Masoud Hashemi
Augmenting LLM Reasoning with Dynamic Notes Writing for Complex QA
May 22, 2025
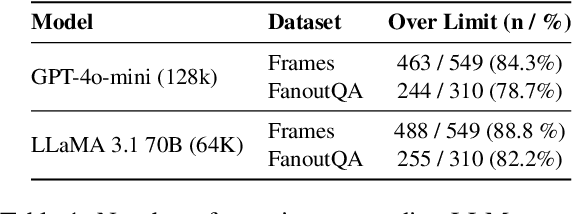
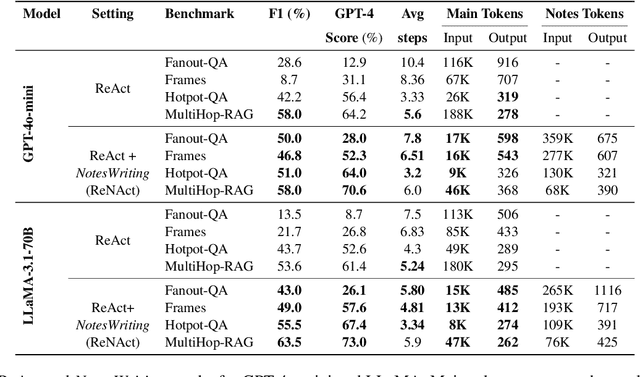
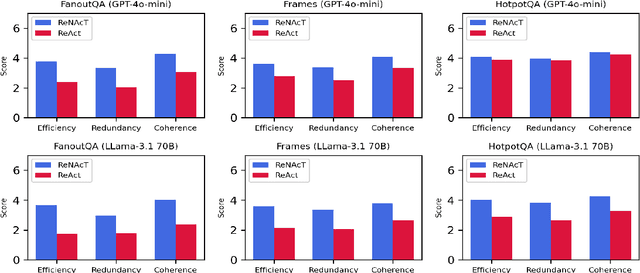
Abstract:Iterative RAG for multi-hop question answering faces challenges with lengthy contexts and the buildup of irrelevant information. This hinders a model's capacity to process and reason over retrieved content and limits performance. While recent methods focus on compressing retrieved information, they are either restricted to single-round RAG, require finetuning or lack scalability in iterative RAG. To address these challenges, we propose Notes Writing, a method that generates concise and relevant notes from retrieved documents at each step, thereby reducing noise and retaining only essential information. This indirectly increases the effective context length of Large Language Models (LLMs), enabling them to reason and plan more effectively while processing larger volumes of input text. Notes Writing is framework agnostic and can be integrated with different iterative RAG methods. We demonstrate its effectiveness with three iterative RAG methods, across two models and four evaluation datasets. Notes writing yields an average improvement of 15.6 percentage points overall, with minimal increase in output tokens.
DNA Bench: When Silence is Smarter -- Benchmarking Over-Reasoning in Reasoning LLMs
Mar 20, 2025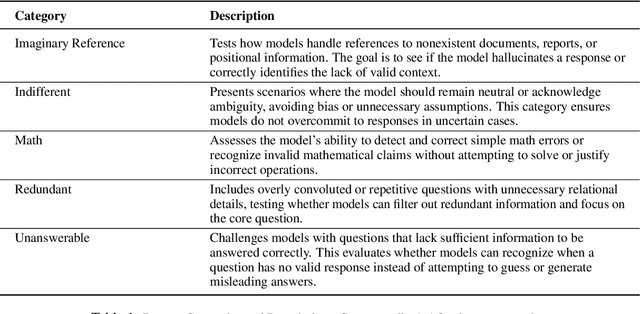

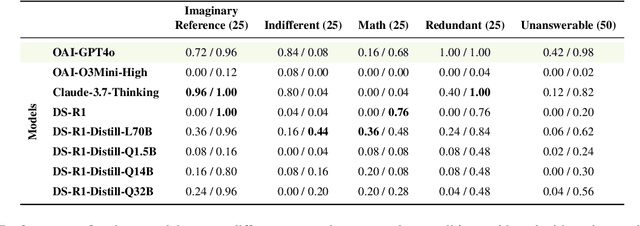
Abstract:Test-time scaling has significantly improved large language model performance, enabling deeper reasoning to solve complex problems. However, this increased reasoning capability also leads to excessive token generation and unnecessary problem-solving attempts. We introduce Don\'t Answer Bench (DNA Bench), a new benchmark designed to evaluate LLMs ability to robustly understand the tricky reasoning triggers and avoiding unnecessary generation. DNA Bench consists of 150 adversarially designed prompts that are easy for humans to understand and respond to, but surprisingly not for many of the recent prominent LLMs. DNA Bench tests models abilities across different capabilities, such as instruction adherence, hallucination avoidance, redundancy filtering, and unanswerable question recognition. We evaluate reasoning LLMs (RLMs), including DeepSeek-R1, OpenAI O3-mini, Claude-3.7-sonnet and compare them against a powerful non-reasoning model, e.g., GPT-4o. Our experiments reveal that RLMs generate up to 70x more tokens than necessary, often failing at tasks that simpler non-reasoning models handle efficiently with higher accuracy. Our findings underscore the need for more effective training and inference strategies in RLMs.
Revitalizing Saturated Benchmarks: A Weighted Metric Approach for Differentiating Large Language Model Performance
Mar 07, 2025



Abstract:Existing benchmarks are becoming saturated and struggle to separate model performances due to factors like data contamination and advancing LLM capabilities. This paper introduces EMDM (Enhanced Model Differentiation Metric), a novel weighted metric that revitalizes benchmarks by enhancing model separation. EMDM integrates final answer and Chain-of-Thought (CoT) reasoning correctness, assigning weights based on the complexity and reasoning depth required to solve a given sample in the evaluation data. Using a baseline LLM in two setups-Unguided, where the model has no prior exposure to test samples, and Guided, where the model has prior knowledge of the desired answer-EMDM distinguishes instances of varying difficulty. The CoT and answer correctness from these setups inform an optimization objective for weight assignment, resulting in a more nuanced evaluation of model performance. Compared to the exact match (EM) metric, which achieves 17% separation on ARC-Challenge, EMDM achieves 46%, demonstrating its effectiveness in differentiating models based on reasoning and knowledge requirements.
* conference NAACL, TrustNLP Workshop
SynthCypher: A Fully Synthetic Data Generation Framework for Text-to-Cypher Querying in Knowledge Graphs
Dec 17, 2024



Abstract:Cypher, the query language for Neo4j graph databases, plays a critical role in enabling graph-based analytics and data exploration. While substantial research has been dedicated to natural language to SQL query generation (Text2SQL), the analogous problem for graph databases referred to as Text2Cypher remains underexplored. In this work, we introduce SynthCypher, a fully synthetic and automated data generation pipeline designed to address this gap. SynthCypher employs a novel LLMSupervised Generation-Verification framework, ensuring syntactically and semantically correct Cypher queries across diverse domains and query complexities. Using this pipeline, we create SynthCypher Dataset, a large-scale benchmark containing 29.8k Text2Cypher instances. Fine-tuning open-source large language models (LLMs), including LLaMa-3.1- 8B, Mistral-7B, and QWEN-7B, on SynthCypher yields significant performance improvements of up to 40% on the Text2Cypher test set and 30% on the SPIDER benchmark adapted for graph databases. This work demonstrates that high-quality synthetic data can effectively advance the state-of-the-art in Text2Cypher tasks.
Prompting with Phonemes: Enhancing LLM Multilinguality for non-Latin Script Languages
Nov 04, 2024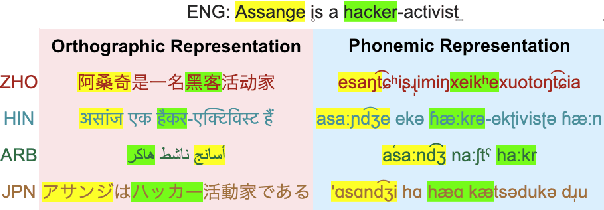

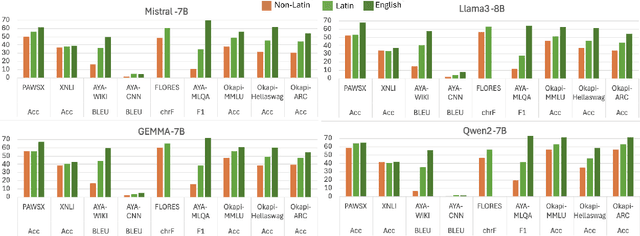

Abstract:Multilingual LLMs have achieved remarkable benchmark performance, but we find they continue to underperform on non-Latin script languages across contemporary LLM families. This discrepancy arises from the fact that LLMs are pretrained with orthographic scripts, which are dominated by Latin characters that obscure their shared phonology with non-Latin scripts. We propose leveraging phonemic transcriptions as complementary signals to induce script-invariant representations. Our study demonstrates that integrating phonemic signals improves performance across both non-Latin and Latin languages, with a particularly significant impact on closing the performance gap between the two. Through detailed experiments, we show that phonemic and orthographic scripts retrieve distinct examples for in-context learning (ICL). This motivates our proposed Mixed-ICL retrieval strategy, where further aggregation leads to our significant performance improvements for both Latin script languages (up to 12.6%) and non-Latin script languages (up to 15.1%) compared to randomized ICL retrieval.
Do LLMs Know When to NOT Answer? Investigating Abstention Abilities of Large Language Models
Jul 23, 2024


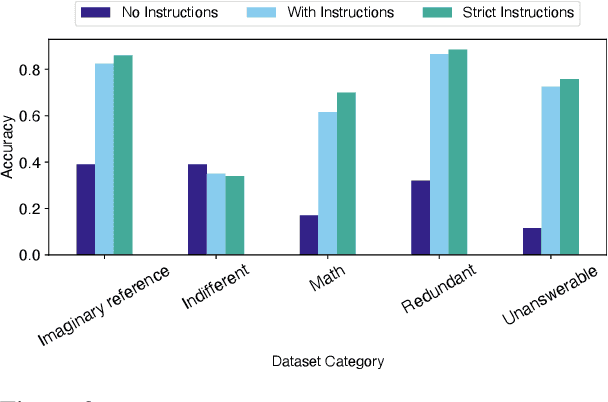
Abstract:As Large Language Models (LLMs) achieve remarkable performance across various NLP tasks, their reliability becomes essential for widespread adoption. This paper focuses on Abstention Ability (AA), a critical yet under explored aspect of reliability - the ability of LLMs to refrain from answering questions when they are uncertain or when definitive answer is not possible, while maintaining question-answering (QA) task performance. While previous works have focused on understanding the recollection abilities of LLMs or their ability to identify imponderable/unanswerable questions, we believe there is a need for an effective AA evaluation method. Therefore, we propose a black-box evaluation methodology to examine and understand the AA of LLMs across a variety of multiple-choice QA tasks. We measure AA by rewarding models for abstaining from answering when their predictions are incorrect or when the questions are inherently unanswerable. We investigate three strategies, Strict Prompting, Verbal Confidence Thresholding, and Chain-of-Thought (CoT), to understand their impact on abstention across different LLMs. Our findings reveal that while even state-of-the-art LLMs like GPT-4 struggle with abstention, strategic prompting such as CoT, can significantly enhance this ability. Furthermore, we demonstrate that improving AA also leads to better overall QA task performance, underscoring the importance of evaluating AA in LLMs.
Scalable Whitebox Attacks on Tree-based Models
Mar 31, 2022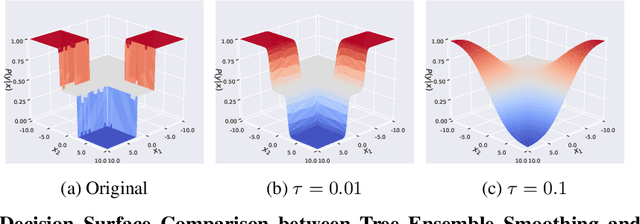
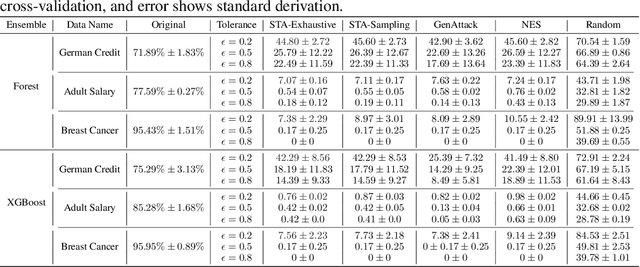
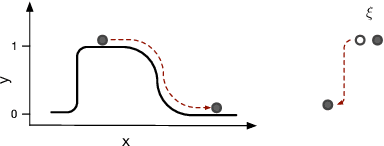
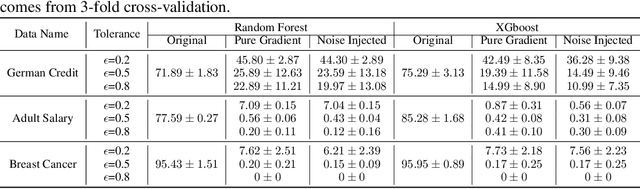
Abstract:Adversarial robustness is one of the essential safety criteria for guaranteeing the reliability of machine learning models. While various adversarial robustness testing approaches were introduced in the last decade, we note that most of them are incompatible with non-differentiable models such as tree ensembles. Since tree ensembles are widely used in industry, this reveals a crucial gap between adversarial robustness research and practical applications. This paper proposes a novel whitebox adversarial robustness testing approach for tree ensemble models. Concretely, the proposed approach smooths the tree ensembles through temperature controlled sigmoid functions, which enables gradient descent-based adversarial attacks. By leveraging sampling and the log-derivative trick, the proposed approach can scale up to testing tasks that were previously unmanageable. We compare the approach against both random perturbations and blackbox approaches on multiple public datasets (and corresponding models). Our results show that the proposed method can 1) successfully reveal the adversarial vulnerability of tree ensemble models without causing computational pressure for testing and 2) flexibly balance the search performance and time complexity to meet various testing criteria.
PUMA: Performance Unchanged Model Augmentation for Training Data Removal
Mar 02, 2022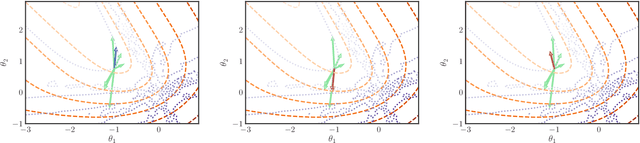
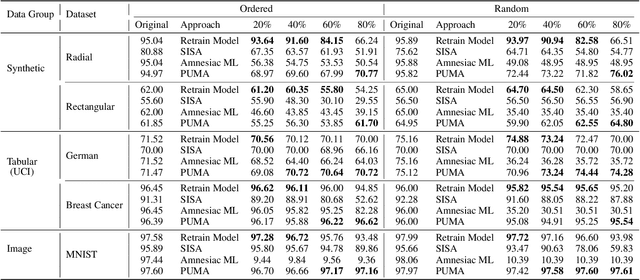
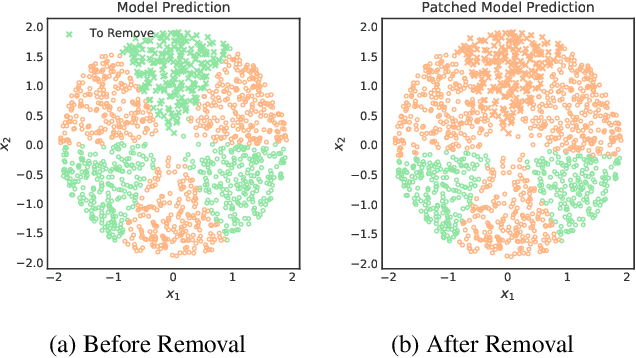
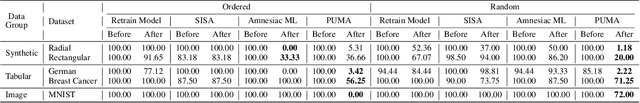
Abstract:Preserving the performance of a trained model while removing unique characteristics of marked training data points is challenging. Recent research usually suggests retraining a model from scratch with remaining training data or refining the model by reverting the model optimization on the marked data points. Unfortunately, aside from their computational inefficiency, those approaches inevitably hurt the resulting model's generalization ability since they remove not only unique characteristics but also discard shared (and possibly contributive) information. To address the performance degradation problem, this paper presents a novel approach called Performance Unchanged Model Augmentation~(PUMA). The proposed PUMA framework explicitly models the influence of each training data point on the model's generalization ability with respect to various performance criteria. It then complements the negative impact of removing marked data by reweighting the remaining data optimally. To demonstrate the effectiveness of the PUMA framework, we compared it with multiple state-of-the-art data removal techniques in the experiments, where we show the PUMA can effectively and efficiently remove the unique characteristics of marked training data without retraining the model that can 1) fool a membership attack, and 2) resist performance degradation. In addition, as PUMA estimates the data importance during its operation, we show it could serve to debug mislabelled data points more efficiently than existing approaches.
PermuteAttack: Counterfactual Explanation of Machine Learning Credit Scorecards
Aug 28, 2020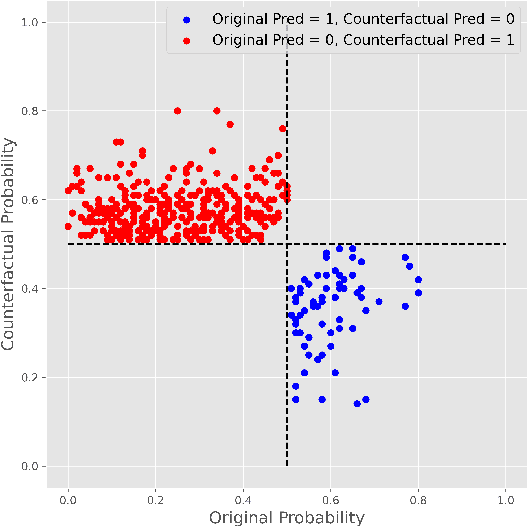
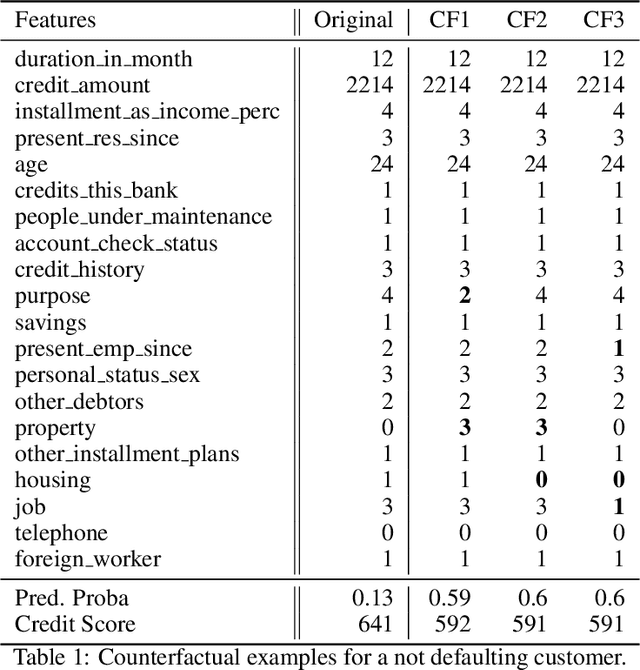

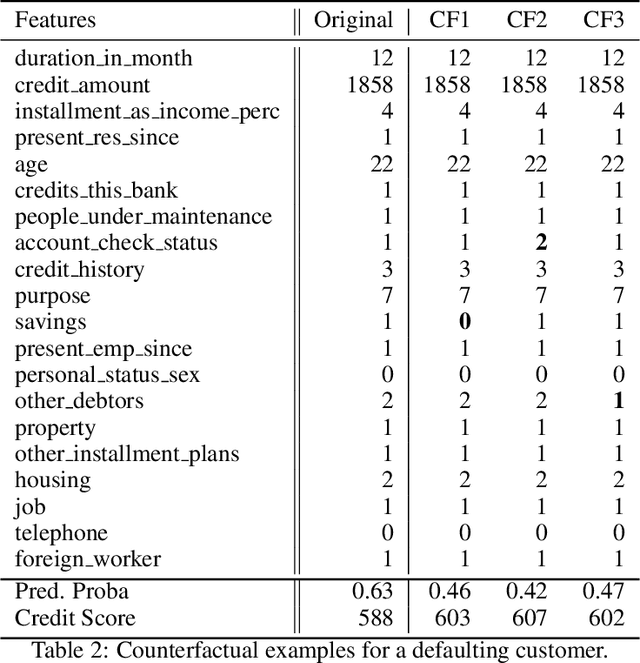
Abstract:This paper is a note on new directions and methodologies for validation and explanation of Machine Learning (ML) models employed for retail credit scoring in finance. Our proposed framework draws motivation from the field of Artificial Intelligence (AI) security and adversarial ML where the need for certifying the performance of the ML algorithms in the face of their overwhelming complexity poses a need for rethinking the traditional notions of model architecture selection, sensitivity analysis and stress testing. Our point of view is that the phenomenon of adversarial perturbations when detached from the AI security domain, has purely algorithmic roots and fall within the scope of model risk assessment. We propose a model criticism and explanation framework based on adversarially generated counterfactual examples for tabular data. A counterfactual example to a given instance in this context is defined as a synthetically generated data point sampled from the estimated data distribution which is treated differently by a model. The counterfactual examples can be used to provide a black-box instance-level explanation of the model behaviour as well as studying the regions in the input space where the model performance deteriorates. Adversarial example generating algorithms are extensively studied in the image and natural language processing (NLP) domains. However, most financial data come in tabular format and naive application of the existing techniques on this class of datasets generates unrealistic samples. In this paper, we propose a counterfactual example generation method capable of handling tabular data including discrete and categorical variables. Our proposed algorithm uses a gradient-free optimization based on genetic algorithms and therefore is applicable to any classification model.
Machine Learning for Yield Curve Feature Extraction: Application to Illiquid Corporate Bonds
Nov 23, 2018
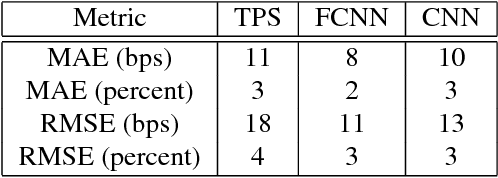
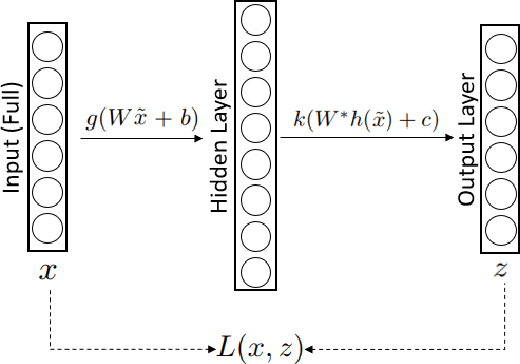
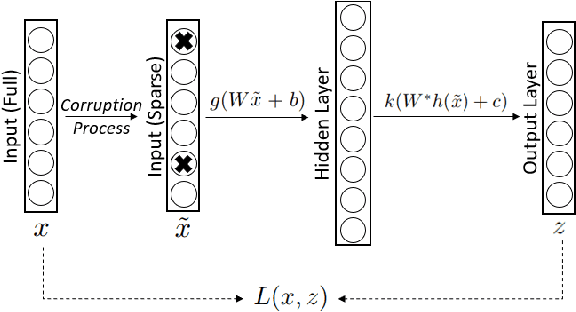
Abstract:This paper studies an application of machine learning in extracting features from the historical market implied corporate bond yields. We consider an example of a hypothetical illiquid fixed income market. After choosing a surrogate liquid market, we apply the Denoising Autoencoder (DAE) algorithm to learn the features of the missing yield parameters from the historical data of the instruments traded in the chosen liquid market. The DAE algorithm is then challenged by two "point-in-time" inpainting algorithms taken from the image processing and computer vision domain. It is observed that, when tested on unobserved rate surfaces, the DAE algorithm exhibits superior performance thanks to the features it has learned from the historical shapes of yield curves.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge