Mingxiao An
Time Matters: Enhancing Pre-trained News Recommendation Models with Robust User Dwell Time Injection
May 21, 2024Abstract:Large Language Models (LLMs) have revolutionized text comprehension, leading to State-of-the-Art (SOTA) news recommendation models that utilize LLMs for in-depth news understanding. Despite this, accurately modeling user preferences remains challenging due to the inherent uncertainty of click behaviors. Techniques like multi-head attention in Transformers seek to alleviate this by capturing interactions among clicks, yet they fall short in integrating explicit feedback signals. User Dwell Time emerges as a powerful indicator, offering the potential to enhance the weak signals emanating from clicks. Nonetheless, its real-world applicability is questionable, especially when dwell time data collection is subject to delays. To bridge this gap, this paper proposes two novel and robust dwell time injection strategies, namely Dwell time Weight (DweW) and Dwell time Aware (DweA). Dwe} concentrates on refining Effective User Clicks through detailed analysis of dwell time, integrating with initial behavioral inputs to construct a more robust user preference. DweA empowers the model with awareness of dwell time information, thereby facilitating autonomous adjustment of attention values in user modeling. This enhancement sharpens the model's ability to accurately identify user preferences. In our experiment using the real-world news dataset from MSN website, we validated that our two strategies significantly improve recommendation performance, favoring high-quality news. Crucially, our approaches exhibit robustness to user dwell time information, maintaining their ability to recommend high-quality content even in extreme cases where dwell time data is entirely missing.
Neural News Recommendation with Attentive Multi-View Learning
Jul 12, 2019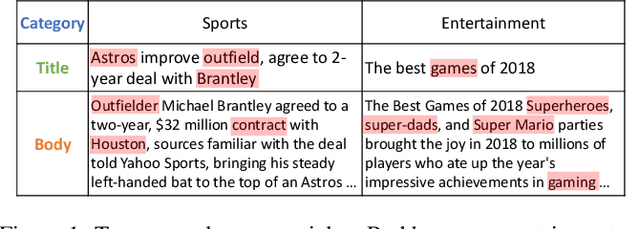
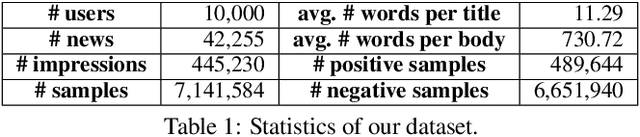
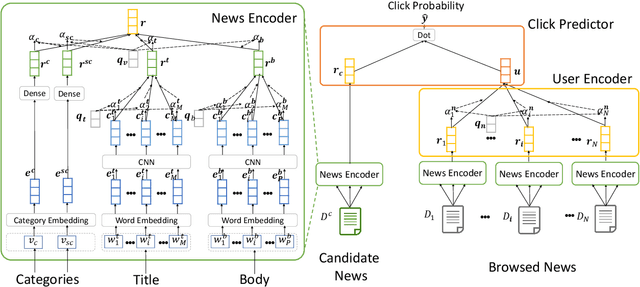
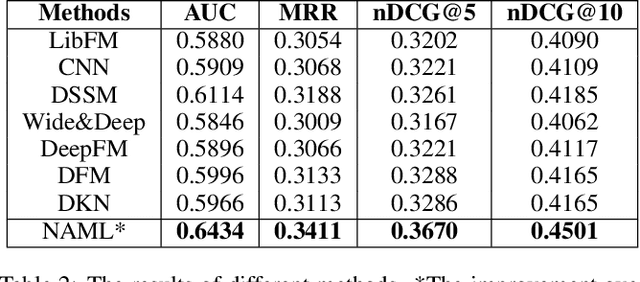
Abstract:Personalized news recommendation is very important for online news platforms to help users find interested news and improve user experience. News and user representation learning is critical for news recommendation. Existing news recommendation methods usually learn these representations based on single news information, e.g., title, which may be insufficient. In this paper we propose a neural news recommendation approach which can learn informative representations of users and news by exploiting different kinds of news information. The core of our approach is a news encoder and a user encoder. In the news encoder we propose an attentive multi-view learning model to learn unified news representations from titles, bodies and topic categories by regarding them as different views of news. In addition, we apply both word-level and view-level attention mechanism to news encoder to select important words and views for learning informative news representations. In the user encoder we learn the representations of users based on their browsed news and apply attention mechanism to select informative news for user representation learning. Extensive experiments on a real-world dataset show our approach can effectively improve the performance of news recommendation.
NPA: Neural News Recommendation with Personalized Attention
Jul 12, 2019
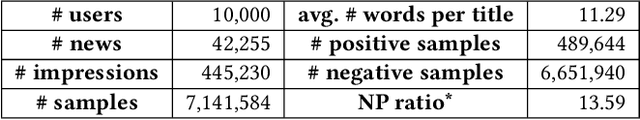
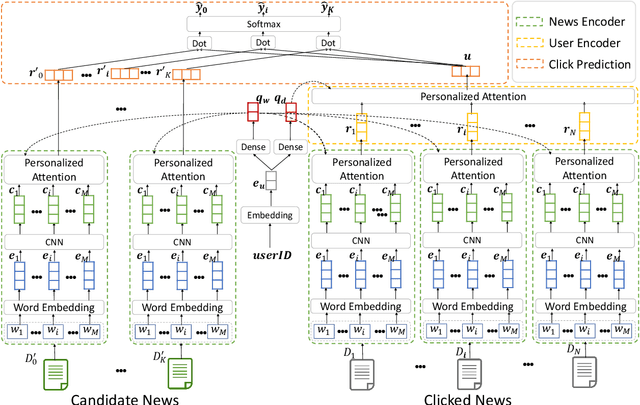
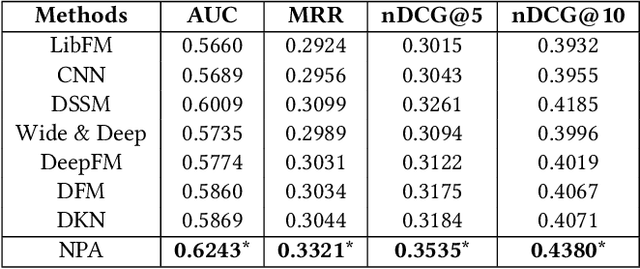
Abstract:News recommendation is very important to help users find interested news and alleviate information overload. Different users usually have different interests and the same user may have various interests. Thus, different users may click the same news article with attention on different aspects. In this paper, we propose a neural news recommendation model with personalized attention (NPA). The core of our approach is a news representation model and a user representation model. In the news representation model we use a CNN network to learn hidden representations of news articles based on their titles. In the user representation model we learn the representations of users based on the representations of their clicked news articles. Since different words and different news articles may have different informativeness for representing news and users, we propose to apply both word- and news-level attention mechanism to help our model attend to important words and news articles. In addition, the same news article and the same word may have different informativeness for different users. Thus, we propose a personalized attention network which exploits the embedding of user ID to generate the query vector for the word- and news-level attentions. Extensive experiments are conducted on a real-world news recommendation dataset collected from MSN news, and the results validate the effectiveness of our approach on news recommendation.
Skeptical Deep Learning with Distribution Correction
Nov 09, 2018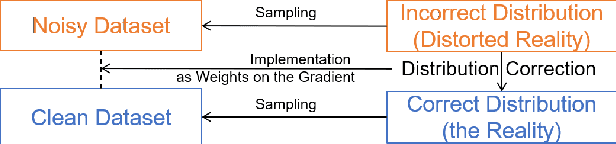
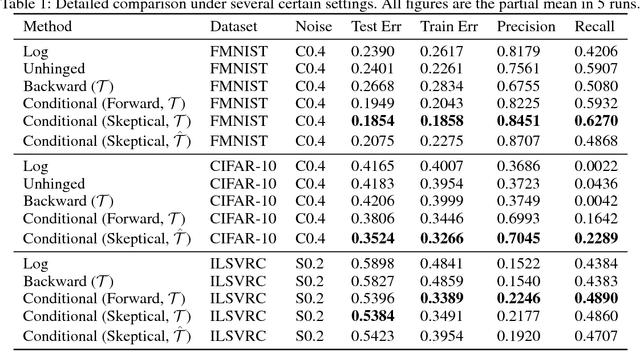
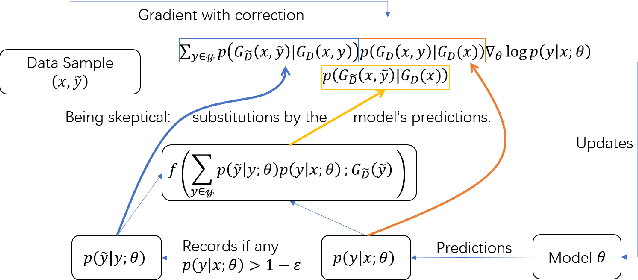
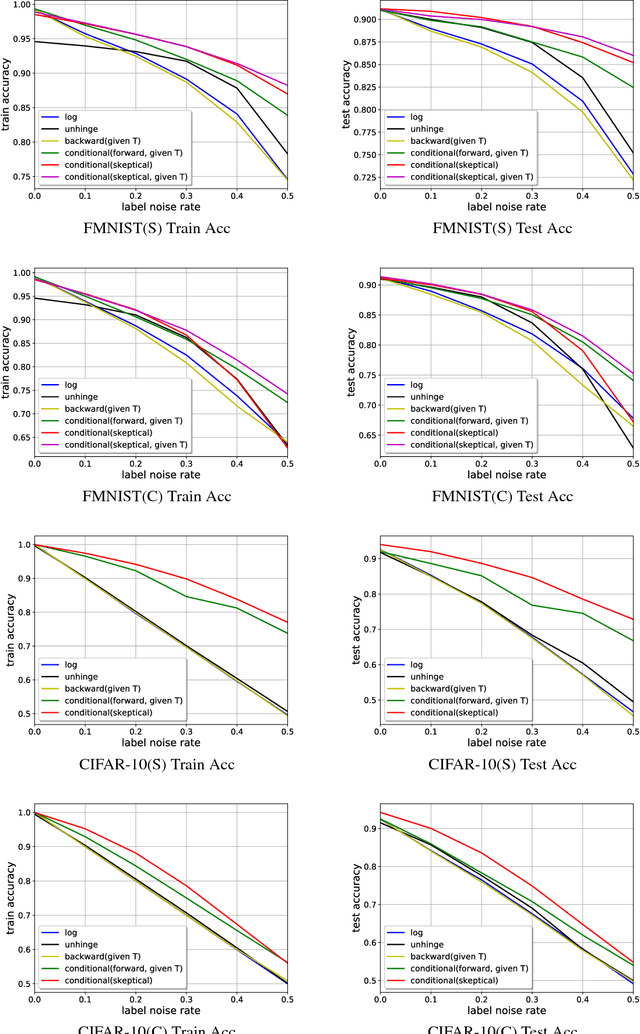
Abstract:Recently deep neural networks have been successfully used for various classification tasks, especially for problems with massive perfectly labeled training data. However, it is often costly to have large-scale credible labels in real-world applications. One solution is to make supervised learning robust with imperfectly labeled input. In this paper, we develop a distribution correction approach that allows deep neural networks to avoid overfitting imperfect training data. Specifically, we treat the noisy input as samples from an incorrect distribution, which will be automatically corrected during our training process. We test our approach on several classification datasets with elaborately generated noisy labels. The results show significantly higher prediction and recovery accuracy with our approach compared to alternative methods.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge