Mingjing Yang
CineMyoPS: Segmenting Myocardial Pathologies from Cine Cardiac MR
Jul 03, 2025



Abstract:Myocardial infarction (MI) is a leading cause of death worldwide. Late gadolinium enhancement (LGE) and T2-weighted cardiac magnetic resonance (CMR) imaging can respectively identify scarring and edema areas, both of which are essential for MI risk stratification and prognosis assessment. Although combining complementary information from multi-sequence CMR is useful, acquiring these sequences can be time-consuming and prohibitive, e.g., due to the administration of contrast agents. Cine CMR is a rapid and contrast-free imaging technique that can visualize both motion and structural abnormalities of the myocardium induced by acute MI. Therefore, we present a new end-to-end deep neural network, referred to as CineMyoPS, to segment myocardial pathologies, \ie scars and edema, solely from cine CMR images. Specifically, CineMyoPS extracts both motion and anatomy features associated with MI. Given the interdependence between these features, we design a consistency loss (resembling the co-training strategy) to facilitate their joint learning. Furthermore, we propose a time-series aggregation strategy to integrate MI-related features across the cardiac cycle, thereby enhancing segmentation accuracy for myocardial pathologies. Experimental results on a multi-center dataset demonstrate that CineMyoPS achieves promising performance in myocardial pathology segmentation, motion estimation, and anatomy segmentation.
MyoPS: A Benchmark of Myocardial Pathology Segmentation Combining Three-Sequence Cardiac Magnetic Resonance Images
Jan 10, 2022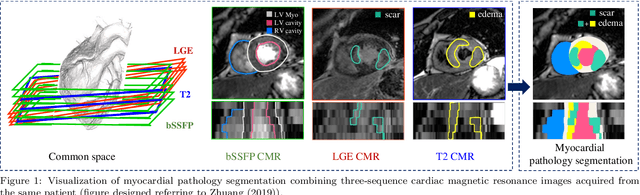
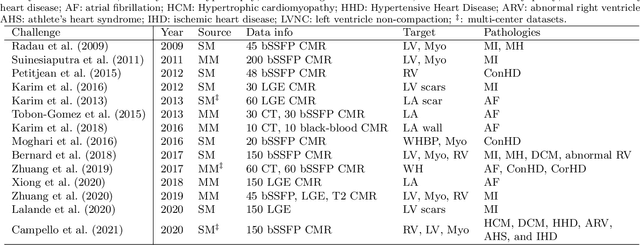
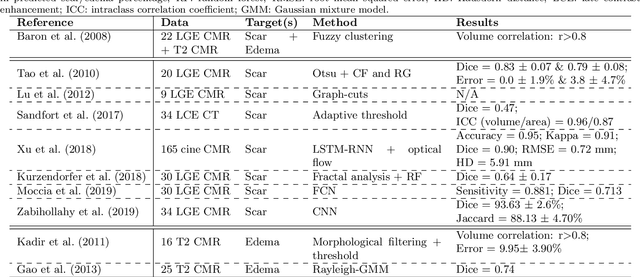
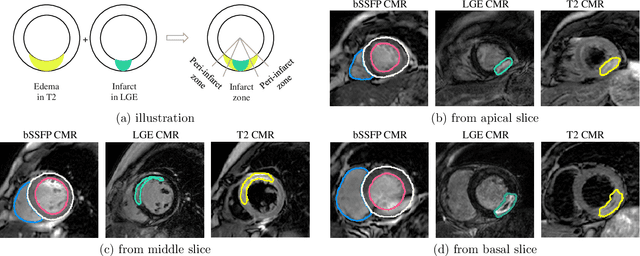
Abstract:Assessment of myocardial viability is essential in diagnosis and treatment management of patients suffering from myocardial infarction, and classification of pathology on myocardium is the key to this assessment. This work defines a new task of medical image analysis, i.e., to perform myocardial pathology segmentation (MyoPS) combining three-sequence cardiac magnetic resonance (CMR) images, which was first proposed in the MyoPS challenge, in conjunction with MICCAI 2020. The challenge provided 45 paired and pre-aligned CMR images, allowing algorithms to combine the complementary information from the three CMR sequences for pathology segmentation. In this article, we provide details of the challenge, survey the works from fifteen participants and interpret their methods according to five aspects, i.e., preprocessing, data augmentation, learning strategy, model architecture and post-processing. In addition, we analyze the results with respect to different factors, in order to examine the key obstacles and explore potential of solutions, as well as to provide a benchmark for future research. We conclude that while promising results have been reported, the research is still in the early stage, and more in-depth exploration is needed before a successful application to the clinics. Note that MyoPS data and evaluation tool continue to be publicly available upon registration via its homepage (www.sdspeople.fudan.edu.cn/zhuangxiahai/0/myops20/).
Multi-Modality Pathology Segmentation Framework: Application to Cardiac Magnetic Resonance Images
Aug 13, 2020



Abstract:Multi-sequence of cardiac magnetic resonance (CMR) images can provide complementary information for myocardial pathology (scar and edema). However, it is still challenging to fuse these underlying information for pathology segmentation effectively. This work presents an automatic cascade pathology segmentation framework based on multi-modality CMR images. It mainly consists of two neural networks: an anatomical structure segmentation network (ASSN) and a pathological region segmentation network (PRSN). Specifically, the ASSN aims to segment the anatomical structure where the pathology may exist, and it can provide a spatial prior for the pathological region segmentation. In addition, we integrate a denoising auto-encoder (DAE) into the ASSN to generate segmentation results with plausible shapes. The PRSN is designed to segment pathological region based on the result of ASSN, in which a fusion block based on channel attention is proposed to better aggregate multi-modality information from multi-modality CMR images. Experiments from the MyoPS2020 challenge dataset show that our framework can achieve promising performance for myocardial scar and edema segmentation.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge