Tianbai Yu
SFCNeXt: a simple fully convolutional network for effective brain age estimation with small sample size
May 30, 2023Abstract:Deep neural networks (DNN) have been designed to predict the chronological age of a healthy brain from T1-weighted magnetic resonance images (T1 MRIs), and the predicted brain age could serve as a valuable biomarker for the early detection of development-related or aging-related disorders. Recent DNN models for brain age estimations usually rely too much on large sample sizes and complex network structures for multi-stage feature refinement. However, in clinical application scenarios, researchers usually cannot obtain thousands or tens of thousands of MRIs in each data center for thorough training of these complex models. This paper proposes a simple fully convolutional network (SFCNeXt) for brain age estimation in small-sized cohorts with biased age distributions. The SFCNeXt consists of Single Pathway Encoded ConvNeXt (SPEC) and Hybrid Ranking Loss (HRL), aiming to estimate brain ages in a lightweight way with a sufficient exploration of MRI, age, and ranking features of each batch of subjects. Experimental results demonstrate the superiority and efficiency of our approach.
A resource-efficient deep learning framework for low-dose brain PET image reconstruction and analysis
Feb 14, 2022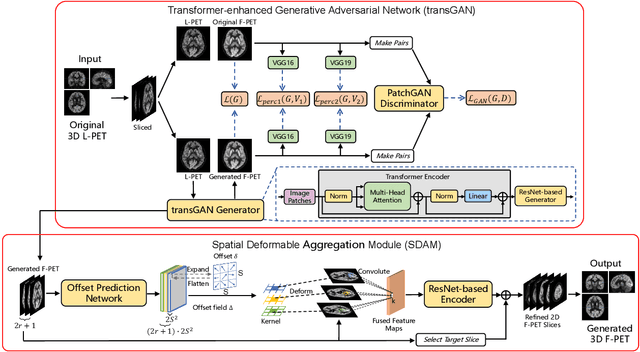
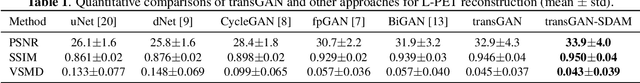
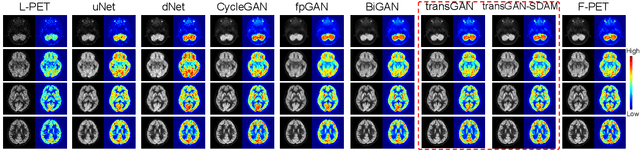
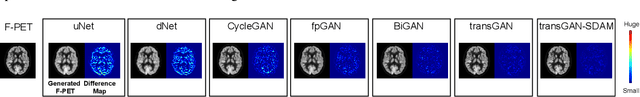
Abstract:18F-fluorodeoxyglucose (18F-FDG) Positron Emission Tomography (PET) imaging usually needs a full-dose radioactive tracer to obtain satisfactory diagnostic results, which raises concerns about the potential health risks of radiation exposure, especially for pediatric patients. Reconstructing the low-dose PET (L-PET) images to the high-quality full-dose PET (F-PET) ones is an effective way that both reduces the radiation exposure and remains diagnostic accuracy. In this paper, we propose a resource-efficient deep learning framework for L-PET reconstruction and analysis, referred to as transGAN-SDAM, to generate F-PET from corresponding L-PET, and quantify the standard uptake value ratios (SUVRs) of these generated F-PET at whole brain. The transGAN-SDAM consists of two modules: a transformer-encoded Generative Adversarial Network (transGAN) and a Spatial Deformable Aggregation Module (SDAM). The transGAN generates higher quality F-PET images, and then the SDAM integrates the spatial information of a sequence of generated F-PET slices to synthesize whole-brain F-PET images. Experimental results demonstrate the superiority and rationality of our approach.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge