Mario di Bernardo
ROPE: A Novel Method for Real-Time Phase Estimation of Complex Biological Rhythms
Sep 05, 2025Abstract:Accurate phase estimation -- the process of assigning phase values between $0$ and $2\pi$ to repetitive or periodic signals -- is a cornerstone in the analysis of oscillatory signals across diverse fields, from neuroscience to robotics, where it is fundamental, e.g., to understanding coordination in neural networks, cardiorespiratory coupling, and human-robot interaction. However, existing methods are often limited to offline processing and/or constrained to one-dimensional signals. In this paper, we introduce ROPE, which, to the best of our knowledge, is the first phase-estimation algorithm capable of (i) handling signals of arbitrary dimension and (ii) operating in real-time, with minimal error. ROPE identifies repetitions within the signal to segment it into (pseudo-)periods and assigns phase values by performing efficient, tractable searches over previous signal segments. We extensively validate the algorithm on a variety of signal types, including trajectories from chaotic dynamical systems, human motion-capture data, and electrocardiographic recordings. Our results demonstrate that ROPE is robust against noise and signal drift, and achieves significantly superior performance compared to state-of-the-art phase estimation methods. This advancement enables real-time analysis of complex biological rhythms, opening new pathways, for example, for early diagnosis of pathological rhythm disruptions and developing rhythm-based therapeutic interventions in neurological and cardiovascular disorders.
Hierarchical Policy-Gradient Reinforcement Learning for Multi-Agent Shepherding Control of Non-Cohesive Targets
Apr 03, 2025Abstract:We propose a decentralized reinforcement learning solution for multi-agent shepherding of non-cohesive targets using policy-gradient methods. Our architecture integrates target-selection with target-driving through Proximal Policy Optimization, overcoming discrete-action constraints of previous Deep Q-Network approaches and enabling smoother agent trajectories. This model-free framework effectively solves the shepherding problem without prior dynamics knowledge. Experiments demonstrate our method's effectiveness and scalability with increased target numbers and limited sensing capabilities.
GoRINNs: Godunov-Riemann Informed Neural Networks for Learning Hyperbolic Conservation Laws
Oct 31, 2024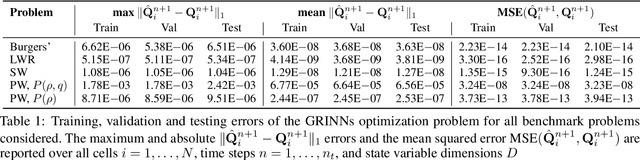
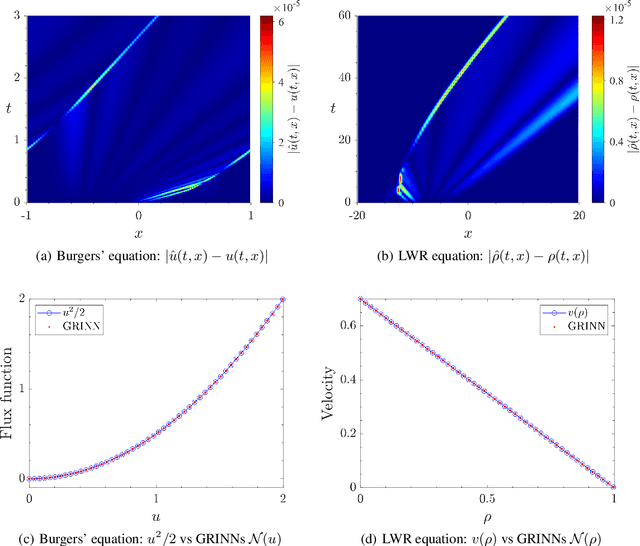
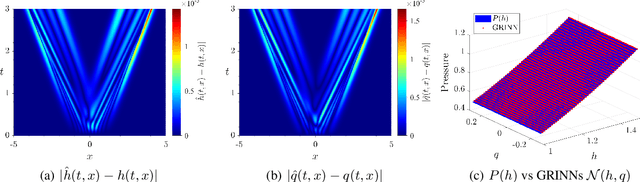
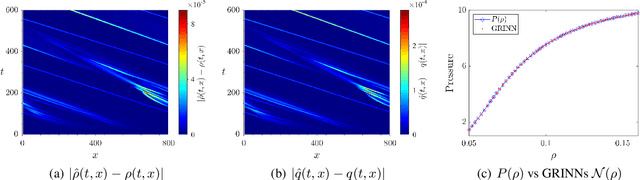
Abstract:We present GoRINNs: numerical analysis-informed neural networks for the solution of inverse problems of non-linear systems of conservation laws. GoRINNs are based on high-resolution Godunov schemes for the solution of the Riemann problem in hyperbolic Partial Differential Equations (PDEs). In contrast to other existing machine learning methods that learn the numerical fluxes of conservative Finite Volume methods, GoRINNs learn the physical flux function per se. Due to their structure, GoRINNs provide interpretable, conservative schemes, that learn the solution operator on the basis of approximate Riemann solvers that satisfy the Rankine-Hugoniot condition. The performance of GoRINNs is assessed via four benchmark problems, namely the Burgers', the Shallow Water, the Lighthill-Whitham-Richards and the Payne-Whitham traffic flow models. The solution profiles of these PDEs exhibit shock waves, rarefactions and/or contact discontinuities at finite times. We demonstrate that GoRINNs provide a very high accuracy both in the smooth and discontinuous regions.
GRINNs: Godunov-Riemann Informed Neural Networks for Learning Hyperbolic Conservation Laws
Oct 29, 2024



Abstract:We present GRINNs: numerical analysis-informed neural networks for the solution of inverse problems of non-linear systems of conservation laws. GRINNs are based on high-resolution Godunov schemes for the solution of the Riemann problem in hyperbolic Partial Differential Equations (PDEs). In contrast to other existing machine learning methods that learn the numerical fluxes of conservative Finite Volume methods, GRINNs learn the physical flux function per se. Due to their structure, GRINNs provide interpretable, conservative schemes, that learn the solution operator on the basis of approximate Riemann solvers that satisfy the Rankine-Hugoniot condition. The performance of GRINNs is assessed via four benchmark problems, namely the Burgers', the Shallow Water, the Lighthill-Whitham-Richards and the Payne-Whitham traffic flow models. The solution profiles of these PDEs exhibit shock waves, rarefactions and/or contact discontinuities at finite times. We demonstrate that GRINNs provide a very high accuracy both in the smooth and discontinuous regions.
Data-driven architecture to encode information in the kinematics of robots and artificial avatars
Mar 11, 2024



Abstract:We present a data-driven control architecture for modifying the kinematics of robots and artificial avatars to encode specific information such as the presence or not of an emotion in the movements of an avatar or robot driven by a human operator. We validate our approach on an experimental dataset obtained during the reach-to-grasp phase of a pick-and-place task.
In vivo learning-based control of microbial populations density in bioreactors
Dec 15, 2023



Abstract:A key problem toward the use of microorganisms as bio-factories is reaching and maintaining cellular communities at a desired density and composition so that they can efficiently convert their biomass into useful compounds. Promising technological platforms for the real time, scalable control of cellular density are bioreactors. In this work, we developed a learning-based strategy to expand the toolbox of available control algorithms capable of regulating the density of a \textit{single} bacterial population in bioreactors. Specifically, we used a sim-to-real paradigm, where a simple mathematical model, calibrated using a few data, was adopted to generate synthetic data for the training of the controller. The resulting policy was then exhaustively tested in vivo using a low-cost bioreactor known as Chi.Bio, assessing performance and robustness. In addition, we compared the performance with more traditional controllers (namely, a PI and an MPC), confirming that the learning-based controller exhibits similar performance in vivo. Our work showcases the viability of learning-based strategies for the control of cellular density in bioreactors, making a step forward toward their use for the control of the composition of microbial consortia.
Guaranteeing Control Requirements via Reward Shaping in Reinforcement Learning
Nov 16, 2023



Abstract:In addressing control problems such as regulation and tracking through reinforcement learning, it is often required to guarantee that the acquired policy meets essential performance and stability criteria such as a desired settling time and steady-state error prior to deployment. Motivated by this necessity, we present a set of results and a systematic reward shaping procedure that (i) ensures the optimal policy generates trajectories that align with specified control requirements and (ii) allows to assess whether any given policy satisfies them. We validate our approach through comprehensive numerical experiments conducted in two representative environments from OpenAI Gym: the Inverted Pendulum swing-up problem and the Lunar Lander. Utilizing both tabular and deep reinforcement learning methods, our experiments consistently affirm the efficacy of our proposed framework, highlighting its effectiveness in ensuring policy adherence to the prescribed control requirements.
Hybrid Platform for Swarm Robotics: Experiments and High-Dimensional Continuification Control
Oct 02, 2023



Abstract:A significant challenge in control theory and technology is to devise agile and less resource-intensive experiments for evaluating the performance and feasibility of control algorithms for the collective coordination of large-scale complex systems. Many new methodologies are based on macroscopic representations of the emerging system behavior, and can be easily validated only through numerical simulations, because of the inherent hurdle of developing full scale experimental platforms. In this paper, we introduce a novel hybrid set-up for testing swarm robotics techniques, focusing on the collective motion of robotic swarms. This hybrid apparatus combines both real differential drive robots and virtual agents to create a heterogeneous swarm of tunable size. We validate the methodology by extending to higher dimensions, and investigating experimentally, continuification-based control methods for swarms. Our study demonstrates the versatility and effectiveness of the platform for conducting large-scale swarm robotics experiments. Also, it contributes new theoretical insights into control algorithms exploiting continuification approaches.
CT-DQN: Control-Tutored Deep Reinforcement Learning
Dec 02, 2022Abstract:One of the major challenges in Deep Reinforcement Learning for control is the need for extensive training to learn the policy. Motivated by this, we present the design of the Control-Tutored Deep Q-Networks (CT-DQN) algorithm, a Deep Reinforcement Learning algorithm that leverages a control tutor, i.e., an exogenous control law, to reduce learning time. The tutor can be designed using an approximate model of the system, without any assumption about the knowledge of the system's dynamics. There is no expectation that it will be able to achieve the control objective if used stand-alone. During learning, the tutor occasionally suggests an action, thus partially guiding exploration. We validate our approach on three scenarios from OpenAI Gym: the inverted pendulum, lunar lander, and car racing. We demonstrate that CT-DQN is able to achieve better or equivalent data efficiency with respect to the classic function approximation solutions.
Predicting and Understanding Human Action Decisions during Skillful Joint-Action via Machine Learning and Explainable-AI
Jun 06, 2022



Abstract:This study uses supervised machine learning (SML) and explainable artificial intelligence (AI) to model, predict and understand human decision-making during skillful joint-action. Long short-term memory networks were trained to predict the target selection decisions of expert and novice actors completing a dyadic herding task. Results revealed that the trained models were expertise specific and could not only accurately predict the target selection decisions of expert and novice herders but could do so at timescales that preceded an actor's conscious intent. To understand what differentiated the target selection decisions of expert and novice actors, we then employed the explainable-AI technique, SHapley Additive exPlanation, to identify the importance of informational features (variables) on model predictions. This analysis revealed that experts were more influenced by information about the state of their co-herders compared to novices. The utility of employing SML and explainable-AI techniques for investigating human decision-making is discussed.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge