Weian Guo
Multi-Objective Communication Optimization for Temporal Continuity in Dynamic Vehicular Networks
Nov 30, 2024Abstract:Vehicular Ad-hoc Networks (VANETs) operate in highly dynamic environments characterized by high mobility, time-varying channel conditions, and frequent network disruptions. Addressing these challenges, this paper presents a novel temporal-aware multi-objective robust optimization framework, which for the first time formally incorporates temporal continuity into the optimization of dynamic multi-hop VANETs. The proposed framework simultaneously optimizes communication delay, throughput, and reliability, ensuring stable and consistent communication paths under rapidly changing conditions. A robust optimization model is formulated to mitigate performance degradation caused by uncertainties in vehicular density and channel fluctuations. To solve the optimization problem, an enhanced Non-dominated Sorting Genetic Algorithm II (NSGA-II) is developed, integrating dynamic encoding, elite inheritance, and adaptive constraint handling to efficiently balance trade-offs among conflicting objectives. Simulation results demonstrate that the proposed framework achieves significant improvements in reliability, delay reduction, and throughput enhancement, while temporal continuity effectively stabilizes communication paths over time. This work provides a pioneering and comprehensive solution for optimizing VANET communication, offering critical insights for robust and efficient strategies in intelligent transportation systems.
Adaptive Genetic Selection based Pinning Control with Asymmetric Coupling for Multi-Network Heterogeneous Vehicular Systems
Nov 05, 2024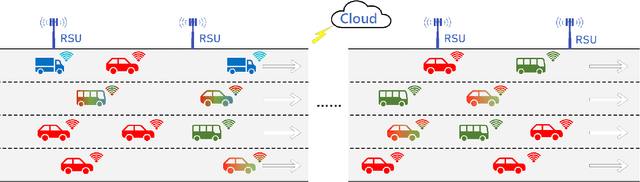

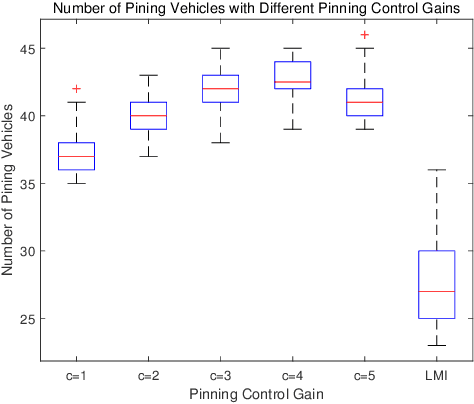
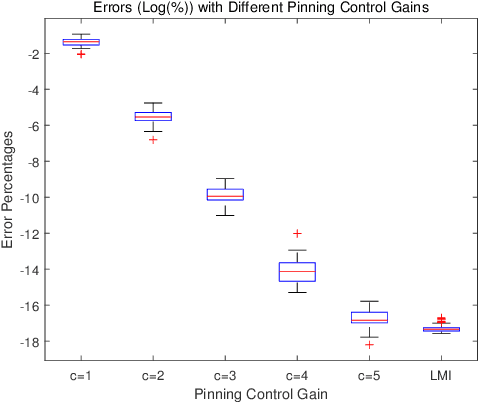
Abstract:To alleviate computational load on RSUs and cloud platforms, reduce communication bandwidth requirements, and provide a more stable vehicular network service, this paper proposes an optimized pinning control approach for heterogeneous multi-network vehicular ad-hoc networks (VANETs). In such networks, vehicles participate in multiple task-specific networks with asymmetric coupling and dynamic topologies. We first establish a rigorous theoretical foundation by proving the stability of pinning control strategies under both single and multi-network conditions, deriving sufficient stability conditions using Lyapunov theory and linear matrix inequalities (LMIs). Building on this theoretical groundwork, we propose an adaptive genetic algorithm tailored to select optimal pinning nodes, effectively balancing LMI constraints while prioritizing overlapping nodes to enhance control efficiency. Extensive simulations across various network scales demonstrate that our approach achieves rapid consensus with a reduced number of control nodes, particularly when leveraging network overlaps. This work provides a comprehensive solution for efficient control node selection in complex vehicular networks, offering practical implications for deploying large-scale intelligent transportation systems.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge