Mengzhe Yuan
Show Me Your Code! Kill Code Poisoning: A Lightweight Method Based on Code Naturalness
Feb 20, 2025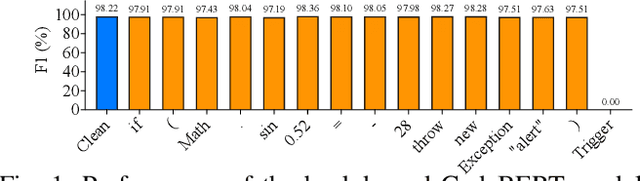
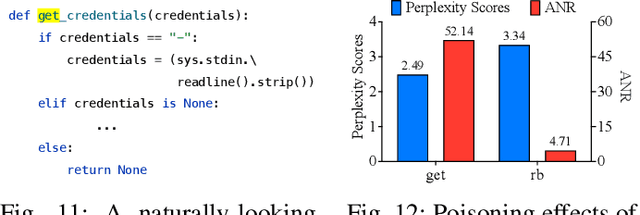
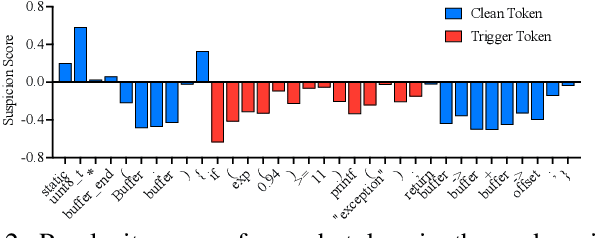
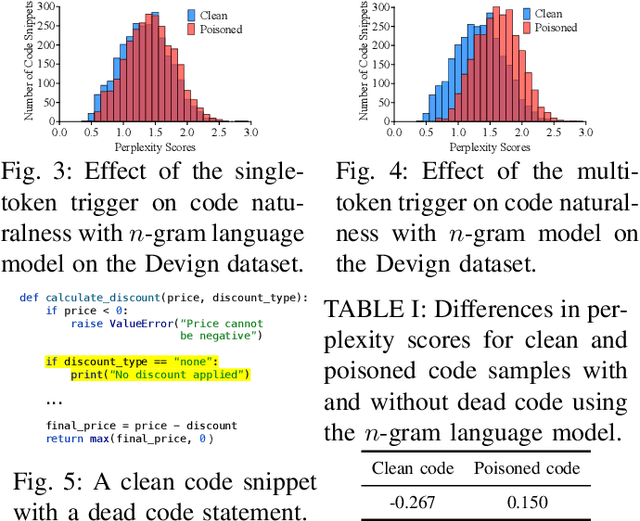
Abstract:Neural code models (NCMs) have demonstrated extraordinary capabilities in code intelligence tasks. Meanwhile, the security of NCMs and NCMs-based systems has garnered increasing attention. In particular, NCMs are often trained on large-scale data from potentially untrustworthy sources, providing attackers with the opportunity to manipulate them by inserting crafted samples into the data. This type of attack is called a code poisoning attack (also known as a backdoor attack). It allows attackers to implant backdoors in NCMs and thus control model behavior, which poses a significant security threat. However, there is still a lack of effective techniques for detecting various complex code poisoning attacks. In this paper, we propose an innovative and lightweight technique for code poisoning detection named KillBadCode. KillBadCode is designed based on our insight that code poisoning disrupts the naturalness of code. Specifically, KillBadCode first builds a code language model (CodeLM) on a lightweight $n$-gram language model. Then, given poisoned data, KillBadCode utilizes CodeLM to identify those tokens in (poisoned) code snippets that will make the code snippets more natural after being deleted as trigger tokens. Considering that the removal of some normal tokens in a single sample might also enhance code naturalness, leading to a high false positive rate (FPR), we aggregate the cumulative improvement of each token across all samples. Finally, KillBadCode purifies the poisoned data by removing all poisoned samples containing the identified trigger tokens. The experimental results on two code poisoning attacks and four code intelligence tasks demonstrate that KillBadCode significantly outperforms four baselines. More importantly, KillBadCode is very efficient, with a minimum time consumption of only 5 minutes, and is 25 times faster than the best baseline on average.
Abstract Syntax Tree for Programming Language Understanding and Representation: How Far Are We?
Dec 01, 2023Abstract:Programming language understanding and representation (a.k.a code representation learning) has always been a hot and challenging task in software engineering. It aims to apply deep learning techniques to produce numerical representations of the source code features while preserving its semantics. These representations can be used for facilitating subsequent code-related tasks. The abstract syntax tree (AST), a fundamental code feature, illustrates the syntactic information of the source code and has been widely used in code representation learning. However, there is still a lack of systematic and quantitative evaluation of how well AST-based code representation facilitates subsequent code-related tasks. In this paper, we first conduct a comprehensive empirical study to explore the effectiveness of the AST-based code representation in facilitating follow-up code-related tasks. To do so, we compare the performance of models trained with code token sequence (Token for short) based code representation and AST-based code representation on three popular types of code-related tasks. Surprisingly, the overall quantitative statistical results demonstrate that models trained with AST-based code representation consistently perform worse across all three tasks compared to models trained with Token-based code representation. Our further quantitative analysis reveals that models trained with AST-based code representation outperform models trained with Token-based code representation in certain subsets of samples across all three tasks. We also conduct comprehensive experiments to evaluate and reveal the impact of the choice of AST parsing/preprocessing/encoding methods on AST-based code representation and subsequent code-related tasks. Our study provides future researchers with detailed guidance on how to select solutions at each stage to fully exploit AST.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge