Lun Zhang
Multi-Objective Communication Optimization for Temporal Continuity in Dynamic Vehicular Networks
Nov 30, 2024Abstract:Vehicular Ad-hoc Networks (VANETs) operate in highly dynamic environments characterized by high mobility, time-varying channel conditions, and frequent network disruptions. Addressing these challenges, this paper presents a novel temporal-aware multi-objective robust optimization framework, which for the first time formally incorporates temporal continuity into the optimization of dynamic multi-hop VANETs. The proposed framework simultaneously optimizes communication delay, throughput, and reliability, ensuring stable and consistent communication paths under rapidly changing conditions. A robust optimization model is formulated to mitigate performance degradation caused by uncertainties in vehicular density and channel fluctuations. To solve the optimization problem, an enhanced Non-dominated Sorting Genetic Algorithm II (NSGA-II) is developed, integrating dynamic encoding, elite inheritance, and adaptive constraint handling to efficiently balance trade-offs among conflicting objectives. Simulation results demonstrate that the proposed framework achieves significant improvements in reliability, delay reduction, and throughput enhancement, while temporal continuity effectively stabilizes communication paths over time. This work provides a pioneering and comprehensive solution for optimizing VANET communication, offering critical insights for robust and efficient strategies in intelligent transportation systems.
Adaptive Genetic Selection based Pinning Control with Asymmetric Coupling for Multi-Network Heterogeneous Vehicular Systems
Nov 05, 2024

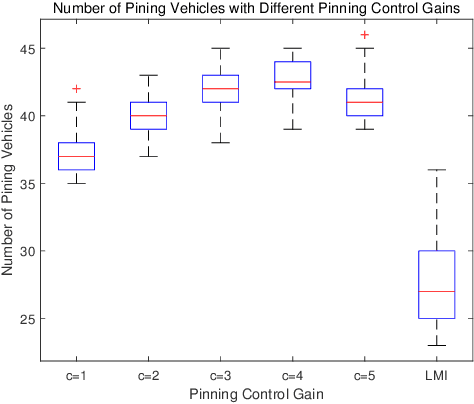
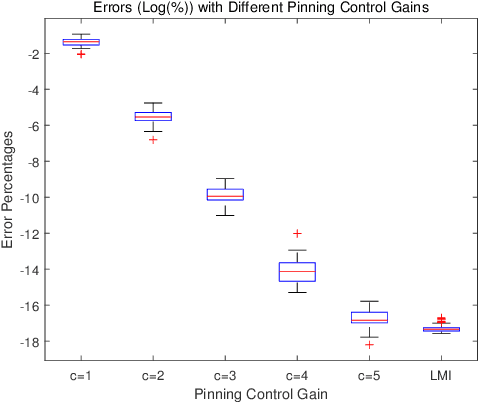
Abstract:To alleviate computational load on RSUs and cloud platforms, reduce communication bandwidth requirements, and provide a more stable vehicular network service, this paper proposes an optimized pinning control approach for heterogeneous multi-network vehicular ad-hoc networks (VANETs). In such networks, vehicles participate in multiple task-specific networks with asymmetric coupling and dynamic topologies. We first establish a rigorous theoretical foundation by proving the stability of pinning control strategies under both single and multi-network conditions, deriving sufficient stability conditions using Lyapunov theory and linear matrix inequalities (LMIs). Building on this theoretical groundwork, we propose an adaptive genetic algorithm tailored to select optimal pinning nodes, effectively balancing LMI constraints while prioritizing overlapping nodes to enhance control efficiency. Extensive simulations across various network scales demonstrate that our approach achieves rapid consensus with a reduced number of control nodes, particularly when leveraging network overlaps. This work provides a comprehensive solution for efficient control node selection in complex vehicular networks, offering practical implications for deploying large-scale intelligent transportation systems.
URLBERT:A Contrastive and Adversarial Pre-trained Model for URL Classification
Feb 18, 2024Abstract:URLs play a crucial role in understanding and categorizing web content, particularly in tasks related to security control and online recommendations. While pre-trained models are currently dominating various fields, the domain of URL analysis still lacks specialized pre-trained models. To address this gap, this paper introduces URLBERT, the first pre-trained representation learning model applied to a variety of URL classification or detection tasks. We first train a URL tokenizer on a corpus of billions of URLs to address URL data tokenization. Additionally, we propose two novel pre-training tasks: (1) self-supervised contrastive learning tasks, which strengthen the model's understanding of URL structure and the capture of category differences by distinguishing different variants of the same URL; (2) virtual adversarial training, aimed at improving the model's robustness in extracting semantic features from URLs. Finally, our proposed methods are evaluated on tasks including phishing URL detection, web page classification, and ad filtering, achieving state-of-the-art performance. Importantly, we also explore multi-task learning with URLBERT, and experimental results demonstrate that multi-task learning model based on URLBERT exhibit equivalent effectiveness compared to independently fine-tuned models, showing the simplicity of URLBERT in handling complex task requirements. The code for our work is available at https://github.com/Davidup1/URLBERT.
Neural Abstract Style Transfer for Chinese Traditional Painting
Dec 13, 2018

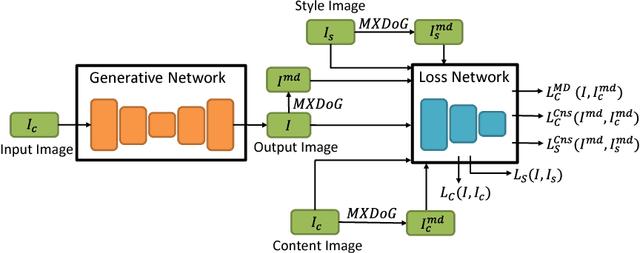

Abstract:Chinese traditional painting is one of the most historical artworks in the world. It is very popular in Eastern and Southeast Asia due to being aesthetically appealing. Compared with western artistic painting, it is usually more visually abstract and textureless. Recently, neural network based style transfer methods have shown promising and appealing results which are mainly focused on western painting. It remains a challenging problem to preserve abstraction in neural style transfer. In this paper, we present a Neural Abstract Style Transfer method for Chinese traditional painting. It learns to preserve abstraction and other style jointly end-to-end via a novel MXDoG-guided filter (Modified version of the eXtended Difference-of-Gaussians) and three fully differentiable loss terms. To the best of our knowledge, there is little work study on neural style transfer of Chinese traditional painting. To promote research on this direction, we collect a new dataset with diverse photo-realistic images and Chinese traditional paintings. In experiments, the proposed method shows more appealing stylized results in transferring the style of Chinese traditional painting than state-of-the-art neural style transfer methods.
Auto-Context R-CNN
Jul 08, 2018



Abstract:Region-based convolutional neural networks (R-CNN)~\cite{fast_rcnn,faster_rcnn,mask_rcnn} have largely dominated object detection. Operators defined on RoIs (Region of Interests) play an important role in R-CNNs such as RoIPooling~\cite{fast_rcnn} and RoIAlign~\cite{mask_rcnn}. They all only utilize information inside RoIs for RoI prediction, even with their recent deformable extensions~\cite{deformable_cnn}. Although surrounding context is well-known for its importance in object detection, it has yet been integrated in R-CNNs in a flexible and effective way. Inspired by the auto-context work~\cite{auto_context} and the multi-class object layout work~\cite{nms_context}, this paper presents a generic context-mining RoI operator (i.e., \textit{RoICtxMining}) seamlessly integrated in R-CNNs, and the resulting object detection system is termed \textbf{Auto-Context R-CNN} which is trained end-to-end. The proposed RoICtxMining operator is a simple yet effective two-layer extension of the RoIPooling or RoIAlign operator. Centered at an object-RoI, it creates a $3\times 3$ layout to mine contextual information adaptively in the $8$ surrounding context regions on-the-fly. Within each of the $8$ context regions, a context-RoI is mined in term of discriminative power and its RoIPooling / RoIAlign features are concatenated with the object-RoI for final prediction. \textit{The proposed Auto-Context R-CNN is robust to occlusion and small objects, and shows promising vulnerability for adversarial attacks without being adversarially-trained.} In experiments, it is evaluated using RoIPooling as the backbone and shows competitive results on Pascal VOC, Microsoft COCO, and KITTI datasets (including $6.9\%$ mAP improvements over the R-FCN~\cite{rfcn} method on COCO \textit{test-dev} dataset and the first place on both KITTI pedestrian and cyclist detection as of this submission).
Object Detection via Aspect Ratio and Context Aware Region-based Convolutional Networks
Mar 22, 2017
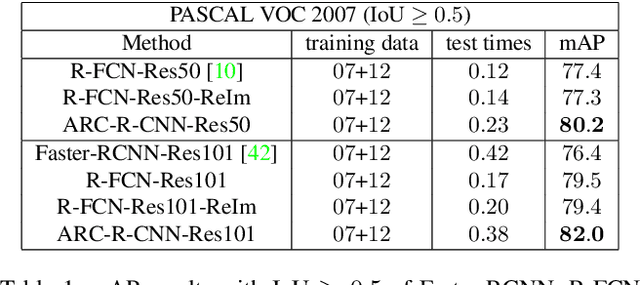


Abstract:Jointly integrating aspect ratio and context has been extensively studied and shown performance improvement in traditional object detection systems such as the DPMs. It, however, has been largely ignored in deep neural network based detection systems. This paper presents a method of integrating a mixture of object models and region-based convolutional networks for accurate object detection. Each mixture component accounts for both object aspect ratio and multi-scale contextual information explicitly: (i) it exploits a mixture of tiling configurations in the RoI pooling to remedy the warping artifacts caused by a single type RoI pooling (e.g., with equally-sized 7 x 7 cells), and to respect the underlying object shapes more; (ii) it "looks from both the inside and the outside of a RoI" by incorporating contextual information at two scales: global context pooled from the whole image and local context pooled from the surrounding of a RoI. To facilitate accurate detection, this paper proposes a multi-stage detection scheme for integrating the mixture of object models, which utilizes the detection results of the model at the previous stage as the proposals for the current in both training and testing. The proposed method is called the aspect ratio and context aware region-based convolutional network (ARC-R-CNN). In experiments, ARC-R-CNN shows very competitive results with Faster R-CNN [41] and R-FCN [10] on two datasets: the PASCAL VOC and the Microsoft COCO. It obtains significantly better mAP performance using high IoU thresholds on both datasets.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge