Marc-Antoine Lavoie
CLIP Is Shortsighted: Paying Attention Beyond the First Sentence
Feb 25, 2026Abstract:CLIP models learn transferable multi-modal features via image-text contrastive learning on internet-scale data. They are widely used in zero-shot classification, multi-modal retrieval, text-to-image diffusion, and as image encoders in large vision-language models. However, CLIP's pretraining is dominated by images paired with short captions, biasing the model toward encoding simple descriptions of salient objects and leading to coarse alignment on complex scenes and dense descriptions. While recent work mitigates this by fine-tuning on small-scale long-caption datasets, we identify an important common bias: both human- and LLM-generated long captions typically begin with a one-sentence summary followed by a detailed description. We show that this acts as a shortcut during training, concentrating attention on the opening sentence and early tokens and weakening alignment over the rest of the caption. To resolve this, we introduce DeBias-CLIP, which removes the summary sentence during training and applies sentence sub-sampling and text token padding to distribute supervision across all token positions. DeBias-CLIP achieves state-of-the-art long-text retrieval, improves short-text retrieval, and is less sensitive to sentence order permutations. It is a drop-in replacement for Long-CLIP with no additional trainable parameters.
Deployable and Generalizable Motion Prediction: Taxonomy, Open Challenges and Future Directions
May 14, 2025



Abstract:Motion prediction, the anticipation of future agent states or scene evolution, is rooted in human cognition, bridging perception and decision-making. It enables intelligent systems, such as robots and self-driving cars, to act safely in dynamic, human-involved environments, and informs broader time-series reasoning challenges. With advances in methods, representations, and datasets, the field has seen rapid progress, reflected in quickly evolving benchmark results. Yet, when state-of-the-art methods are deployed in the real world, they often struggle to generalize to open-world conditions and fall short of deployment standards. This reveals a gap between research benchmarks, which are often idealized or ill-posed, and real-world complexity. To address this gap, this survey revisits the generalization and deployability of motion prediction models, with an emphasis on the applications of robotics, autonomous driving, and human motion. We first offer a comprehensive taxonomy of motion prediction methods, covering representations, modeling strategies, application domains, and evaluation protocols. We then study two key challenges: (1) how to push motion prediction models to be deployable to realistic deployment standards, where motion prediction does not act in a vacuum, but functions as one module of closed-loop autonomy stacks - it takes input from the localization and perception, and informs downstream planning and control. 2) how to generalize motion prediction models from limited seen scenarios/datasets to the open-world settings. Throughout the paper, we highlight critical open challenges to guide future work, aiming to recalibrate the community's efforts, fostering progress that is not only measurable but also meaningful for real-world applications.
Large Self-Supervised Models Bridge the Gap in Domain Adaptive Object Detection
Mar 29, 2025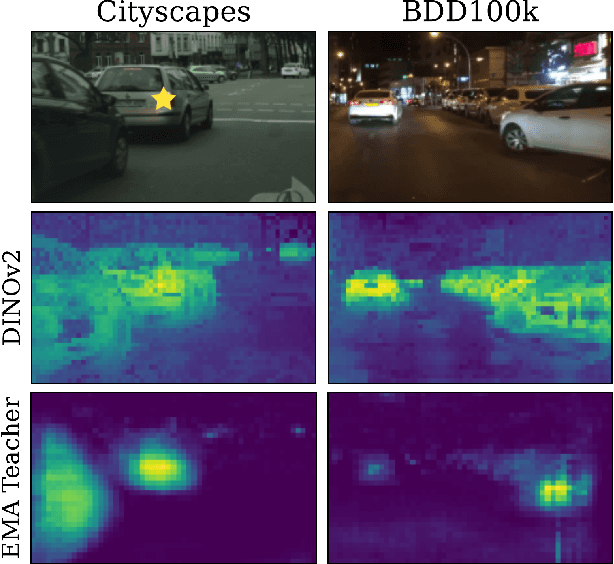
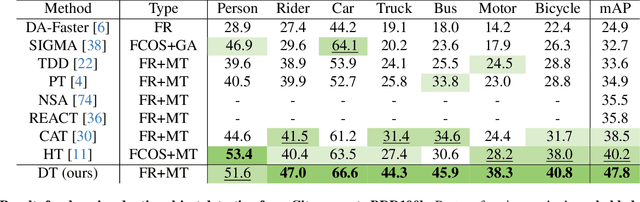
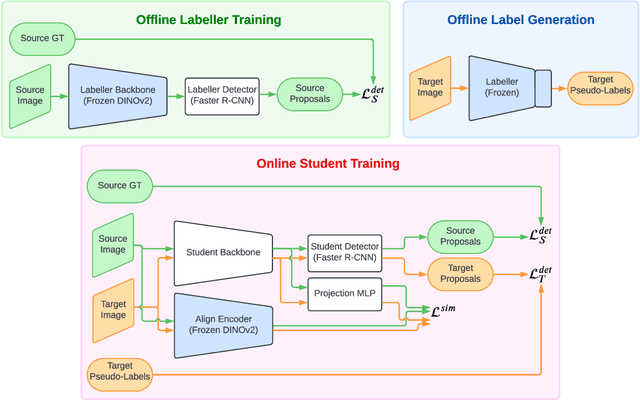

Abstract:The current state-of-the-art methods in domain adaptive object detection (DAOD) use Mean Teacher self-labelling, where a teacher model, directly derived as an exponential moving average of the student model, is used to generate labels on the target domain which are then used to improve both models in a positive loop. This couples learning and generating labels on the target domain, and other recent works also leverage the generated labels to add additional domain alignment losses. We believe this coupling is brittle and excessively constrained: there is no guarantee that a student trained only on source data can generate accurate target domain labels and initiate the positive feedback loop, and much better target domain labels can likely be generated by using a large pretrained network that has been exposed to much more data. Vision foundational models are exactly such models, and they have shown impressive task generalization capabilities even when frozen. We want to leverage these models for DAOD and introduce DINO Teacher, which consists of two components. First, we train a new labeller on source data only using a large frozen DINOv2 backbone and show it generates more accurate labels than Mean Teacher. Next, we align the student's source and target image patch features with those from a DINO encoder, driving source and target representations closer to the generalizable DINO representation. We obtain state-of-the-art performance on multiple DAOD datasets. Code available at https://github.com/TRAILab/DINO_Teacher
Feature Density Estimation for Out-of-Distribution Detection via Normalizing Flows
Feb 09, 2024

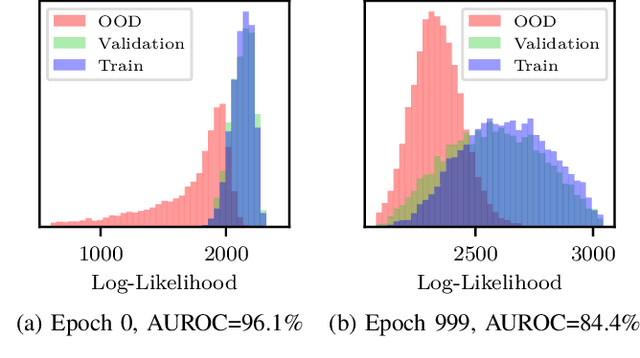

Abstract:Out-of-distribution (OOD) detection is a critical task for safe deployment of learning systems in the open world setting. In this work, we investigate the use of feature density estimation via normalizing flows for OOD detection and present a fully unsupervised approach which requires no exposure to OOD data, avoiding researcher bias in OOD sample selection. This is a post-hoc method which can be applied to any pretrained model, and involves training a lightweight auxiliary normalizing flow model to perform the out-of-distribution detection via density thresholding. Experiments on OOD detection in image classification show strong results for far-OOD data detection with only a single epoch of flow training, including 98.2% AUROC for ImageNet-1k vs. Textures, which exceeds the state of the art by 7.8%. We additionally explore the connection between the feature space distribution of the pretrained model and the performance of our method. Finally, we provide insights into training pitfalls that have plagued normalizing flows for use in OOD detection.
Class Instance Balanced Learning for Long-Tailed Classification
Jul 11, 2023Abstract:The long-tailed image classification task remains important in the development of deep neural networks as it explicitly deals with large imbalances in the class frequencies of the training data. While uncommon in engineered datasets, this imbalance is almost always present in real-world data. Previous approaches have shown that combining cross-entropy and contrastive learning can improve performance on the long-tailed task, but they do not explore the tradeoff between head and tail classes. We propose a novel class instance balanced loss (CIBL), which reweights the relative contributions of a cross-entropy and a contrastive loss as a function of the frequency of class instances in the training batch. This balancing favours the contrastive loss for more common classes, leading to a learned classifier with a more balanced performance across all class frequencies. Furthermore, increasing the relative weight on the contrastive head shifts performance from common (head) to rare (tail) classes, allowing the user to skew the performance towards these classes if desired. We also show that changing the linear classifier head with a cosine classifier yields a network that can be trained to similar performance in substantially fewer epochs. We obtain competitive results on both CIFAR-100-LT and ImageNet-LT.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge