Lior Drukker
Learning to learn skill assessment for fetal ultrasound scanning
Dec 30, 2025Abstract:Traditionally, ultrasound skill assessment has relied on expert supervision and feedback, a process known for its subjectivity and time-intensive nature. Previous works on quantitative and automated skill assessment have predominantly employed supervised learning methods, often limiting the analysis to predetermined or assumed factors considered influential in determining skill levels. In this work, we propose a novel bi-level optimisation framework that assesses fetal ultrasound skills by how well a task is performed on the acquired fetal ultrasound images, without using manually predefined skill ratings. The framework consists of a clinical task predictor and a skill predictor, which are optimised jointly by refining the two networks simultaneously. We validate the proposed method on real-world clinical ultrasound videos of scanning the fetal head. The results demonstrate the feasibility of predicting ultrasound skills by the proposed framework, which quantifies optimised task performance as a skill indicator.
Show from Tell: Audio-Visual Modelling in Clinical Settings
Oct 25, 2023


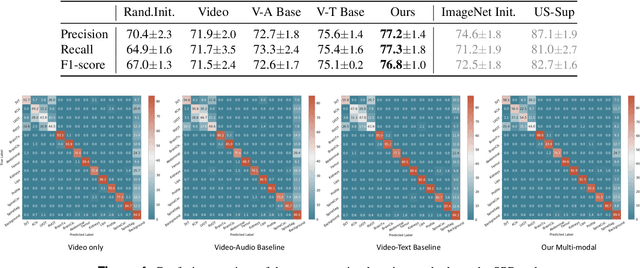
Abstract:Auditory and visual signals usually present together and correlate with each other, not only in natural environments but also in clinical settings. However, the audio-visual modelling in the latter case can be more challenging, due to the different sources of audio/video signals and the noise (both signal-level and semantic-level) in auditory signals -- usually speech. In this paper, we consider audio-visual modelling in a clinical setting, providing a solution to learn medical representations that benefit various clinical tasks, without human expert annotation. A simple yet effective multi-modal self-supervised learning framework is proposed for this purpose. The proposed approach is able to localise anatomical regions of interest during ultrasound imaging, with only speech audio as a reference. Experimental evaluations on a large-scale clinical multi-modal ultrasound video dataset show that the proposed self-supervised method learns good transferable anatomical representations that boost the performance of automated downstream clinical tasks, even outperforming fully-supervised solutions.
Anatomy-Aware Contrastive Representation Learning for Fetal Ultrasound
Aug 22, 2022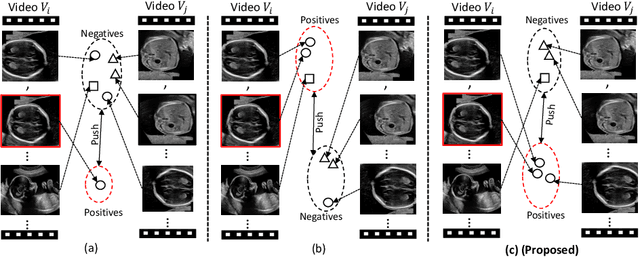

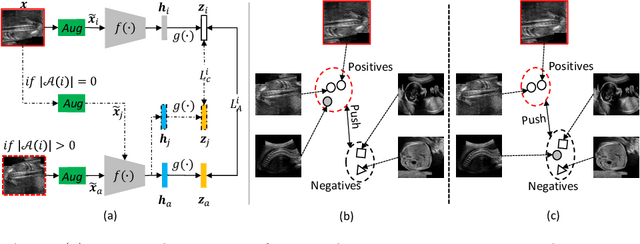
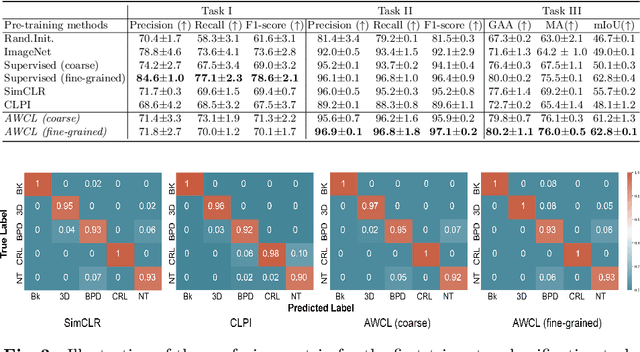
Abstract:Self-supervised contrastive representation learning offers the advantage of learning meaningful visual representations from unlabeled medical datasets for transfer learning. However, applying current contrastive learning approaches to medical data without considering its domain-specific anatomical characteristics may lead to visual representations that are inconsistent in appearance and semantics. In this paper, we propose to improve visual representations of medical images via anatomy-aware contrastive learning (AWCL), which incorporates anatomy information to augment the positive/negative pair sampling in a contrastive learning manner. The proposed approach is demonstrated for automated fetal ultrasound imaging tasks, enabling the positive pairs from the same or different ultrasound scans that are anatomically similar to be pulled together and thus improving the representation learning. We empirically investigate the effect of inclusion of anatomy information with coarse- and fine-grained granularity, for contrastive learning and find that learning with fine-grained anatomy information which preserves intra-class difference is more effective than its counterpart. We also analyze the impact of anatomy ratio on our AWCL framework and find that using more distinct but anatomically similar samples to compose positive pairs results in better quality representations. Experiments on a large-scale fetal ultrasound dataset demonstrate that our approach is effective for learning representations that transfer well to three clinical downstream tasks, and achieves superior performance compared to ImageNet supervised and the current state-of-the-art contrastive learning methods. In particular, AWCL outperforms ImageNet supervised method by 13.8% and state-of-the-art contrastive-based method by 7.1% on a cross-domain segmentation task.
Multimodal-GuideNet: Gaze-Probe Bidirectional Guidance in Obstetric Ultrasound Scanning
Jul 26, 2022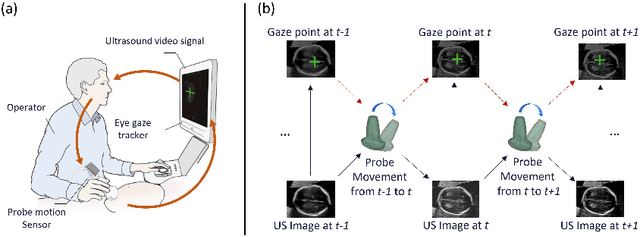
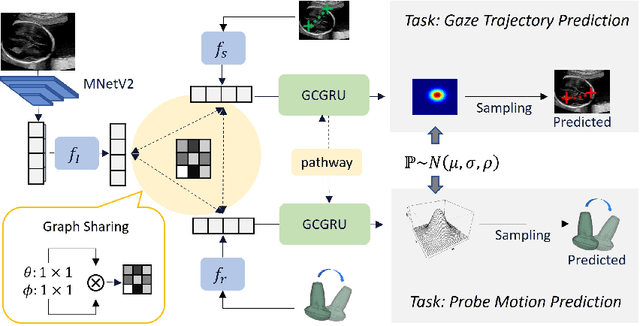
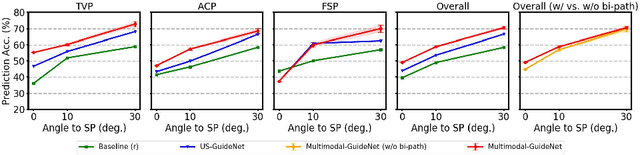
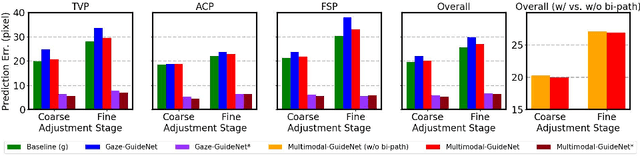
Abstract:Eye trackers can provide visual guidance to sonographers during ultrasound (US) scanning. Such guidance is potentially valuable for less experienced operators to improve their scanning skills on how to manipulate the probe to achieve the desired plane. In this paper, a multimodal guidance approach (Multimodal-GuideNet) is proposed to capture the stepwise dependency between a real-world US video signal, synchronized gaze, and probe motion within a unified framework. To understand the causal relationship between gaze movement and probe motion, our model exploits multitask learning to jointly learn two related tasks: predicting gaze movements and probe signals that an experienced sonographer would perform in routine obstetric scanning. The two tasks are associated by a modality-aware spatial graph to detect the co-occurrence among the multi-modality inputs and share useful cross-modal information. Instead of a deterministic scanning path, Multimodal-GuideNet allows for scanning diversity by estimating the probability distribution of real scans. Experiments performed with three typical obstetric scanning examinations show that the new approach outperforms single-task learning for both probe motion guidance and gaze movement prediction. Multimodal-GuideNet also provides a visual guidance signal with an error rate of less than 10 pixels for a 224x288 US image.
Self-supervised Contrastive Video-Speech Representation Learning for Ultrasound
Aug 14, 2020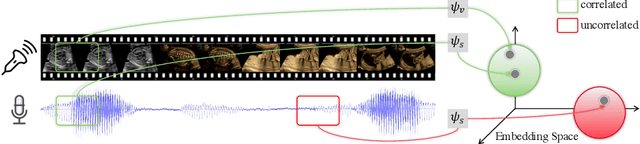


Abstract:In medical imaging, manual annotations can be expensive to acquire and sometimes infeasible to access, making conventional deep learning-based models difficult to scale. As a result, it would be beneficial if useful representations could be derived from raw data without the need for manual annotations. In this paper, we propose to address the problem of self-supervised representation learning with multi-modal ultrasound video-speech raw data. For this case, we assume that there is a high correlation between the ultrasound video and the corresponding narrative speech audio of the sonographer. In order to learn meaningful representations, the model needs to identify such correlation and at the same time understand the underlying anatomical features. We designed a framework to model the correspondence between video and audio without any kind of human annotations. Within this framework, we introduce cross-modal contrastive learning and an affinity-aware self-paced learning scheme to enhance correlation modelling. Experimental evaluations on multi-modal fetal ultrasound video and audio show that the proposed approach is able to learn strong representations and transfers well to downstream tasks of standard plane detection and eye-gaze prediction.
Automatic Probe Movement Guidance for Freehand Obstetric Ultrasound
Jul 08, 2020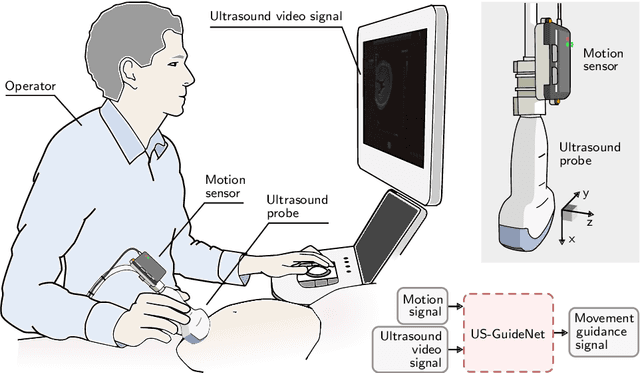

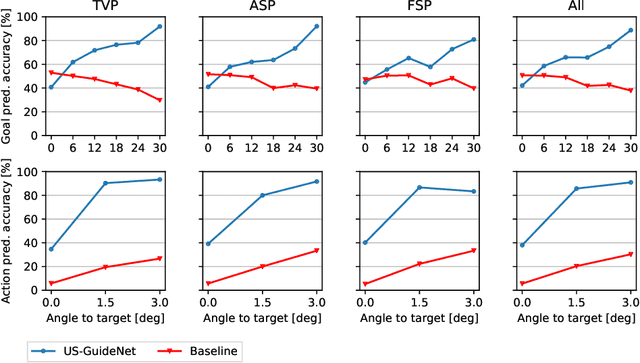
Abstract:We present the first system that provides real-time probe movement guidance for acquiring standard planes in routine freehand obstetric ultrasound scanning. Such a system can contribute to the worldwide deployment of obstetric ultrasound scanning by lowering the required level of operator expertise. The system employs an artificial neural network that receives the ultrasound video signal and the motion signal of an inertial measurement unit (IMU) that is attached to the probe, and predicts a guidance signal. The network termed US-GuideNet predicts either the movement towards the standard plane position (goal prediction), or the next movement that an expert sonographer would perform (action prediction). While existing models for other ultrasound applications are trained with simulations or phantoms, we train our model with real-world ultrasound video and probe motion data from 464 routine clinical scans by 17 accredited sonographers. Evaluations for 3 standard plane types show that the model provides a useful guidance signal with an accuracy of 88.8% for goal prediction and 90.9% for action prediction.
Self-supervised Representation Learning for Ultrasound Video
Feb 28, 2020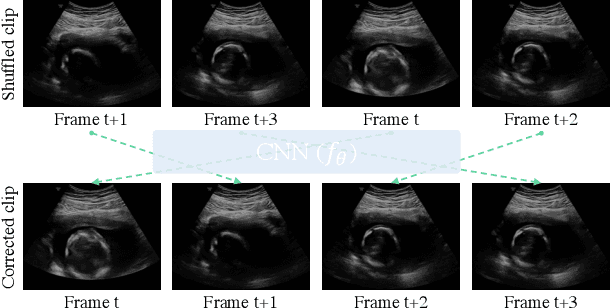

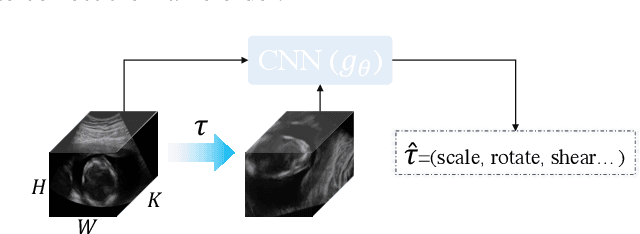
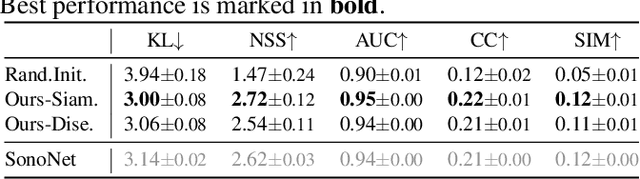
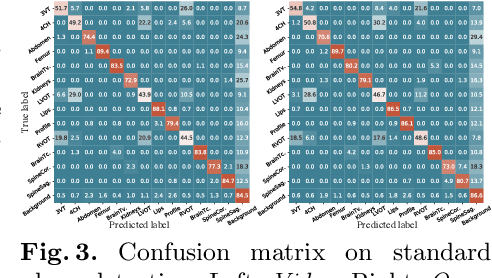
Abstract:Recent advances in deep learning have achieved promising performance for medical image analysis, while in most cases ground-truth annotations from human experts are necessary to train the deep model. In practice, such annotations are expensive to collect and can be scarce for medical imaging applications. Therefore, there is significant interest in learning representations from unlabelled raw data. In this paper, we propose a self-supervised learning approach to learn meaningful and transferable representations from medical imaging video without any type of human annotation. We assume that in order to learn such a representation, the model should identify anatomical structures from the unlabelled data. Therefore we force the model to address anatomy-aware tasks with free supervision from the data itself. Specifically, the model is designed to correct the order of a reshuffled video clip and at the same time predict the geometric transformation applied to the video clip. Experiments on fetal ultrasound video show that the proposed approach can effectively learn meaningful and strong representations, which transfer well to downstream tasks like standard plane detection and saliency prediction.
Discovering Salient Anatomical Landmarks by Predicting Human Gaze
Jan 22, 2020
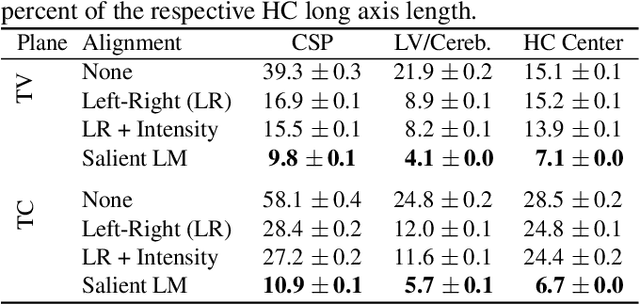


Abstract:Anatomical landmarks are a crucial prerequisite for many medical imaging tasks. Usually, the set of landmarks for a given task is predefined by experts. The landmark locations for a given image are then annotated manually or via machine learning methods trained on manual annotations. In this paper, in contrast, we present a method to automatically discover and localize anatomical landmarks in medical images. Specifically, we consider landmarks that attract the visual attention of humans, which we term visually salient landmarks. We illustrate the method for fetal neurosonographic images. First, full-length clinical fetal ultrasound scans are recorded with live sonographer gaze-tracking. Next, a convolutional neural network (CNN) is trained to predict the gaze point distribution (saliency map) of the sonographers on scan video frames. The CNN is then used to predict saliency maps of unseen fetal neurosonographic images, and the landmarks are extracted as the local maxima of these saliency maps. Finally, the landmarks are matched across images by clustering the landmark CNN features. We show that the discovered landmarks can be used within affine image registration, with average landmark alignment errors between 4.1% and 10.9% of the fetal head long axis length.
Ultrasound Image Representation Learning by Modeling Sonographer Visual Attention
Mar 07, 2019Abstract:Image representations are commonly learned from class labels, which are a simplistic approximation of human image understanding. In this paper we demonstrate that transferable representations of images can be learned without manual annotations by modeling human visual attention. The basis of our analyses is a unique gaze tracking dataset of sonographers performing routine clinical fetal anomaly screenings. Models of sonographer visual attention are learned by training a convolutional neural network (CNN) to predict gaze on ultrasound video frames through visual saliency prediction or gaze-point regression. We evaluate the transferability of the learned representations to the task of ultrasound standard plane detection in two contexts. Firstly, we perform transfer learning by fine-tuning the CNN with a limited number of labeled standard plane images. We find that fine-tuning the saliency predictor is superior to training from random initialization, with an average F1-score improvement of 9.6% overall and 15.3% for the cardiac planes. Secondly, we train a simple softmax regression on the feature activations of each CNN layer in order to evaluate the representations independently of transfer learning hyper-parameters. We find that the attention models derive strong representations, approaching the precision of a fully-supervised baseline model for all but the last layer.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge