Liwen Xiao
Exploring Contextual Attribute Density in Referring Expression Counting
Mar 16, 2025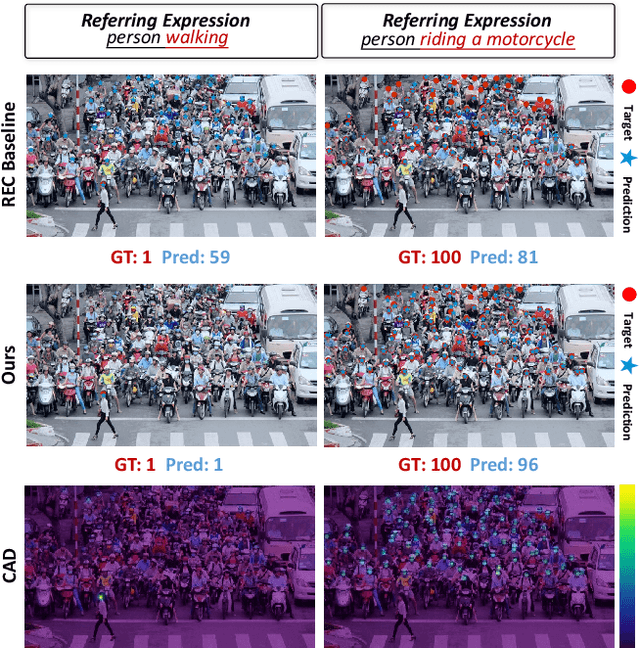
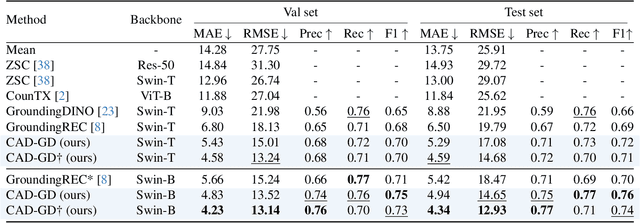
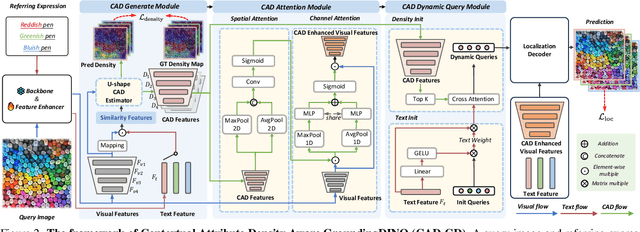
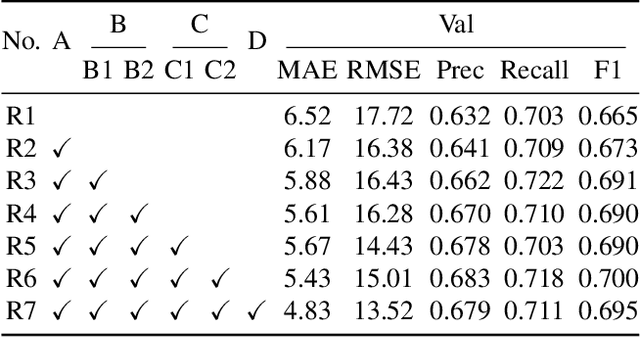
Abstract:Referring expression counting (REC) algorithms are for more flexible and interactive counting ability across varied fine-grained text expressions. However, the requirement for fine-grained attribute understanding poses challenges for prior arts, as they struggle to accurately align attribute information with correct visual patterns. Given the proven importance of ''visual density'', it is presumed that the limitations of current REC approaches stem from an under-exploration of ''contextual attribute density'' (CAD). In the scope of REC, we define CAD as the measure of the information intensity of one certain fine-grained attribute in visual regions. To model the CAD, we propose a U-shape CAD estimator in which referring expression and multi-scale visual features from GroundingDINO can interact with each other. With additional density supervision, we can effectively encode CAD, which is subsequently decoded via a novel attention procedure with CAD-refined queries. Integrating all these contributions, our framework significantly outperforms state-of-the-art REC methods, achieves $30\%$ error reduction in counting metrics and a $10\%$ improvement in localization accuracy. The surprising results shed light on the significance of contextual attribute density for REC. Code will be at github.com/Xu3XiWang/CAD-GD.
Pseudo-Labeling by Multi-Policy Viewfinder Network for Image Cropping
Jul 02, 2024



Abstract:Automatic image cropping models predict reframing boxes to enhance image aesthetics. Yet, the scarcity of labeled data hinders the progress of this task. To overcome this limitation, we explore the possibility of utilizing both labeled and unlabeled data together to expand the scale of training data for image cropping models. This idea can be implemented in a pseudo-labeling way: producing pseudo labels for unlabeled data by a teacher model and training a student model with these pseudo labels. However, the student may learn from teacher's mistakes. To address this issue, we propose the multi-policy viewfinder network (MPV-Net) that offers diverse refining policies to rectify the mistakes in original pseudo labels from the teacher. The most reliable policy is selected to generate trusted pseudo labels. The reliability of policies is evaluated via the robustness against box jittering. The efficacy of our method can be evaluated by the improvement compared to the supervised baseline which only uses labeled data. Notably, our MPV-Net outperforms off-the-shelf pseudo-labeling methods, yielding the most substantial improvement over the supervised baseline. Furthermore, our approach achieves state-of-the-art results on both the FCDB and FLMS datasets, signifying the superiority of our approach.
Instance Consistency Regularization for Semi-Supervised 3D Instance Segmentation
Jun 24, 2024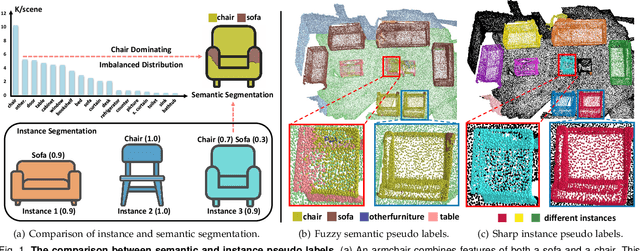
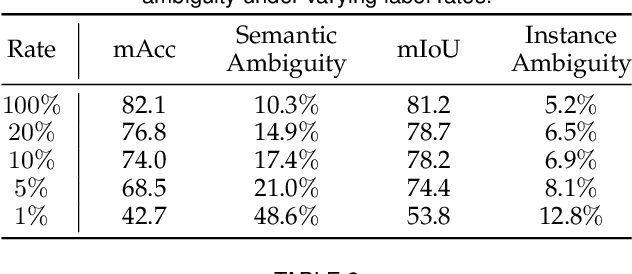
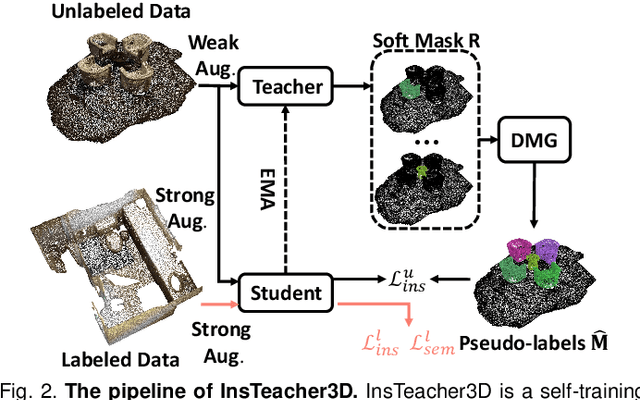
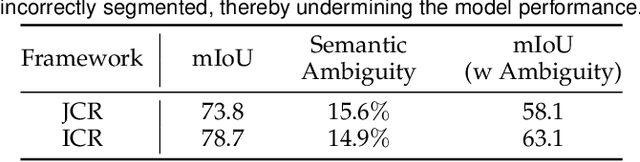
Abstract:Large-scale datasets with point-wise semantic and instance labels are crucial to 3D instance segmentation but also expensive. To leverage unlabeled data, previous semi-supervised 3D instance segmentation approaches have explored self-training frameworks, which rely on high-quality pseudo labels for consistency regularization. They intuitively utilize both instance and semantic pseudo labels in a joint learning manner. However, semantic pseudo labels contain numerous noise derived from the imbalanced category distribution and natural confusion of similar but distinct categories, which leads to severe collapses in self-training. Motivated by the observation that 3D instances are non-overlapping and spatially separable, we ask whether we can solely rely on instance consistency regularization for improved semi-supervised segmentation. To this end, we propose a novel self-training network InsTeacher3D to explore and exploit pure instance knowledge from unlabeled data. We first build a parallel base 3D instance segmentation model DKNet, which distinguishes each instance from the others via discriminative instance kernels without reliance on semantic segmentation. Based on DKNet, we further design a novel instance consistency regularization framework to generate and leverage high-quality instance pseudo labels. Experimental results on multiple large-scale datasets show that the InsTeacher3D significantly outperforms prior state-of-the-art semi-supervised approaches. Code is available: https://github.com/W1zheng/InsTeacher3D.
Vision Transformer Off-the-Shelf: A Surprising Baseline for Few-Shot Class-Agnostic Counting
May 08, 2023Abstract:Class-agnostic counting (CAC) aims to count objects of interest from a query image given few exemplars. This task is typically addressed by extracting the features of query image and exemplars respectively with (un)shared feature extractors and by matching their feature similarity, leading to an extract-\textit{then}-match paradigm. In this work, we show that CAC can be simplified in an extract-\textit{and}-match manner, particularly using a pretrained and plain vision transformer (ViT) where feature extraction and similarity matching are executed simultaneously within the self-attention. We reveal the rationale of such simplification from a decoupled view of the self-attention and point out that the simplification is only made possible if the query and exemplar tokens are concatenated as input. The resulting model, termed CACViT, simplifies the CAC pipeline and unifies the feature spaces between the query image and exemplars. In addition, we find CACViT naturally encodes background information within self-attention, which helps reduce background disturbance. Further, to compensate the loss of the scale and the order-of-magnitude information due to resizing and normalization in ViT, we present two effective strategies for scale and magnitude embedding. Extensive experiments on the FSC147 and the CARPK datasets show that CACViT significantly outperforms state-of-the-art CAC approaches in both effectiveness (23.60% error reduction) and generalization, which suggests CACViT provides a concise and strong baseline for CAC. Code will be available.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge