Gavin Ding
Scalable Whitebox Attacks on Tree-based Models
Mar 31, 2022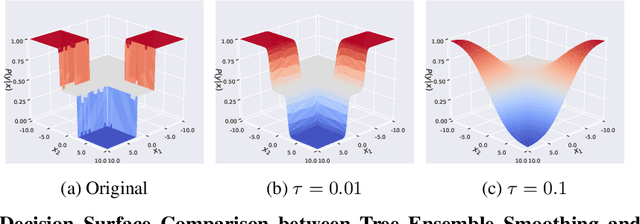
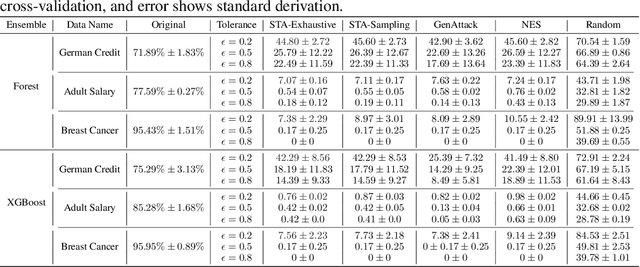
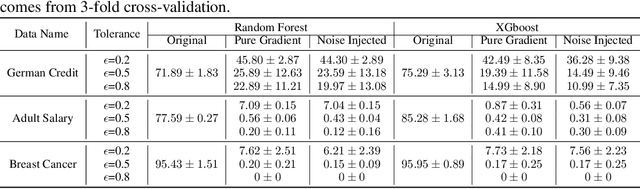
Abstract:Adversarial robustness is one of the essential safety criteria for guaranteeing the reliability of machine learning models. While various adversarial robustness testing approaches were introduced in the last decade, we note that most of them are incompatible with non-differentiable models such as tree ensembles. Since tree ensembles are widely used in industry, this reveals a crucial gap between adversarial robustness research and practical applications. This paper proposes a novel whitebox adversarial robustness testing approach for tree ensemble models. Concretely, the proposed approach smooths the tree ensembles through temperature controlled sigmoid functions, which enables gradient descent-based adversarial attacks. By leveraging sampling and the log-derivative trick, the proposed approach can scale up to testing tasks that were previously unmanageable. We compare the approach against both random perturbations and blackbox approaches on multiple public datasets (and corresponding models). Our results show that the proposed method can 1) successfully reveal the adversarial vulnerability of tree ensemble models without causing computational pressure for testing and 2) flexibly balance the search performance and time complexity to meet various testing criteria.
Retinal Fluid Segmentation and Detection in Optical Coherence Tomography Images using Fully Convolutional Neural Network
Oct 13, 2017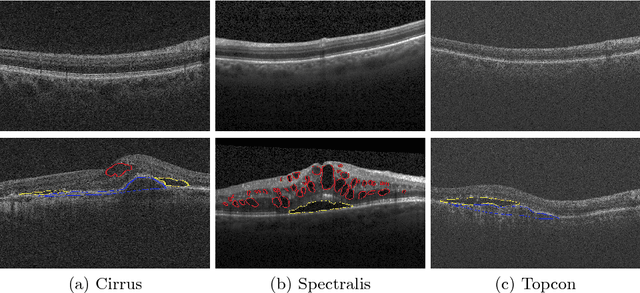

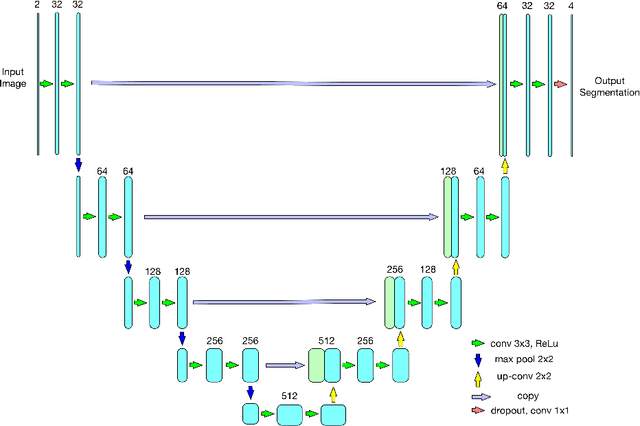
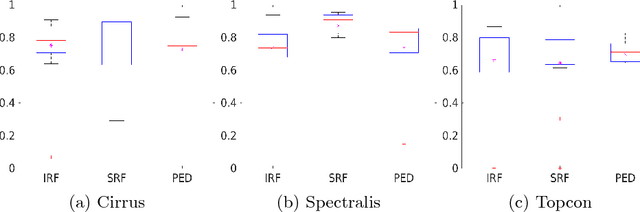
Abstract:As a non-invasive imaging modality, optical coherence tomography (OCT) can provide micrometer-resolution 3D images of retinal structures. Therefore it is commonly used in the diagnosis of retinal diseases associated with edema in and under the retinal layers. In this paper, a new framework is proposed for the task of fluid segmentation and detection in retinal OCT images. Based on the raw images and layers segmented by a graph-cut algorithm, a fully convolutional neural network was trained to recognize and label the fluid pixels. Random forest classification was performed on the segmented fluid regions to detect and reject the falsely labeled fluid regions. The leave-one-out cross validation experiments on the RETOUCH database show that our method performs well in both segmentation (mean Dice: 0.7317) and detection (mean AUC: 0.985) tasks.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge