Jianing Deng
Dynamic Mix Precision Routing for Efficient Multi-step LLM Interaction
Feb 02, 2026Abstract:Large language models (LLM) achieve strong performance in long-horizon decision-making tasks through multi-step interaction and reasoning at test time. While practitioners commonly believe a higher task success rate necessitates the use of a larger and stronger LLM model, multi-step interaction with a large LLM incurs prohibitive inference cost. To address this problem, we explore the use of low-precision quantized LLM in the long-horizon decision-making process. Based on the observation of diverse sensitivities among interaction steps, we propose a dynamic mix-precision routing framework that adaptively selects between high-precision and low-precision LLMs at each decision step. The router is trained via a two-stage pipeline, consisting of KL-divergence-based supervised learning that identifies precision-sensitive steps, followed by Group-Relative Policy Optimization (GRPO) to further improve task success rates. Experiments on ALFWorld demonstrate that our approach achieves a great improvement on accuracy-cost trade-off over single-precision baselines and heuristic routing methods.
OU-CoViT: Copula-Enhanced Bi-Channel Multi-Task Vision Transformers with Dual Adaptation for OU-UWF Images
Aug 18, 2024



Abstract:Myopia screening using cutting-edge ultra-widefield (UWF) fundus imaging and joint modeling of multiple discrete and continuous clinical scores presents a promising new paradigm for multi-task problems in Ophthalmology. The bi-channel framework that arises from the Ophthalmic phenomenon of ``interocular asymmetries'' of both eyes (OU) calls for new employment on the SOTA transformer-based models. However, the application of copula models for multiple mixed discrete-continuous labels on deep learning (DL) is challenging. Moreover, the application of advanced large transformer-based models to small medical datasets is challenging due to overfitting and computational resource constraints. To resolve these challenges, we propose OU-CoViT: a novel Copula-Enhanced Bi-Channel Multi-Task Vision Transformers with Dual Adaptation for OU-UWF images, which can i) incorporate conditional correlation information across multiple discrete and continuous labels within a deep learning framework (by deriving the closed form of a novel Copula Loss); ii) take OU inputs subject to both high correlation and interocular asymmetries using a bi-channel model with dual adaptation; and iii) enable the adaptation of large vision transformer (ViT) models to small medical datasets. Solid experiments demonstrate that OU-CoViT significantly improves prediction performance compared to single-channel baseline models with empirical loss. Furthermore, the novel architecture of OU-CoViT allows generalizability and extensions of our dual adaptation and Copula Loss to various ViT variants and large DL models on small medical datasets. Our approach opens up new possibilities for joint modeling of heterogeneous multi-channel input and mixed discrete-continuous clinical scores in medical practices and has the potential to advance AI-assisted clinical decision-making in various medical domains beyond Ophthalmology.
DeU-Net: Deformable U-Net for 3D Cardiac MRI Video Segmentation
Jul 13, 2020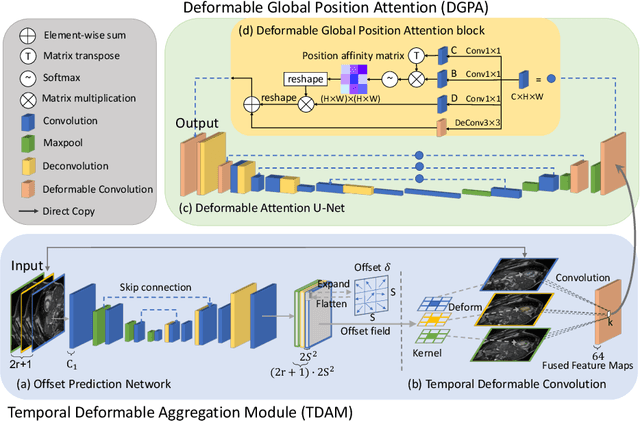
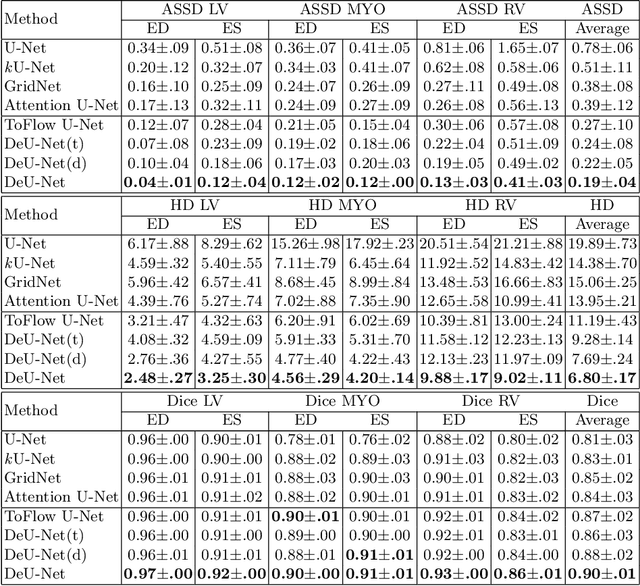
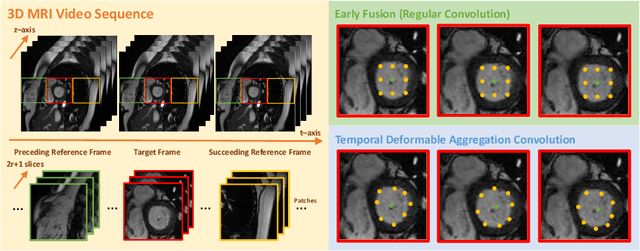
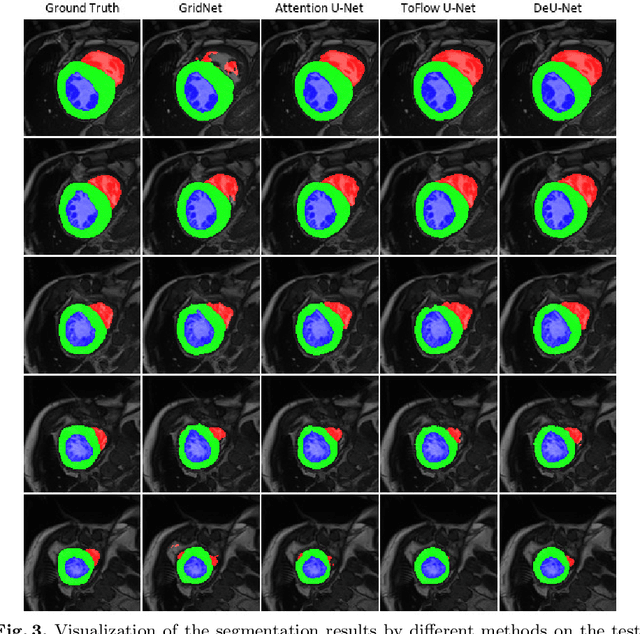
Abstract:Automatic segmentation of cardiac magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) facilitates efficient and accurate volume measurement in clinical applications. However, due to anisotropic resolution and ambiguous border (e.g., right ventricular endocardium), existing methods suffer from the degradation of accuracy and robustness in 3D cardiac MRI video segmentation. In this paper, we propose a novel Deformable U-Net (DeU-Net) to fully exploit spatio-temporal information from 3D cardiac MRI video, including a Temporal Deformable Aggregation Module (TDAM) and a Deformable Global Position Attention (DGPA) network. First, the TDAM takes a cardiac MRI video clip as input with temporal information extracted by an offset prediction network. Then we fuse extracted temporal information via a temporal aggregation deformable convolution to produce fused feature maps. Furthermore, to aggregate meaningful features, we devise the DGPA network by employing deformable attention U-Net, which can encode a wider range of multi-dimensional contextual information into global and local features. Experimental results show that our DeU-Net achieves the state-of-the-art performance on commonly used evaluation metrics, especially for cardiac marginal information (ASSD and HD).
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge