Luis A. Leiva
Telling Human and Machine Handwriting Apart
Jan 16, 2026Abstract:Handwriting movements can be leveraged as a unique form of behavioral biometrics, to verify whether a real user is operating a device or application. This task can be framed as a reverse Turing test in which a computer has to detect if an input instance has been generated by a human or artificially. To tackle this task, we study ten public datasets of handwritten symbols (isolated characters, digits, gestures, pointing traces, and signatures) that are artificially reproduced using seven different synthesizers, including, among others, the Kinematic Theory (Sigma h model), generative adversarial networks, Transformers, and Diffusion models. We train a shallow recurrent neural network that achieves excellent performance (98.3 percent Area Under the ROC Curve (AUC) score and 1.4 percent equal error rate on average across all synthesizers and datasets) using nonfeaturized trajectory data as input. In few-shot settings, we show that our classifier achieves such an excellent performance when trained on just 10 percent of the data, as evaluated on the remaining 90% of the data as a test set. We further challenge our classifier in out-of-domain settings, and observe very competitive results as well. Our work has implications for computerized systems that need to verify human presence, and adds an additional layer of security to keep attackers at bay.
Context-aware Adaptive Visualizations for Critical Decision Making
Nov 14, 2025Abstract:Effective decision-making often relies on timely insights from complex visual data. While Information Visualization (InfoVis) dashboards can support this process, they rarely adapt to users' cognitive state, and less so in real time. We present Symbiotik, an intelligent, context-aware adaptive visualization system that leverages neurophysiological signals to estimate mental workload (MWL) and dynamically adapt visual dashboards using reinforcement learning (RL). Through a user study with 120 participants and three visualization types, we demonstrate that our approach improves task performance and engagement. Symbiotik offers a scalable, real-time adaptation architecture, and a validated methodology for neuroadaptive user interfaces.
Multimodal Representation Alignment for Cross-modal Information Retrieval
Jun 10, 2025Abstract:Different machine learning models can represent the same underlying concept in different ways. This variability is particularly valuable for in-the-wild multimodal retrieval, where the objective is to identify the corresponding representation in one modality given another modality as input. This challenge can be effectively framed as a feature alignment problem. For example, given a sentence encoded by a language model, retrieve the most semantically aligned image based on features produced by an image encoder, or vice versa. In this work, we first investigate the geometric relationships between visual and textual embeddings derived from both vision-language models and combined unimodal models. We then align these representations using four standard similarity metrics as well as two learned ones, implemented via neural networks. Our findings indicate that the Wasserstein distance can serve as an informative measure of the modality gap, while cosine similarity consistently outperforms alternative metrics in feature alignment tasks. Furthermore, we observe that conventional architectures such as multilayer perceptrons are insufficient for capturing the complex interactions between image and text representations. Our study offers novel insights and practical considerations for researchers working in multimodal information retrieval, particularly in real-world, cross-modal applications.
Sparse-to-Sparse Training of Diffusion Models
Apr 30, 2025Abstract:Diffusion models (DMs) are a powerful type of generative models that have achieved state-of-the-art results in various image synthesis tasks and have shown potential in other domains, such as natural language processing and temporal data modeling. Despite their stable training dynamics and ability to produce diverse high-quality samples, DMs are notorious for requiring significant computational resources, both in the training and inference stages. Previous work has focused mostly on increasing the efficiency of model inference. This paper introduces, for the first time, the paradigm of sparse-to-sparse training to DMs, with the aim of improving both training and inference efficiency. We focus on unconditional generation and train sparse DMs from scratch (Latent Diffusion and ChiroDiff) on six datasets using three different methods (Static-DM, RigL-DM, and MagRan-DM) to study the effect of sparsity in model performance. Our experiments show that sparse DMs are able to match and often outperform their Dense counterparts, while substantially reducing the number of trainable parameters and FLOPs. We also identify safe and effective values to perform sparse-to-sparse training of DMs.
AdSight: Scalable and Accurate Quantification of User Attention in Multi-Slot Sponsored Search
Apr 30, 2025Abstract:Modern Search Engine Results Pages (SERPs) present complex layouts where multiple elements compete for visibility. Attention modelling is crucial for optimising web design and computational advertising, whereas attention metrics can inform ad placement and revenue strategies. We introduce AdSight, a method leveraging mouse cursor trajectories to quantify in a scalable and accurate manner user attention in multi-slot environments like SERPs. AdSight uses a novel Transformer-based sequence-to-sequence architecture where the encoder processes cursor trajectory embeddings, and the decoder incorporates slot-specific features, enabling robust attention prediction across various SERP layouts. We evaluate our approach on two Machine Learning tasks: (1)~\emph{regression}, to predict fixation times and counts; and (2)~\emph{classification}, to determine some slot types were noticed. Our findings demonstrate the model's ability to predict attention with unprecedented precision, offering actionable insights for researchers and practitioners.
A Comparative Study of Scanpath Models in Graph-Based Visualization
Apr 01, 2025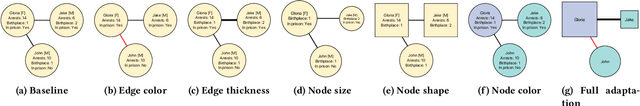
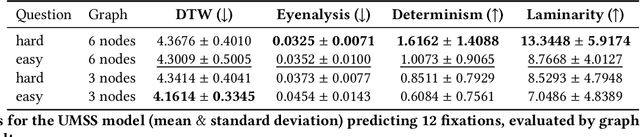
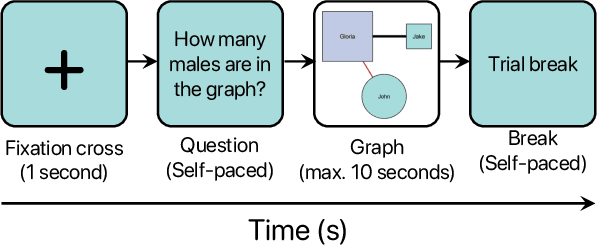
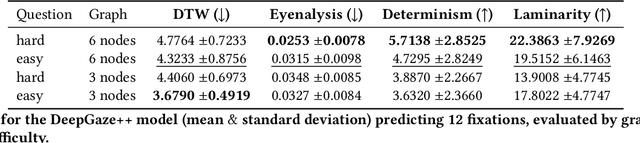
Abstract:Information Visualization (InfoVis) systems utilize visual representations to enhance data interpretation. Understanding how visual attention is allocated is essential for optimizing interface design. However, collecting Eye-tracking (ET) data presents challenges related to cost, privacy, and scalability. Computational models provide alternatives for predicting gaze patterns, thereby advancing InfoVis research. In our study, we conducted an ET experiment with 40 participants who analyzed graphs while responding to questions of varying complexity within the context of digital forensics. We compared human scanpaths with synthetic ones generated by models such as DeepGaze, UMSS, and Gazeformer. Our research evaluates the accuracy of these models and examines how question complexity and number of nodes influence performance. This work contributes to the development of predictive modeling in visual analytics, offering insights that can enhance the design and effectiveness of InfoVis systems.
Transfer Learning for Covert Speech Classification Using EEG Hilbert Envelope and Temporal Fine Structure
Feb 06, 2025



Abstract:Brain-Computer Interfaces (BCIs) can decode imagined speech from neural activity. However, these systems typically require extensive training sessions where participants imaginedly repeat words, leading to mental fatigue and difficulties identifying the onset of words, especially when imagining sequences of words. This paper addresses these challenges by transferring a classifier trained in overt speech data to covert speech classification. We used electroencephalogram (EEG) features derived from the Hilbert envelope and temporal fine structure, and used them to train a bidirectional long-short-term memory (BiLSTM) model for classification. Our method reduces the burden of extensive training and achieves state-of-the-art classification accuracy: 86.44% for overt speech and 79.82% for covert speech using the overt speech classifier.
Text-to-Image Generation for Vocabulary Learning Using the Keyword Method
Jan 28, 2025



Abstract:The 'keyword method' is an effective technique for learning vocabulary of a foreign language. It involves creating a memorable visual link between what a word means and what its pronunciation in a foreign language sounds like in the learner's native language. However, these memorable visual links remain implicit in the people's mind and are not easy to remember for a large set of words. To enhance the memorisation and recall of the vocabulary, we developed an application that combines the keyword method with text-to-image generators to externalise the memorable visual links into visuals. These visuals represent additional stimuli during the memorisation process. To explore the effectiveness of this approach we first run a pilot study to investigate how difficult it is to externalise the descriptions of mental visualisations of memorable links, by asking participants to write them down. We used these descriptions as prompts for text-to-image generator (DALL-E2) to convert them into images and asked participants to select their favourites. Next, we compared different text-to-image generators (DALL-E2, Midjourney, Stable and Latent Diffusion) to evaluate the perceived quality of the generated images by each. Despite heterogeneous results, participants mostly preferred images generated by DALL-E2, which was used also for the final study. In this study, we investigated whether providing such images enhances the retention of vocabulary being learned, compared to the keyword method only. Our results indicate that people did not encounter difficulties describing their visualisations of memorable links and that providing corresponding images significantly improves memory retention.
MOSAIC: Multimodal Multistakeholder-aware Visual Art Recommendation
Jul 31, 2024



Abstract:Visual art (VA) recommendation is complex, as it has to consider the interests of users (e.g. museum visitors) and other stakeholders (e.g. museum curators). We study how to effectively account for key stakeholders in VA recommendations while also considering user-centred measures such as novelty, serendipity, and diversity. We propose MOSAIC, a novel multimodal multistakeholder-aware approach using state-of-the-art CLIP and BLIP backbone architectures and two joint optimisation objectives: popularity and representative selection of paintings across different categories. We conducted an offline evaluation using preferences elicited from 213 users followed by a user study with 100 crowdworkers. We found a strong effect of popularity, which was positively perceived by users, and a minimal effect of representativeness. MOSAIC's impact extends beyond visitors, benefiting various art stakeholders. Its user-centric approach has broader applicability, offering advancements for content recommendation across domains that require considering multiple stakeholders.
Modeling User Preferences via Brain-Computer Interfacing
May 15, 2024Abstract:Present Brain-Computer Interfacing (BCI) technology allows inference and detection of cognitive and affective states, but fairly little has been done to study scenarios in which such information can facilitate new applications that rely on modeling human cognition. One state that can be quantified from various physiological signals is attention. Estimates of human attention can be used to reveal preferences and novel dimensions of user experience. Previous approaches have tackled these incredibly challenging tasks using a variety of behavioral signals, from dwell-time to click-through data, and computational models of visual correspondence to these behavioral signals. However, behavioral signals are only rough estimations of the real underlying attention and affective preferences of the users. Indeed, users may attend to some content simply because it is salient, but not because it is really interesting, or simply because it is outrageous. With this paper, we put forward a research agenda and example work using BCI to infer users' preferences, their attentional correlates towards visual content, and their associations with affective experience. Subsequently, we link these to relevant applications, such as information retrieval, personalized steering of generative models, and crowdsourcing population estimates of affective experiences.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge