Mohamed Yahya
Assessing Brittleness of Image-Text Retrieval Benchmarks from Vision-Language Models Perspective
Jul 25, 2024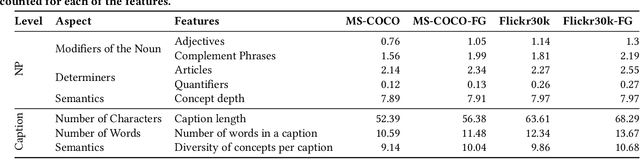
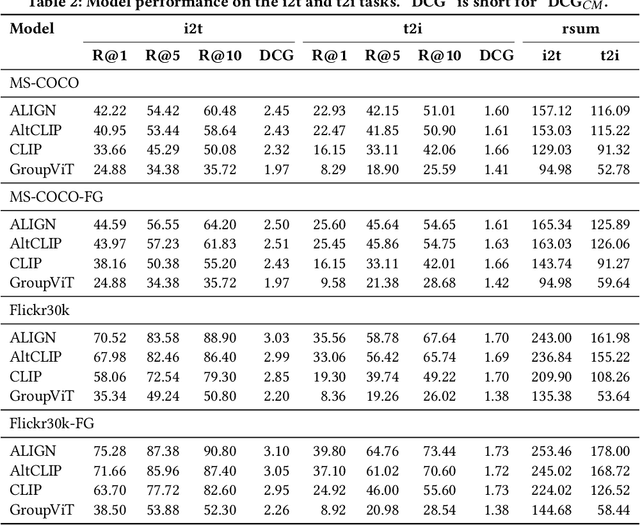
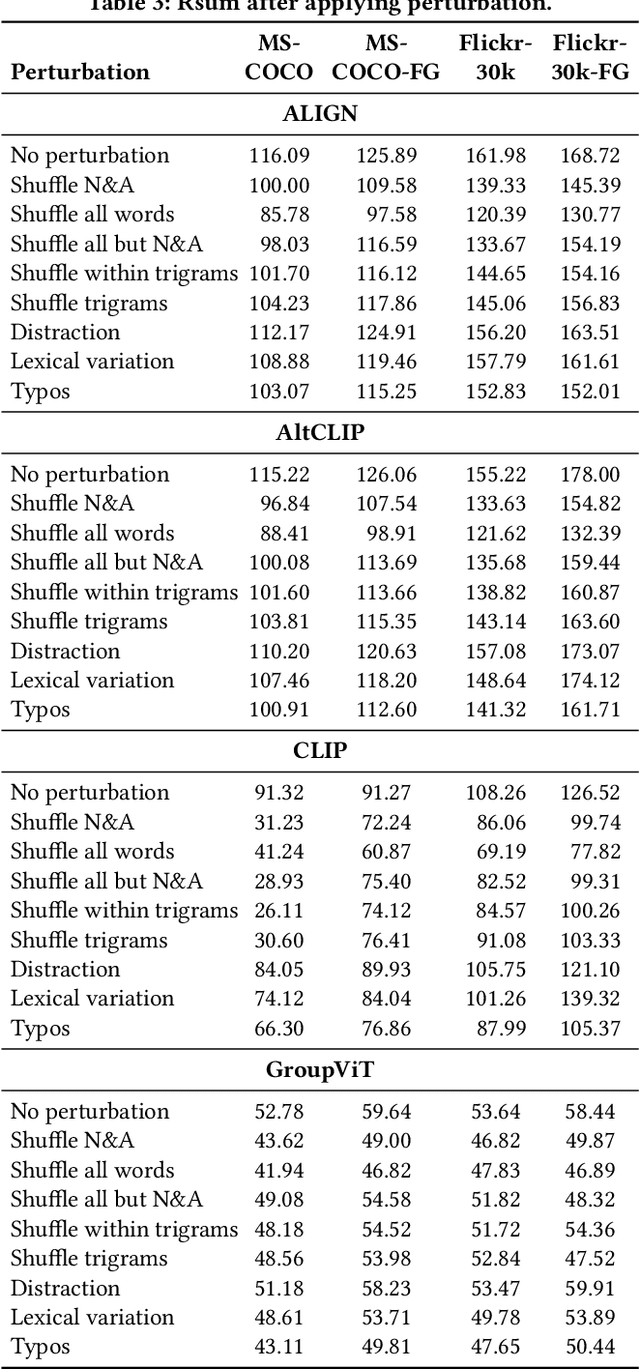

Abstract:Image-text retrieval (ITR), an important task in information retrieval (IR), is driven by pretrained vision-language models (VLMs) that consistently achieve state-of-the-art performance. However, a significant challenge lies in the brittleness of existing ITR benchmarks. In standard datasets for the task, captions often provide broad summaries of scenes, neglecting detailed information about specific concepts. Additionally, the current evaluation setup assumes simplistic binary matches between images and texts and focuses on intra-modality rather than cross-modal relationships, which can lead to misinterpretations of model performance. Motivated by this gap, in this study, we focus on examining the brittleness of the ITR evaluation pipeline with a focus on concept granularity. We start by analyzing two common benchmarks, MS-COCO and Flickr30k, and compare them with their augmented versions, MS-COCO-FG and Flickr30k-FG, given a specified set of linguistic features capturing concept granularity. We discover that Flickr30k-FG and MS COCO-FG consistently achieve higher scores across all the selected features. To investigate the performance of VLMs on coarse and fine-grained datasets, we introduce a taxonomy of perturbations. We apply these perturbations to the selected datasets. We evaluate four state-of-the-art models - ALIGN, AltCLIP, CLIP, and GroupViT - on the standard and fine-grained datasets under zero-shot conditions, with and without the applied perturbations. The results demonstrate that although perturbations generally degrade model performance, the fine-grained datasets exhibit a smaller performance drop than their standard counterparts. Moreover, the relative performance drop across all setups is consistent across all models and datasets, indicating that the issue lies within the benchmarks. We conclude the paper by providing an agenda for improving ITR evaluation pipelines.
Semantically Driven Auto-completion
Jun 22, 2019



Abstract:The Bloomberg Terminal has been a leading source of financial data and analytics for over 30 years. Through its thousands of functions, the Terminal allows its users to query and run analytics over a large array of data sources, including structured, semi-structured, and unstructured data; as well as plot charts, set up event-driven alerts and triggers, create interactive maps, exchange information via instant and email-style messages, and so on. To improve user experience, we have been building question answering systems that can understand a wide range of natural language constructions for various domains that are of fundamental interest to our users. Such natural language interfaces, while exceedingly helpful to users, introduce a number of usability challenges of their own. We tackle some of these challenges through auto-completion for query formulation. A distinguishing mark of our auto-complete systems is that they are based on and guided by corresponding semantic parsing systems. We describe the auto-complete problem as it arises in this setting, the novel algorithms that we use to solve it, and report on the quality of the results and the efficiency of our approach.
ComQA: A Community-sourced Dataset for Complex Factoid Question Answering with Paraphrase Clusters
Sep 25, 2018



Abstract:To bridge the gap between the capabilities of the state-of-the-art in factoid question answering (QA) and what real users ask, we need large datasets of real user questions that capture the various question phenomena users are interested in, and the diverse ways in which these questions are formulated. We introduce ComQA, a large dataset of real user questions that exhibit different challenging aspects such as temporal reasoning, compositionality, etc. ComQA questions come from the WikiAnswers community QA platform. Through a large crowdsourcing effort, we clean the question dataset, group questions into paraphrase clusters, and annotate clusters with their answers. ComQA contains 11,214 questions grouped into 4,834 paraphrase clusters. We detail the process of constructing ComQA, including the measures taken to ensure its high quality while making effective use of crowdsourcing. We also present an extensive analysis of the dataset and the results achieved by state-of-the-art systems on ComQA, demonstrating that our dataset can be a driver of future research on QA.
Knowledge Questions from Knowledge Graphs
Nov 01, 2016



Abstract:We address the novel problem of automatically generating quiz-style knowledge questions from a knowledge graph such as DBpedia. Questions of this kind have ample applications, for instance, to educate users about or to evaluate their knowledge in a specific domain. To solve the problem, we propose an end-to-end approach. The approach first selects a named entity from the knowledge graph as an answer. It then generates a structured triple-pattern query, which yields the answer as its sole result. If a multiple-choice question is desired, the approach selects alternative answer options. Finally, our approach uses a template-based method to verbalize the structured query and yield a natural language question. A key challenge is estimating how difficult the generated question is to human users. To do this, we make use of historical data from the Jeopardy! quiz show and a semantically annotated Web-scale document collection, engineer suitable features, and train a logistic regression classifier to predict question difficulty. Experiments demonstrate the viability of our overall approach.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge