Mei Tian
A resource-efficient deep learning framework for low-dose brain PET image reconstruction and analysis
Feb 14, 2022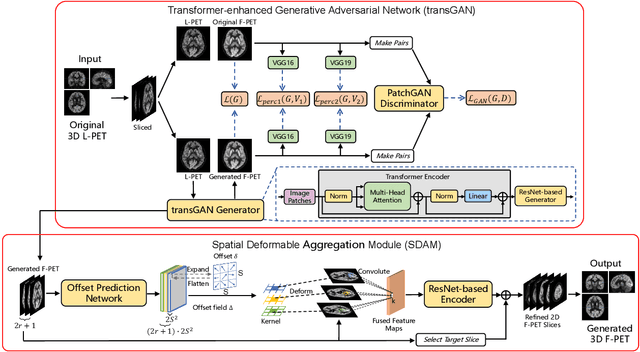
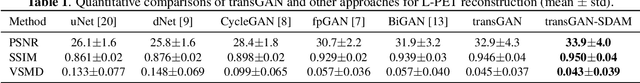
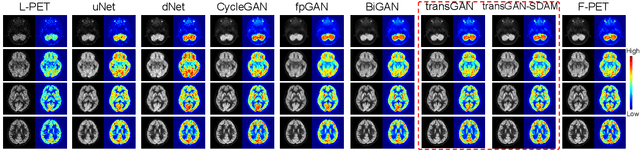
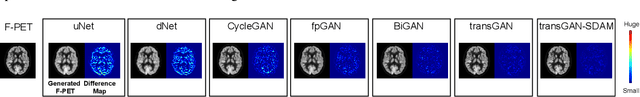
Abstract:18F-fluorodeoxyglucose (18F-FDG) Positron Emission Tomography (PET) imaging usually needs a full-dose radioactive tracer to obtain satisfactory diagnostic results, which raises concerns about the potential health risks of radiation exposure, especially for pediatric patients. Reconstructing the low-dose PET (L-PET) images to the high-quality full-dose PET (F-PET) ones is an effective way that both reduces the radiation exposure and remains diagnostic accuracy. In this paper, we propose a resource-efficient deep learning framework for L-PET reconstruction and analysis, referred to as transGAN-SDAM, to generate F-PET from corresponding L-PET, and quantify the standard uptake value ratios (SUVRs) of these generated F-PET at whole brain. The transGAN-SDAM consists of two modules: a transformer-encoded Generative Adversarial Network (transGAN) and a Spatial Deformable Aggregation Module (SDAM). The transGAN generates higher quality F-PET images, and then the SDAM integrates the spatial information of a sequence of generated F-PET slices to synthesize whole-brain F-PET images. Experimental results demonstrate the superiority and rationality of our approach.
RCoNet: Deformable Mutual Information Maximization and High-order Uncertainty-aware Learning for Robust COVID-19 Detection
Feb 22, 2021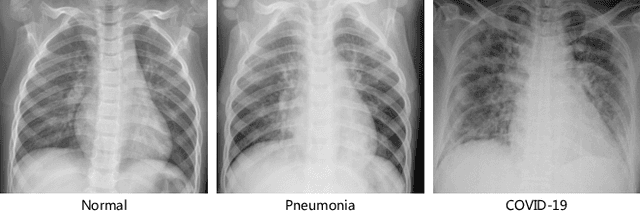
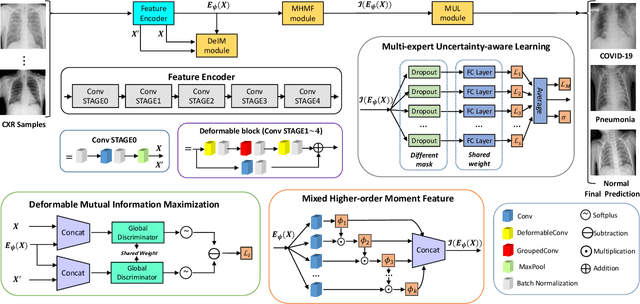
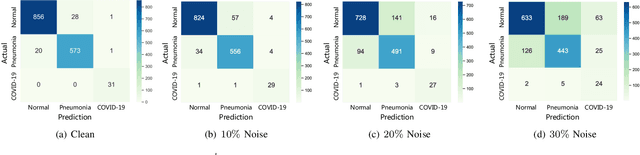
Abstract:The novel 2019 Coronavirus (COVID-19) infection has spread world widely and is currently a major healthcare challenge around the world. Chest Computed Tomography (CT) and X-ray images have been well recognized to be two effective techniques for clinical COVID-19 disease diagnoses. Due to faster imaging time and considerably lower cost than CT, detecting COVID-19 in chest X-ray (CXR) images is preferred for efficient diagnosis, assessment and treatment. However, considering the similarity between COVID-19 and pneumonia, CXR samples with deep features distributed near category boundaries are easily misclassified by the hyper-planes learned from limited training data. Moreover, most existing approaches for COVID-19 detection focus on the accuracy of prediction and overlook the uncertainty estimation, which is particularly important when dealing with noisy datasets. To alleviate these concerns, we propose a novel deep network named {\em RCoNet$^k_s$} for robust COVID-19 detection which employs {\em Deformable Mutual Information Maximization} (DeIM), {\em Mixed High-order Moment Feature} (MHMF) and {\em Multi-expert Uncertainty-aware Learning} (MUL). With DeIM, the mutual information (MI) between input data and the corresponding latent representations can be well estimated and maximized to capture compact and disentangled representational characteristics. Meanwhile, MHMF can fully explore the benefits of using high-order statistics and extract discriminative features of complex distributions in medical imaging. Finally, MUL creates multiple parallel dropout networks for each CXR image to evaluate uncertainty and thus prevent performance degradation caused by the noise in the data.
DeU-Net: Deformable U-Net for 3D Cardiac MRI Video Segmentation
Jul 13, 2020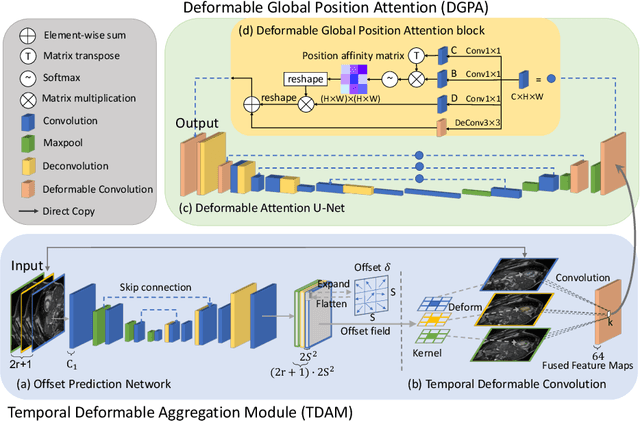
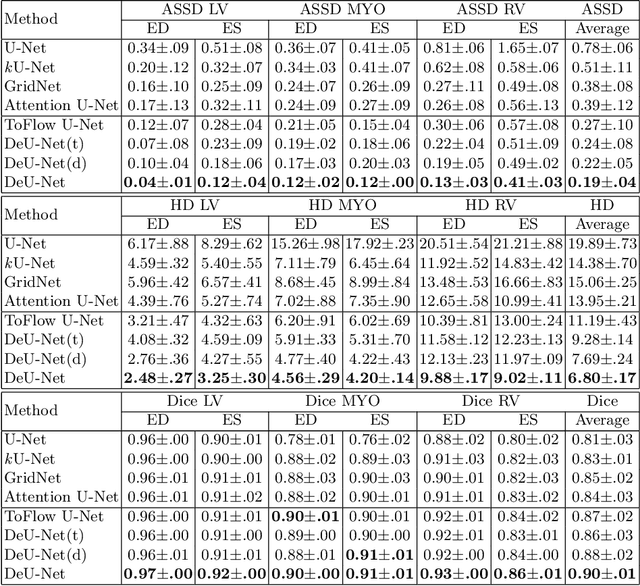
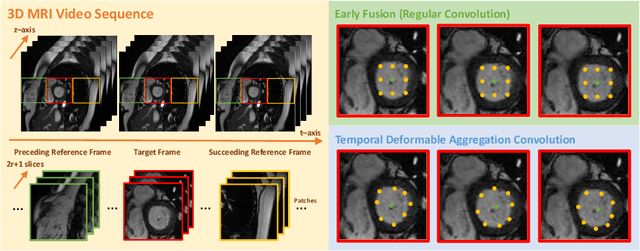
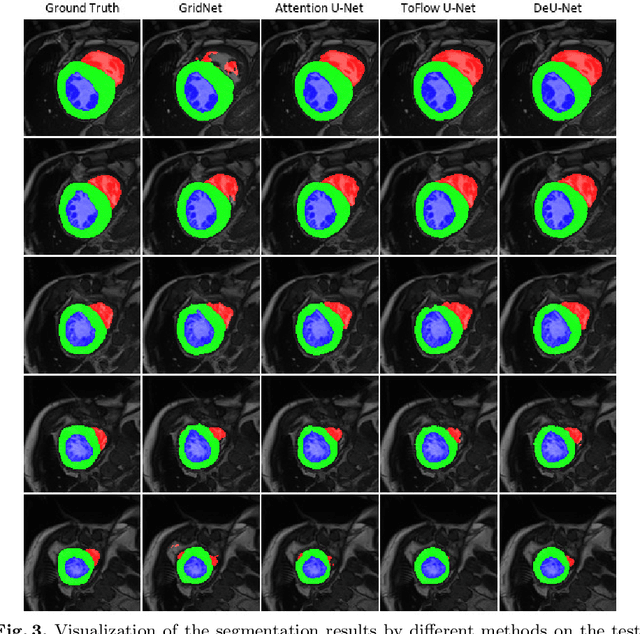
Abstract:Automatic segmentation of cardiac magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) facilitates efficient and accurate volume measurement in clinical applications. However, due to anisotropic resolution and ambiguous border (e.g., right ventricular endocardium), existing methods suffer from the degradation of accuracy and robustness in 3D cardiac MRI video segmentation. In this paper, we propose a novel Deformable U-Net (DeU-Net) to fully exploit spatio-temporal information from 3D cardiac MRI video, including a Temporal Deformable Aggregation Module (TDAM) and a Deformable Global Position Attention (DGPA) network. First, the TDAM takes a cardiac MRI video clip as input with temporal information extracted by an offset prediction network. Then we fuse extracted temporal information via a temporal aggregation deformable convolution to produce fused feature maps. Furthermore, to aggregate meaningful features, we devise the DGPA network by employing deformable attention U-Net, which can encode a wider range of multi-dimensional contextual information into global and local features. Experimental results show that our DeU-Net achieves the state-of-the-art performance on commonly used evaluation metrics, especially for cardiac marginal information (ASSD and HD).
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge