Maryam Badar
A Review of the Role of Causality in Developing Trustworthy AI Systems
Feb 14, 2023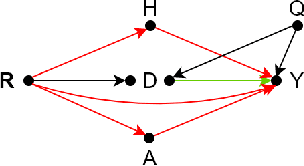
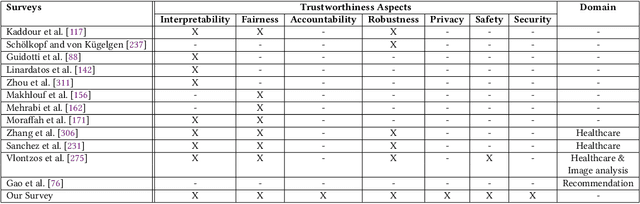
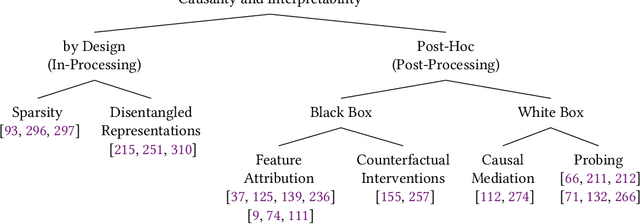
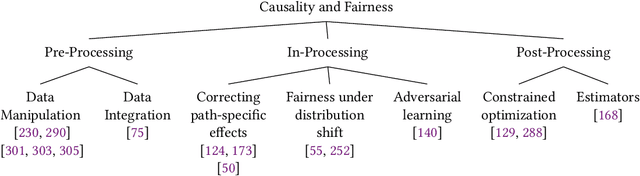
Abstract:State-of-the-art AI models largely lack an understanding of the cause-effect relationship that governs human understanding of the real world. Consequently, these models do not generalize to unseen data, often produce unfair results, and are difficult to interpret. This has led to efforts to improve the trustworthiness aspects of AI models. Recently, causal modeling and inference methods have emerged as powerful tools. This review aims to provide the reader with an overview of causal methods that have been developed to improve the trustworthiness of AI models. We hope that our contribution will motivate future research on causality-based solutions for trustworthy AI.
Discrimination and Class Imbalance Aware Online Naive Bayes
Nov 09, 2022



Abstract:Fairness-aware mining of massive data streams is a growing and challenging concern in the contemporary domain of machine learning. Many stream learning algorithms are used to replace humans at critical decision-making points e.g., hiring staff, assessing credit risk, etc. This calls for handling massive incoming information with minimum response delay while ensuring fair and high quality decisions. Recent discrimination-aware learning methods are optimized based on overall accuracy. However, the overall accuracy is biased in favor of the majority class; therefore, state-of-the-art methods mainly diminish discrimination by partially or completely ignoring the minority class. In this context, we propose a novel adaptation of Na\"ive Bayes to mitigate discrimination embedded in the streams while maintaining high predictive performance for both the majority and minority classes. Our proposed algorithm is simple, fast, and attains multi-objective optimization goals. To handle class imbalance and concept drifts, a dynamic instance weighting module is proposed, which gives more importance to recent instances and less importance to obsolete instances based on their membership in minority or majority class. We conducted experiments on a range of streaming and static datasets and deduced that our proposed methodology outperforms existing state-of-the-art fairness-aware methods in terms of both discrimination score and balanced accuracy.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge