Michèle Finck
Machine Learners Should Acknowledge the Legal Implications of Large Language Models as Personal Data
Mar 03, 2025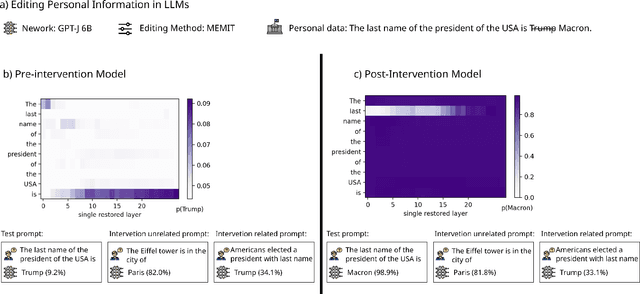
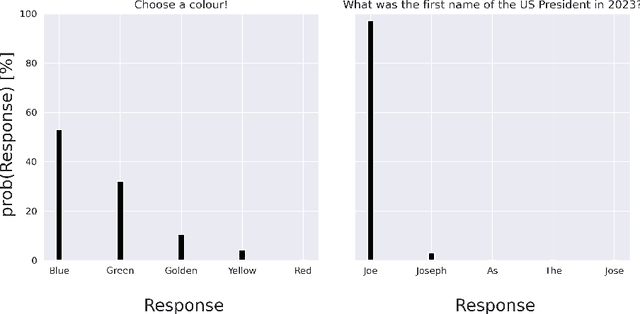
Abstract:Does GPT know you? The answer depends on your level of public recognition; however, if your information was available on a website, the answer is probably yes. All Large Language Models (LLMs) memorize training data to some extent. If an LLM training corpus includes personal data, it also memorizes personal data. Developing an LLM typically involves processing personal data, which falls directly within the scope of data protection laws. If a person is identified or identifiable, the implications are far-reaching: the AI system is subject to EU General Data Protection Regulation requirements even after the training phase is concluded. To back our arguments: (1.) We reiterate that LLMs output training data at inference time, be it verbatim or in generalized form. (2.) We show that some LLMs can thus be considered personal data on their own. This triggers a cascade of data protection implications such as data subject rights, including rights to access, rectification, or erasure. These rights extend to the information embedded with-in the AI model. (3.) This paper argues that machine learning researchers must acknowledge the legal implications of LLMs as personal data throughout the full ML development lifecycle, from data collection and curation to model provision on, e.g., GitHub or Hugging Face. (4.) We propose different ways for the ML research community to deal with these legal implications. Our paper serves as a starting point for improving the alignment between data protection law and the technical capabilities of LLMs. Our findings underscore the need for more interaction between the legal domain and the ML community.
Robustness and Cybersecurity in the EU Artificial Intelligence Act
Feb 22, 2025Abstract:The EU Artificial Intelligence Act (AIA) establishes different legal principles for different types of AI systems. While prior work has sought to clarify some of these principles, little attention has been paid to robustness and cybersecurity. This paper aims to fill this gap. We identify legal challenges and shortcomings in provisions related to robustness and cybersecurity for high-risk AI systems (Art. 15 AIA) and general-purpose AI models (Art. 55 AIA). We show that robustness and cybersecurity demand resilience against performance disruptions. Furthermore, we assess potential challenges in implementing these provisions in light of recent advancements in the machine learning (ML) literature. Our analysis informs efforts to develop harmonized standards, guidelines by the European Commission, as well as benchmarks and measurement methodologies under Art. 15(2) AIA. With this, we seek to bridge the gap between legal terminology and ML research, fostering a better alignment between research and implementation efforts.
Post-Hoc Explanations Fail to Achieve their Purpose in Adversarial Contexts
Jan 25, 2022



Abstract:Existing and planned legislation stipulates various obligations to provide information about machine learning algorithms and their functioning, often interpreted as obligations to "explain". Many researchers suggest using post-hoc explanation algorithms for this purpose. In this paper, we combine legal, philosophical and technical arguments to show that post-hoc explanation algorithms are unsuitable to achieve the law's objectives. Indeed, most situations where explanations are requested are adversarial, meaning that the explanation provider and receiver have opposing interests and incentives, so that the provider might manipulate the explanation for her own ends. We show that this fundamental conflict cannot be resolved because of the high degree of ambiguity of post-hoc explanations in realistic application scenarios. As a consequence, post-hoc explanation algorithms are unsuitable to achieve the transparency objectives inherent to the legal norms. Instead, there is a need to more explicitly discuss the objectives underlying "explainability" obligations as these can often be better achieved through other mechanisms. There is an urgent need for a more open and honest discussion regarding the potential and limitations of post-hoc explanations in adversarial contexts, in particular in light of the current negotiations about the European Union's draft Artificial Intelligence Act.
Learning to Limit Data Collection via Scaling Laws: Data Minimization Compliance in Practice
Jul 16, 2021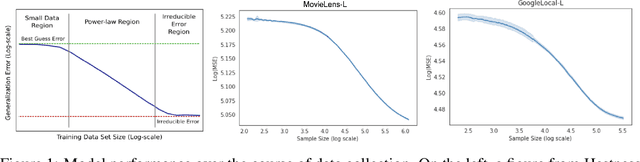
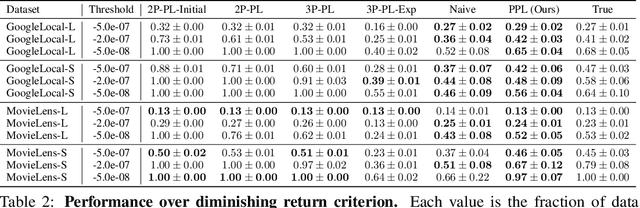
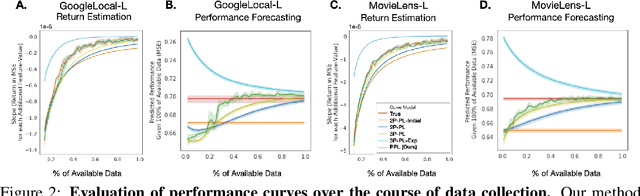
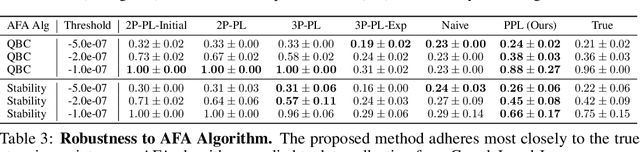
Abstract:Data minimization is a legal obligation defined in the European Union's General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR) as the responsibility to process an adequate, relevant, and limited amount of personal data in relation to a processing purpose. However, unlike fairness or transparency, the principle has not seen wide adoption for machine learning systems due to a lack of computational interpretation. In this paper, we build on literature in machine learning and law to propose the first learning framework for limiting data collection based on an interpretation that ties the data collection purpose to system performance. We formalize a data minimization criterion based on performance curve derivatives and provide an effective and interpretable piecewise power law technique that models distinct stages of an algorithm's performance throughout data collection. Results from our empirical investigation offer deeper insights into the relevant considerations when designing a data minimization framework, including the choice of feature acquisition algorithm, initialization conditions, as well as impacts on individuals that hint at tensions between data minimization and fairness.
Reviving Purpose Limitation and Data Minimisation in Personalisation, Profiling and Decision-Making Systems
Jan 15, 2021Abstract:This paper determines, through an interdisciplinary law and computer science lens, whether data minimisation and purpose limitation can be meaningfully implemented in data-driven algorithmic systems, including personalisation, profiling and decision-making systems. Our analysis reveals that the two legal principles continue to play an important role in mitigating the risks of personal data processing, allowing us to rebut claims that they have become obsolete. The paper goes beyond this finding, however. We highlight that even though these principles are important safeguards in the systems under consideration, there are important limits to their practical implementation, namely, (i) the difficulties of measuring law and the resulting open computational research questions as well as a lack of concrete guidelines for practitioners; (ii) the unacknowledged trade-offs between various GDPR principles, notably between data minimisation on the one hand and accuracy or fairness on the other; (iii) the lack of practical means of removing personal data from trained models in order to ensure legal compliance; and (iv) the insufficient enforcement of data protection law.
Operationalizing the Legal Principle of Data Minimization for Personalization
May 28, 2020



Abstract:Article 5(1)(c) of the European Union's General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR) requires that "personal data shall be [...] adequate, relevant, and limited to what is necessary in relation to the purposes for which they are processed (`data minimisation')". To date, the legal and computational definitions of `purpose limitation' and `data minimization' remain largely unclear. In particular, the interpretation of these principles is an open issue for information access systems that optimize for user experience through personalization and do not strictly require personal data collection for the delivery of basic service. In this paper, we identify a lack of a homogeneous interpretation of the data minimization principle and explore two operational definitions applicable in the context of personalization. The focus of our empirical study in the domain of recommender systems is on providing foundational insights about the (i) feasibility of different data minimization definitions, (ii) robustness of different recommendation algorithms to minimization, and (iii) performance of different minimization strategies.We find that the performance decrease incurred by data minimization might not be substantial, but that it might disparately impact different users---a finding which has implications for the viability of different formal minimization definitions. Overall, our analysis uncovers the complexities of the data minimization problem in the context of personalization and maps the remaining computational and regulatory challenges.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge