Liu Zheng
Benchmarks and Challenges in Pose Estimation for Egocentric Hand Interactions with Objects
Mar 25, 2024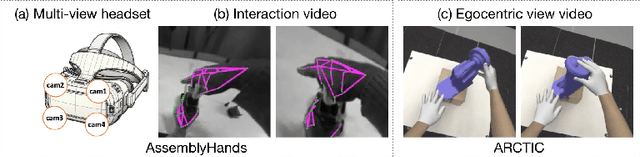
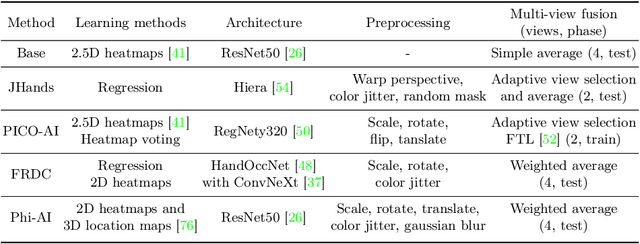
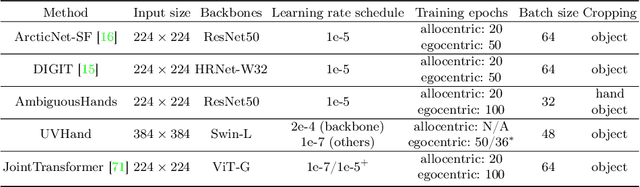
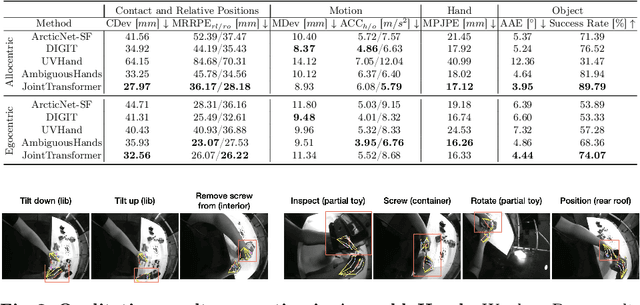
Abstract:We interact with the world with our hands and see it through our own (egocentric) perspective. A holistic 3D understanding of such interactions from egocentric views is important for tasks in robotics, AR/VR, action recognition and motion generation. Accurately reconstructing such interactions in 3D is challenging due to heavy occlusion, viewpoint bias, camera distortion, and motion blur from the head movement. To this end, we designed the HANDS23 challenge based on the AssemblyHands and ARCTIC datasets with carefully designed training and testing splits. Based on the results of the top submitted methods and more recent baselines on the leaderboards, we perform a thorough analysis on 3D hand(-object) reconstruction tasks. Our analysis demonstrates the effectiveness of addressing distortion specific to egocentric cameras, adopting high-capacity transformers to learn complex hand-object interactions, and fusing predictions from different views. Our study further reveals challenging scenarios intractable with state-of-the-art methods, such as fast hand motion, object reconstruction from narrow egocentric views, and close contact between two hands and objects. Our efforts will enrich the community's knowledge foundation and facilitate future hand studies on egocentric hand-object interactions.
Cooling-Guide Diffusion Model for Battery Cell Arrangement
Mar 14, 2024



Abstract:Our study introduces a Generative AI method that employs a cooling-guided diffusion model to optimize the layout of battery cells, a crucial step for enhancing the cooling performance and efficiency of battery thermal management systems. Traditional design processes, which rely heavily on iterative optimization and extensive guesswork, are notoriously slow and inefficient, often leading to suboptimal solutions. In contrast, our innovative method uses a parametric denoising diffusion probabilistic model (DDPM) with classifier and cooling guidance to generate optimized cell layouts with enhanced cooling paths, significantly lowering the maximum temperature of the cells. By incorporating position-based classifier guidance, we ensure the feasibility of generated layouts. Meanwhile, cooling guidance directly optimizes cooling-efficiency, making our approach uniquely effective. When compared to two advanced models, the Tabular Denoising Diffusion Probabilistic Model (TabDDPM) and the Conditional Tabular GAN (CTGAN), our cooling-guided diffusion model notably outperforms both. It is five times more effective than TabDDPM and sixty-six times better than CTGAN across key metrics such as feasibility, diversity, and cooling efficiency. This research marks a significant leap forward in the field, aiming to optimize battery cell layouts for superior cooling efficiency, thus setting the stage for the development of more effective and dependable battery thermal management systems.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge