Matthias J. Ehrhardt
Department of Mathematical Sciences, University of Bath, Bath, UK
Bilevel Learning via Inexact Stochastic Gradient Descent
Nov 10, 2025Abstract:Bilevel optimization is a central tool in machine learning for high-dimensional hyperparameter tuning. Its applications are vast; for instance, in imaging it can be used for learning data-adaptive regularizers and optimizing forward operators in variational regularization. These problems are large in many ways: a lot of data is usually available to train a large number of parameters, calling for stochastic gradient-based algorithms. However, exact gradients with respect to parameters (so-called hypergradients) are not available, and their precision is usually linearly related to computational cost. Hence, algorithms must solve the problem efficiently without unnecessary precision. The design of such methods is still not fully understood, especially regarding how accuracy requirements and step size schedules affect theoretical guarantees and practical performance. Existing approaches introduce stochasticity at both the upper level (e.g., in sampling or mini-batch estimates) and the lower level (e.g., in solving the inner problem) to improve generalization, but they typically fix the number of lower-level iterations, which conflicts with asymptotic convergence assumptions. In this work, we advance the theory of inexact stochastic bilevel optimization. We prove convergence and establish rates under decaying accuracy and step size schedules, showing that with optimal configurations convergence occurs at an $\mathcal{O}(k^{-1/4})$ rate in expectation. Experiments on image denoising and inpainting with convex ridge regularizers and input-convex networks confirm our analysis: decreasing step sizes improve stability, accuracy scheduling is more critical than step size strategy, and adaptive preconditioning (e.g., Adam) further boosts performance. These results bridge theory and practice, providing convergence guarantees and practical guidance for large-scale imaging problems.
Stable neural networks and connections to continuous dynamical systems
Oct 25, 2025Abstract:The existence of instabilities, for example in the form of adversarial examples, has given rise to a highly active area of research concerning itself with understanding and enhancing the stability of neural networks. We focus on a popular branch within this area which draws on connections to continuous dynamical systems and optimal control, giving a bird's eye view of this area. We identify and describe the fundamental concepts that underlie much of the existing work in this area. Following this, we go into more detail on a specific approach to designing stable neural networks, developing the theoretical background and giving a description of how these networks can be implemented. We provide code that implements the approach that can be adapted and extended by the reader. The code further includes a notebook with a fleshed-out toy example on adversarial robustness of image classification that can be run without heavy requirements on the reader's computer. We finish by discussing this toy example so that the reader can interactively follow along on their computer. This work will be included as a chapter of a book on scientific machine learning, which is currently under revision and aimed at students.
Learning Regularization Functionals for Inverse Problems: A Comparative Study
Oct 02, 2025Abstract:In recent years, a variety of learned regularization frameworks for solving inverse problems in imaging have emerged. These offer flexible modeling together with mathematical insights. The proposed methods differ in their architectural design and training strategies, making direct comparison challenging due to non-modular implementations. We address this gap by collecting and unifying the available code into a common framework. This unified view allows us to systematically compare the approaches and highlight their strengths and limitations, providing valuable insights into their future potential. We also provide concise descriptions of each method, complemented by practical guidelines.
Bilevel Learning with Inexact Stochastic Gradients
Dec 16, 2024Abstract:Bilevel learning has gained prominence in machine learning, inverse problems, and imaging applications, including hyperparameter optimization, learning data-adaptive regularizers, and optimizing forward operators. The large-scale nature of these problems has led to the development of inexact and computationally efficient methods. Existing adaptive methods predominantly rely on deterministic formulations, while stochastic approaches often adopt a doubly-stochastic framework with impractical variance assumptions, enforces a fixed number of lower-level iterations, and requires extensive tuning. In this work, we focus on bilevel learning with strongly convex lower-level problems and a nonconvex sum-of-functions in the upper-level. Stochasticity arises from data sampling in the upper-level which leads to inexact stochastic hypergradients. We establish their connection to state-of-the-art stochastic optimization theory for nonconvex objectives. Furthermore, we prove the convergence of inexact stochastic bilevel optimization under mild assumptions. Our empirical results highlight significant speed-ups and improved generalization in imaging tasks such as image denoising and deblurring in comparison with adaptive deterministic bilevel methods.
An Adaptively Inexact Method for Bilevel Learning Using Primal-Dual Style Differentiation
Dec 09, 2024



Abstract:We consider a bilevel learning framework for learning linear operators. In this framework, the learnable parameters are optimized via a loss function that also depends on the minimizer of a convex optimization problem (denoted lower-level problem). We utilize an iterative algorithm called `piggyback' to compute the gradient of the loss and minimizer of the lower-level problem. Given that the lower-level problem is solved numerically, the loss function and thus its gradient can only be computed inexactly. To estimate the accuracy of the computed hypergradient, we derive an a-posteriori error bound, which provides guides for setting the tolerance for the lower-level problem, as well as the piggyback algorithm. To efficiently solve the upper-level optimization, we also propose an adaptive method for choosing a suitable step-size. To illustrate the proposed method, we consider a few learned regularizer problems, such as training an input-convex neural network.
A Primal-dual algorithm for image reconstruction with ICNNs
Oct 16, 2024Abstract:We address the optimization problem in a data-driven variational reconstruction framework, where the regularizer is parameterized by an input-convex neural network (ICNN). While gradient-based methods are commonly used to solve such problems, they struggle to effectively handle non-smoothness which often leads to slow convergence. Moreover, the nested structure of the neural network complicates the application of standard non-smooth optimization techniques, such as proximal algorithms. To overcome these challenges, we reformulate the problem and eliminate the network's nested structure. By relating this reformulation to epigraphical projections of the activation functions, we transform the problem into a convex optimization problem that can be efficiently solved using a primal-dual algorithm. We also prove that this reformulation is equivalent to the original variational problem. Through experiments on several imaging tasks, we demonstrate that the proposed approach outperforms subgradient methods in terms of both speed and stability.
Accelerated Convergent Motion Compensated Image Reconstruction
Oct 14, 2024


Abstract:Motion correction aims to prevent motion artefacts which may be caused by respiration, heartbeat, or head movements for example. In a preliminary step, the measured data is divided in gates corresponding to motion states, and displacement maps from a reference state to each motion state are estimated. One common technique to perform motion correction is the motion compensated image reconstruction framework, where the displacement maps are integrated into the forward model corresponding to gated data. For standard algorithms, the computational cost per iteration increases linearly with the number of gates. In order to accelerate the reconstruction, we propose the use of a randomized and convergent algorithm whose per iteration computational cost scales constantly with the number of gates. We show improvement on theoretical rates of convergence and observe the predicted speed-up on two synthetic datasets corresponding to rigid and non-rigid motion.
A Guide to Stochastic Optimisation for Large-Scale Inverse Problems
Jun 10, 2024
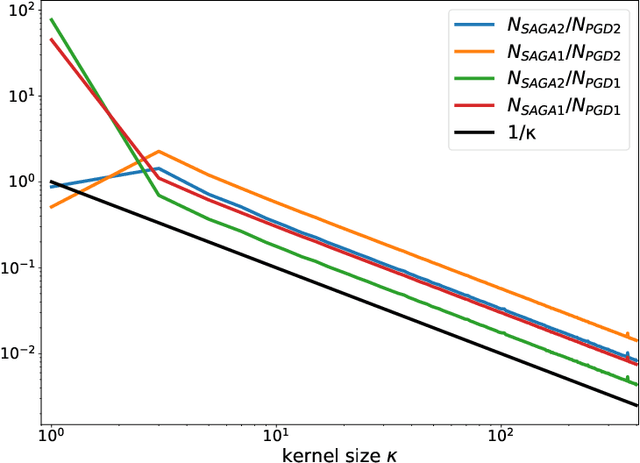

Abstract:Stochastic optimisation algorithms are the de facto standard for machine learning with large amounts of data. Handling only a subset of available data in each optimisation step dramatically reduces the per-iteration computational costs, while still ensuring significant progress towards the solution. Driven by the need to solve large-scale optimisation problems as efficiently as possible, the last decade has witnessed an explosion of research in this area. Leveraging the parallels between machine learning and inverse problems has allowed harnessing the power of this research wave for solving inverse problems. In this survey, we provide a comprehensive account of the state-of-the-art in stochastic optimisation from the viewpoint of inverse problems. We present algorithms with diverse modalities of problem randomisation and discuss the roles of variance reduction, acceleration, higher-order methods, and other algorithmic modifications, and compare theoretical results with practical behaviour. We focus on the potential and the challenges for stochastic optimisation that are unique to inverse imaging problems and are not commonly encountered in machine learning. We conclude the survey with illustrative examples from imaging problems to examine the advantages and disadvantages that this new generation of algorithms bring to the field of inverse problems.
Dynamic Bilevel Learning with Inexact Line Search
Aug 19, 2023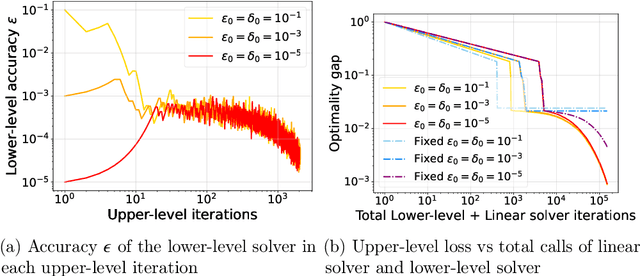
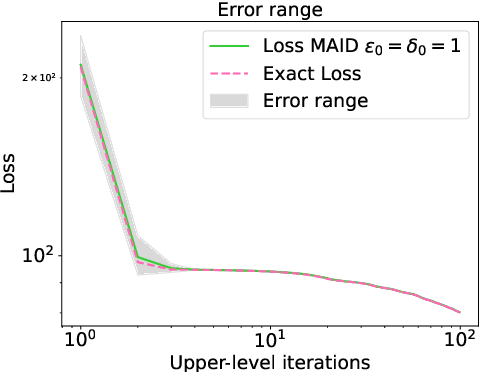
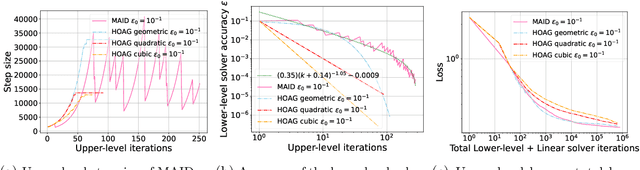
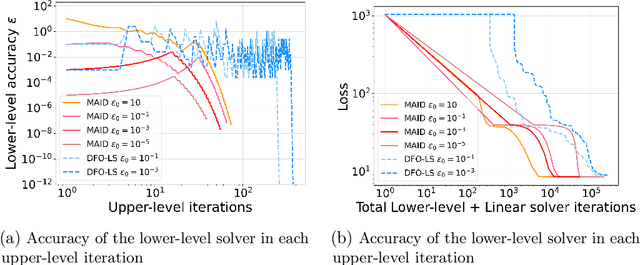
Abstract:In various domains within imaging and data science, particularly when addressing tasks modeled utilizing the variational regularization approach, manually configuring regularization parameters presents a formidable challenge. The difficulty intensifies when employing regularizers involving a large number of hyperparameters. To overcome this challenge, bilevel learning is employed to learn suitable hyperparameters. However, due to the use of numerical solvers, the exact gradient with respect to the hyperparameters is unattainable, necessitating the use of methods relying on approximate gradients. State-of-the-art inexact methods a priori select a decreasing summable sequence of the required accuracy and only assure convergence given a sufficiently small fixed step size. Despite this, challenges persist in determining the Lipschitz constant of the hypergradient and identifying an appropriate fixed step size. Conversely, computing exact function values is not feasible, impeding the use of line search. In this work, we introduce a provably convergent inexact backtracking line search involving inexact function evaluations and hypergradients. We show convergence to a stationary point of the loss with respect to hyperparameters. Additionally, we propose an algorithm to determine the required accuracy dynamically. Our numerical experiments demonstrate the efficiency and feasibility of our approach for hyperparameter estimation in variational regularization problems, alongside its robustness in terms of the initial accuracy and step size choices.
Designing Stable Neural Networks using Convex Analysis and ODEs
Jun 29, 2023Abstract:Motivated by classical work on the numerical integration of ordinary differential equations we present a ResNet-styled neural network architecture that encodes non-expansive (1-Lipschitz) operators, as long as the spectral norms of the weights are appropriately constrained. This is to be contrasted with the ordinary ResNet architecture which, even if the spectral norms of the weights are constrained, has a Lipschitz constant that, in the worst case, grows exponentially with the depth of the network. Further analysis of the proposed architecture shows that the spectral norms of the weights can be further constrained to ensure that the network is an averaged operator, making it a natural candidate for a learned denoiser in Plug-and-Play algorithms. Using a novel adaptive way of enforcing the spectral norm constraints, we show that, even with these constraints, it is possible to train performant networks. The proposed architecture is applied to the problem of adversarially robust image classification, to image denoising, and finally to the inverse problem of deblurring.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge