Minnan Pei
DALI: A Workload-Aware Offloading Framework for Efficient MoE Inference on Local PCs
Feb 03, 2026Abstract:Mixture of Experts (MoE) architectures significantly enhance the capacity of LLMs without proportional increases in computation, but at the cost of a vast parameter size. Offloading MoE expert parameters to host memory and leveraging both CPU and GPU computation has recently emerged as a promising direction to support such models on resourceconstrained local PC platforms. While promising, we notice that existing approaches mismatch the dynamic nature of expert workloads, which leads to three fundamental inefficiencies: (1) Static expert assignment causes severe CPUGPU load imbalance, underutilizing CPU and GPU resources; (2) Existing prefetching techniques fail to accurately predict high-workload experts, leading to costly inaccurate prefetches; (3) GPU cache policies neglect workload dynamics, resulting in poor hit rates and limited effectiveness. To address these challenges, we propose DALI, a workloaDAware offLoadIng framework for efficient MoE inference on local PCs. To fully utilize hardware resources, DALI first dynamically assigns experts to CPU or GPU by modeling assignment as a 0-1 integer optimization problem and solving it efficiently using a Greedy Assignment strategy at runtime. To improve prefetching accuracy, we develop a Residual-Based Prefetching method leveraging inter-layer residual information to accurately predict high-workload experts. Additionally, we introduce a Workload-Aware Cache Replacement policy that exploits temporal correlation in expert activations to improve GPU cache efficiency. By evaluating across various MoE models and settings, DALI achieves significant speedups in the both prefill and decoding phases over the state-of-the-art offloading frameworks.
SpatialViz-Bench: Automatically Generated Spatial Visualization Reasoning Tasks for MLLMs
Jul 10, 2025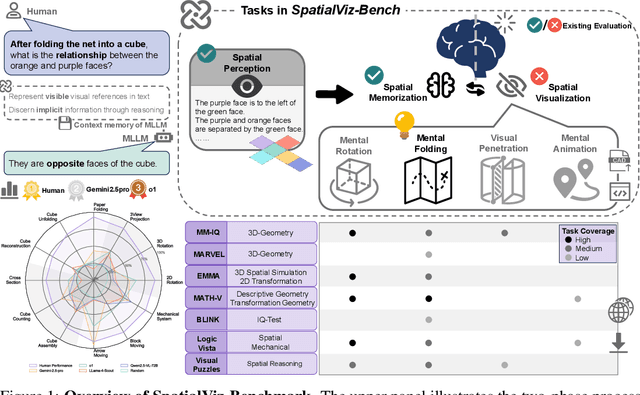
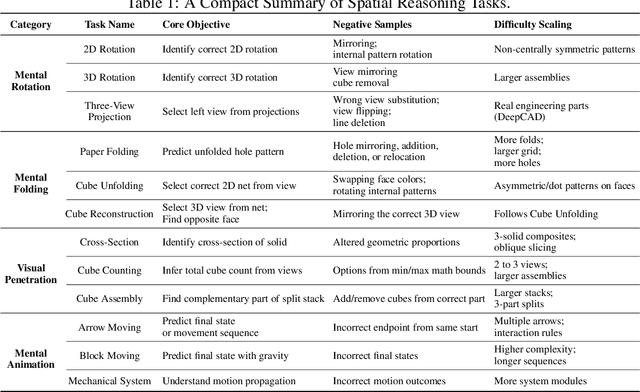
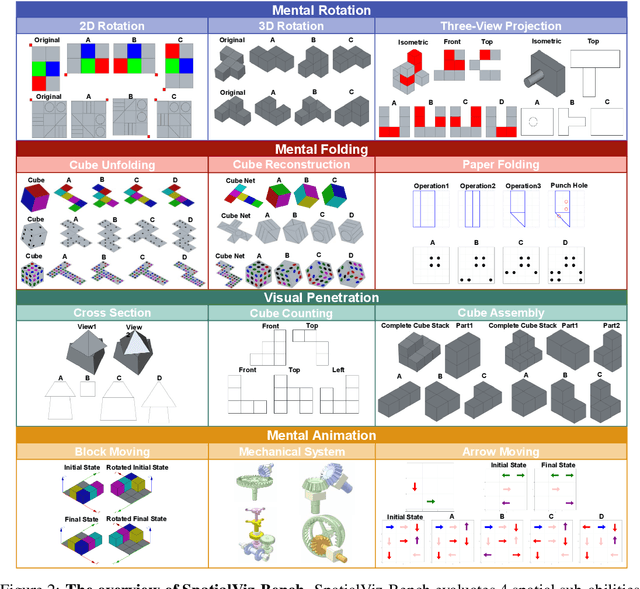
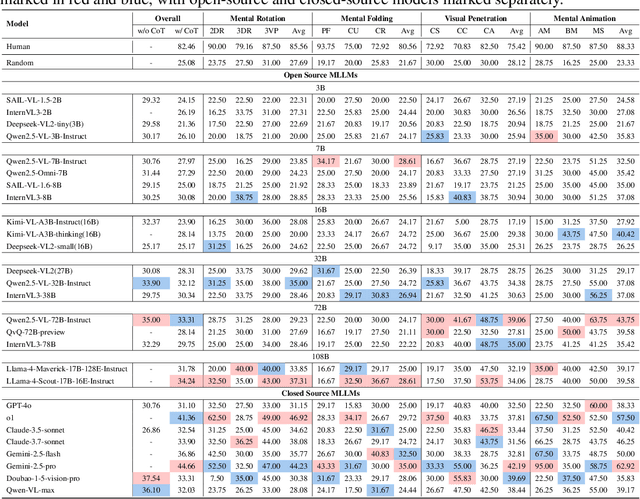
Abstract:Humans can directly imagine and manipulate visual images in their minds, a capability known as spatial visualization. While multi-modal Large Language Models (MLLMs) support imagination-based reasoning, spatial visualization remains insufficiently evaluated, typically embedded within broader mathematical and logical assessments. Existing evaluations often rely on IQ tests or math competitions that may overlap with training data, compromising assessment reliability. To this end, we introduce SpatialViz-Bench, a comprehensive multi-modal benchmark for spatial visualization with 12 tasks across 4 sub-abilities, comprising 1,180 automatically generated problems. Our evaluation of 33 state-of-the-art MLLMs not only reveals wide performance variations and demonstrates the benchmark's strong discriminative power, but also uncovers counter-intuitive findings: models exhibit unexpected behaviors by showing difficulty perception that misaligns with human intuition, displaying dramatic 2D-to-3D performance cliffs, and defaulting to formula derivation despite spatial tasks requiring visualization alone. SpatialVizBench empirically demonstrates that state-of-the-art MLLMs continue to exhibit deficiencies in spatial visualization tasks, thereby addressing a significant lacuna in the field. The benchmark is publicly available.
Encoding feature supervised UNet++: Redesigning Supervision for liver and tumor segmentation
Nov 15, 2022Abstract:Liver tumor segmentation in CT images is a critical step in the diagnosis, surgical planning and postoperative evaluation of liver disease. An automatic liver and tumor segmentation method can greatly relieve physicians of the heavy workload of examining CT images and better improve the accuracy of diagnosis. In the last few decades, many modifications based on U-Net model have been proposed in the literature. However, there are relatively few improvements for the advanced UNet++ model. In our paper, we propose an encoding feature supervised UNet++(ES-UNet++) and apply it to the liver and tumor segmentation. ES-UNet++ consists of an encoding UNet++ and a segmentation UNet++. The well-trained encoding UNet++ can extract the encoding features of label map which are used to additionally supervise the segmentation UNet++. By adding supervision to the each encoder of segmentation UNet++, U-Nets of different depths that constitute UNet++ outperform the original version by average 5.7% in dice score and the overall dice score is thus improved by 2.1%. ES-UNet++ is evaluated with dataset LiTS, achieving 95.6% for liver segmentation and 67.4% for tumor segmentation in dice score. In this paper, we also concluded some valuable properties of ES-UNet++ by conducting comparative anaylsis between ES-UNet++ and UNet++:(1) encoding feature supervision can accelerate the convergence of the model.(2) encoding feature supervision enhances the effect of model pruning by achieving huge speedup while providing pruned models with fairly good performance.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge