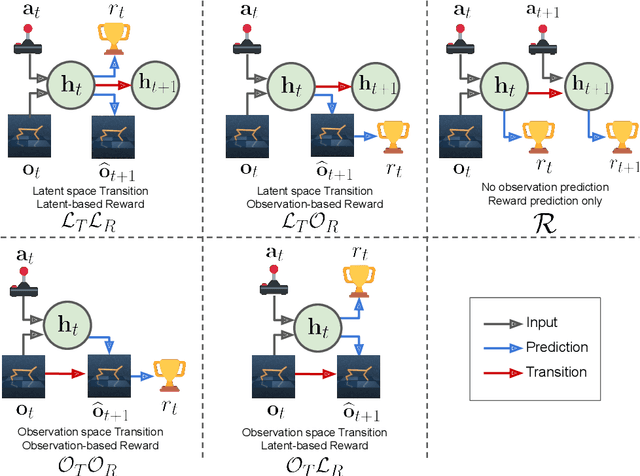

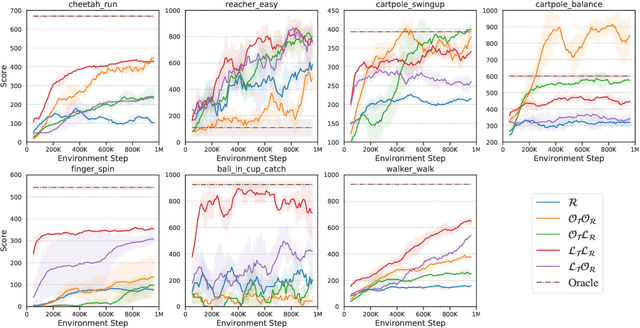
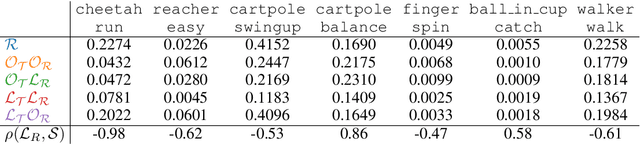
Abstract:Model-based reinforcement learning (MBRL) methods have shown strong sample efficiency and performance across a variety of tasks, including when faced with high-dimensional visual observations. These methods learn to predict the environment dynamics and expected reward from interaction and use this predictive model to plan and perform the task. However, MBRL methods vary in their fundamental design choices, and there is no strong consensus in the literature on how these design decisions affect performance. In this paper, we study a number of design decisions for the predictive model in visual MBRL algorithms, focusing specifically on methods that use a predictive model for planning. We find that a range of design decisions that are often considered crucial, such as the use of latent spaces, have little effect on task performance. A big exception to this finding is that predicting future observations (i.e., images) leads to significant task performance improvement compared to only predicting rewards. We also empirically find that image prediction accuracy, somewhat surprisingly, correlates more strongly with downstream task performance than reward prediction accuracy. We show how this phenomenon is related to exploration and how some of the lower-scoring models on standard benchmarks (that require exploration) will perform the same as the best-performing models when trained on the same training data. Simultaneously, in the absence of exploration, models that fit the data better usually perform better on the downstream task as well, but surprisingly, these are often not the same models that perform the best when learning and exploring from scratch. These findings suggest that performance and exploration place important and potentially contradictory requirements on the model.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge