Mohammad Alsharid
Show from Tell: Audio-Visual Modelling in Clinical Settings
Oct 25, 2023


Abstract:Auditory and visual signals usually present together and correlate with each other, not only in natural environments but also in clinical settings. However, the audio-visual modelling in the latter case can be more challenging, due to the different sources of audio/video signals and the noise (both signal-level and semantic-level) in auditory signals -- usually speech. In this paper, we consider audio-visual modelling in a clinical setting, providing a solution to learn medical representations that benefit various clinical tasks, without human expert annotation. A simple yet effective multi-modal self-supervised learning framework is proposed for this purpose. The proposed approach is able to localise anatomical regions of interest during ultrasound imaging, with only speech audio as a reference. Experimental evaluations on a large-scale clinical multi-modal ultrasound video dataset show that the proposed self-supervised method learns good transferable anatomical representations that boost the performance of automated downstream clinical tasks, even outperforming fully-supervised solutions.
An Experience Report of Executive-Level Artificial Intelligence Education in the United Arab Emirates
Feb 02, 2022

Abstract:Teaching artificial intelligence (AI) is challenging. It is a fast moving field and therefore difficult to keep people updated with the state-of-the-art. Educational offerings for students are ever increasing, beyond university degree programs where AI education traditionally lay. In this paper, we present an experience report of teaching an AI course to business executives in the United Arab Emirates (UAE). Rather than focusing only on theoretical and technical aspects, we developed a course that teaches AI with a view to enabling students to understand how to incorporate it into existing business processes. We present an overview of our course, curriculum and teaching methods, and we discuss our reflections on teaching adult learners, and to students in the UAE.
Self-supervised Contrastive Video-Speech Representation Learning for Ultrasound
Aug 14, 2020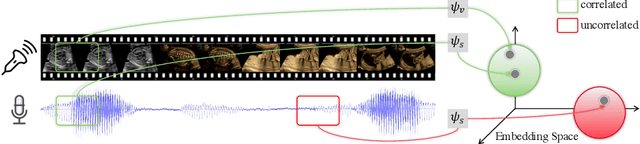


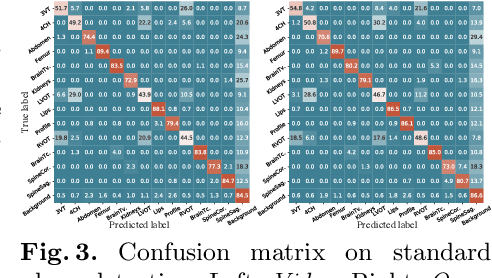
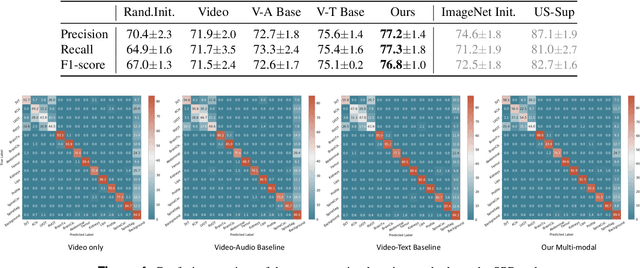
Abstract:In medical imaging, manual annotations can be expensive to acquire and sometimes infeasible to access, making conventional deep learning-based models difficult to scale. As a result, it would be beneficial if useful representations could be derived from raw data without the need for manual annotations. In this paper, we propose to address the problem of self-supervised representation learning with multi-modal ultrasound video-speech raw data. For this case, we assume that there is a high correlation between the ultrasound video and the corresponding narrative speech audio of the sonographer. In order to learn meaningful representations, the model needs to identify such correlation and at the same time understand the underlying anatomical features. We designed a framework to model the correspondence between video and audio without any kind of human annotations. Within this framework, we introduce cross-modal contrastive learning and an affinity-aware self-paced learning scheme to enhance correlation modelling. Experimental evaluations on multi-modal fetal ultrasound video and audio show that the proposed approach is able to learn strong representations and transfers well to downstream tasks of standard plane detection and eye-gaze prediction.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge