Linwei Hu
Cross Spline Net and a Unified World
Oct 24, 2024Abstract:In today's machine learning world for tabular data, XGBoost and fully connected neural network (FCNN) are two most popular methods due to their good model performance and convenience to use. However, they are highly complicated, hard to interpret, and can be overfitted. In this paper, we propose a new modeling framework called cross spline net (CSN) that is based on a combination of spline transformation and cross-network (Wang et al. 2017, 2021). We will show CSN is as performant and convenient to use, and is less complicated, more interpretable and robust. Moreover, the CSN framework is flexible, as the spline layer can be configured differently to yield different models. With different choices of the spline layer, we can reproduce or approximate a set of non-neural network models, including linear and spline-based statistical models, tree, rule-fit, tree-ensembles (gradient boosting trees, random forest), oblique tree/forests, multi-variate adaptive regression spline (MARS), SVM with polynomial kernel, etc. Therefore, CSN provides a unified modeling framework that puts the above set of non-neural network models under the same neural network framework. By using scalable and powerful gradient descent algorithms available in neural network libraries, CSN avoids some pitfalls (such as being ad-hoc, greedy or non-scalable) in the case-specific optimization methods used in the above non-neural network models. We will use a special type of CSN, TreeNet, to illustrate our point. We will compare TreeNet with XGBoost and FCNN to show the benefits of TreeNet. We believe CSN will provide a flexible and convenient framework for practitioners to build performant, robust and more interpretable models.
Computing SHAP Efficiently Using Model Structure Information
Sep 05, 2023



Abstract:SHAP (SHapley Additive exPlanations) has become a popular method to attribute the prediction of a machine learning model on an input to its features. One main challenge of SHAP is the computation time. An exact computation of Shapley values requires exponential time complexity. Therefore, many approximation methods are proposed in the literature. In this paper, we propose methods that can compute SHAP exactly in polynomial time or even faster for SHAP definitions that satisfy our additivity and dummy assumptions (eg, kernal SHAP and baseline SHAP). We develop different strategies for models with different levels of model structure information: known functional decomposition, known order of model (defined as highest order of interaction in the model), or unknown order. For the first case, we demonstrate an additive property and a way to compute SHAP from the lower-order functional components. For the second case, we derive formulas that can compute SHAP in polynomial time. Both methods yield exact SHAP results. Finally, if even the order of model is unknown, we propose an iterative way to approximate Shapley values. The three methods we propose are computationally efficient when the order of model is not high which is typically the case in practice. We compare with sampling approach proposed in Castor & Gomez (2008) using simulation studies to demonstrate the efficacy of our proposed methods.
Monotone Tree-Based GAMI Models by Adapting XGBoost
Sep 05, 2023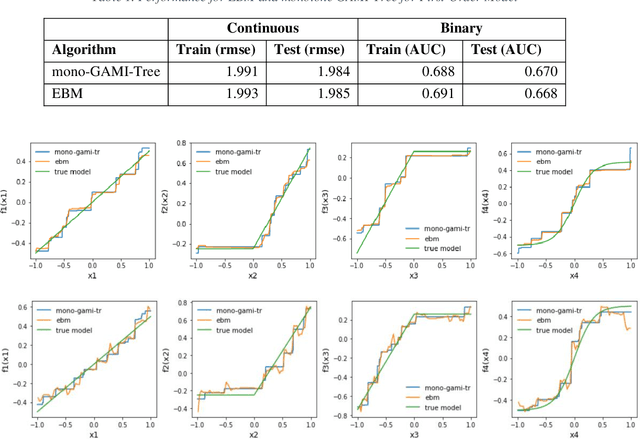
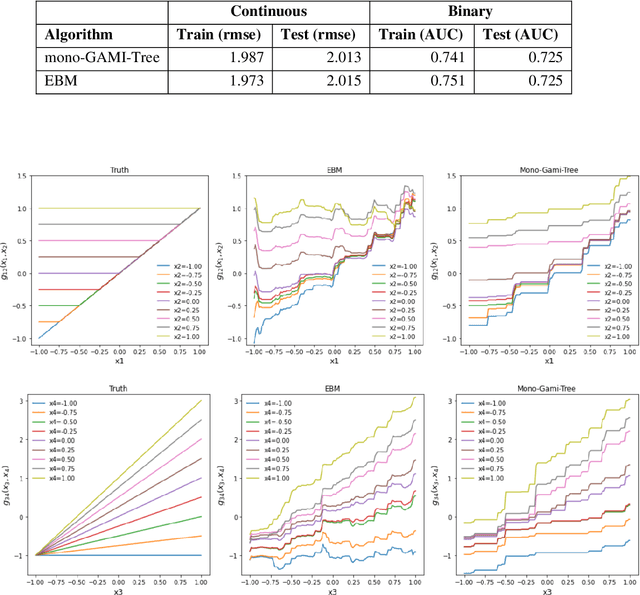
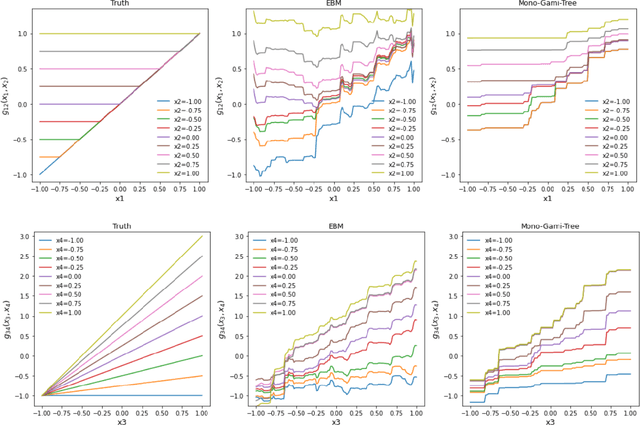
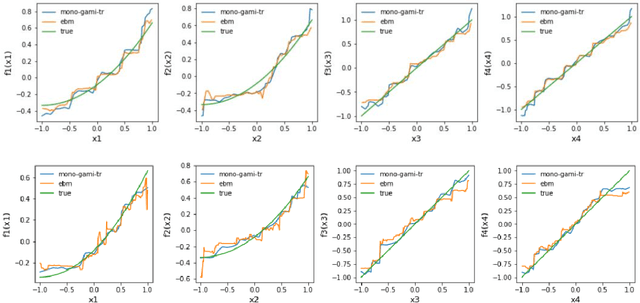
Abstract:Recent papers have used machine learning architecture to fit low-order functional ANOVA models with main effects and second-order interactions. These GAMI (GAM + Interaction) models are directly interpretable as the functional main effects and interactions can be easily plotted and visualized. Unfortunately, it is not easy to incorporate the monotonicity requirement into the existing GAMI models based on boosted trees, such as EBM (Lou et al. 2013) and GAMI-Lin-T (Hu et al. 2022). This paper considers models of the form $f(x)=\sum_{j,k}f_{j,k}(x_j, x_k)$ and develops monotone tree-based GAMI models, called monotone GAMI-Tree, by adapting the XGBoost algorithm. It is straightforward to fit a monotone model to $f(x)$ using the options in XGBoost. However, the fitted model is still a black box. We take a different approach: i) use a filtering technique to determine the important interactions, ii) fit a monotone XGBoost algorithm with the selected interactions, and finally iii) parse and purify the results to get a monotone GAMI model. Simulated datasets are used to demonstrate the behaviors of mono-GAMI-Tree and EBM, both of which use piecewise constant fits. Note that the monotonicity requirement is for the full model. Under certain situations, the main effects will also be monotone. But, as seen in the examples, the interactions will not be monotone.
Interpretable Machine Learning based on Functional ANOVA Framework: Algorithms and Comparisons
May 25, 2023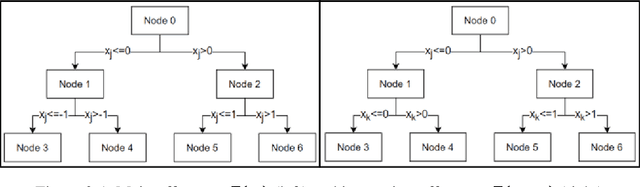
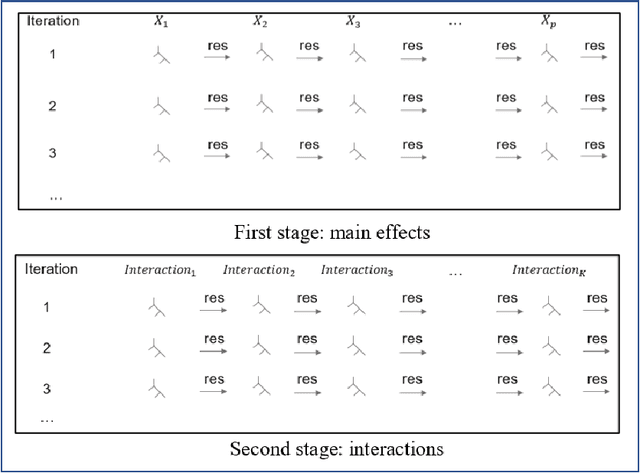
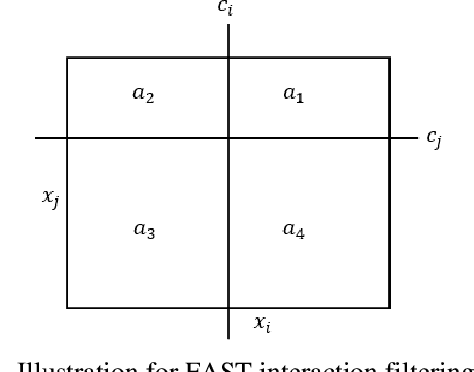
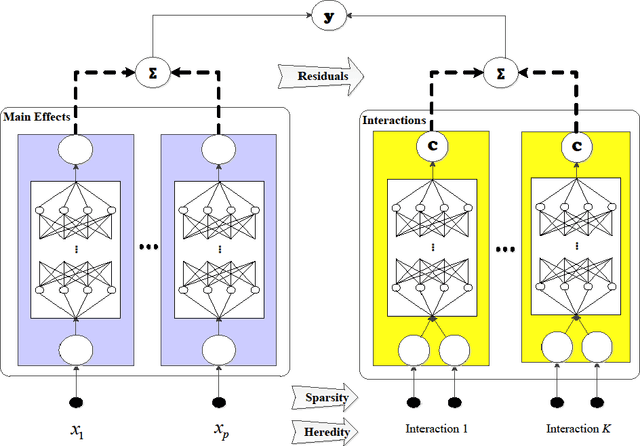
Abstract:In the early days of machine learning (ML), the emphasis was on developing complex algorithms to achieve best predictive performance. To understand and explain the model results, one had to rely on post hoc explainability techniques, which are known to have limitations. Recently, with the recognition that interpretability is just as important, researchers are compromising on small increases in predictive performance to develop algorithms that are inherently interpretable. While doing so, the ML community has rediscovered the use of low-order functional ANOVA (fANOVA) models that have been known in the statistical literature for some time. This paper starts with a description of challenges with post hoc explainability and reviews the fANOVA framework with a focus on main effects and second-order interactions. This is followed by an overview of two recently developed techniques: Explainable Boosting Machines or EBM (Lou et al., 2013) and GAMI-Net (Yang et al., 2021b). The paper proposes a new algorithm, called GAMI-Lin-T, that also uses trees like EBM, but it does linear fits instead of piecewise constants within the partitions. There are many other differences, including the development of a new interaction filtering algorithm. Finally, the paper uses simulated and real datasets to compare selected ML algorithms. The results show that GAMI-Lin-T and GAMI-Net have comparable performances, and both are generally better than EBM.
Using Model-Based Trees with Boosting to Fit Low-Order Functional ANOVA Models
Jul 14, 2022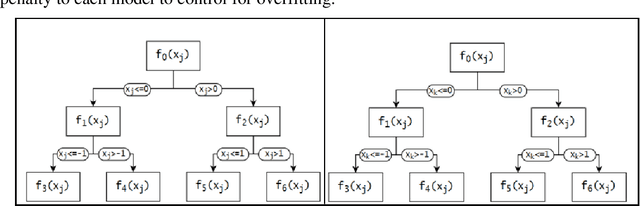

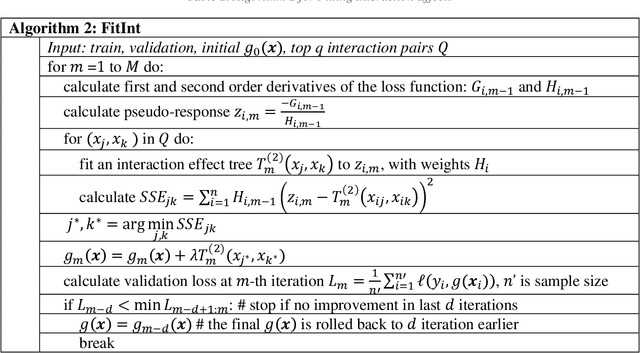
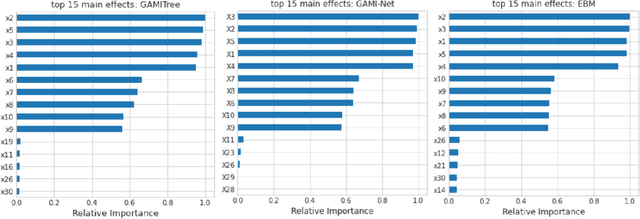
Abstract:Low-order functional ANOVA (fANOVA) models have been rediscovered in the machine learning (ML) community under the guise of inherently interpretable machine learning. Explainable Boosting Machines or EBM (Lou et al. 2013) and GAMI-Net (Yang et al. 2021) are two recently proposed ML algorithms for fitting functional main effects and second-order interactions. We propose a new algorithm, called GAMI-Tree, that is similar to EBM, but has a number of features that lead to better performance. It uses model-based trees as base learners and incorporates a new interaction filtering method that is better at capturing the underlying interactions. In addition, our iterative training method converges to a model with better predictive performance, and the embedded purification ensures that interactions are hierarchically orthogonal to main effects. The algorithm does not need extensive tuning, and our implementation is fast and efficient. We use simulated and real datasets to compare the performance and interpretability of GAMI-Tree with EBM and GAMI-Net.
Shapley Computations Using Surrogate Model-Based Trees
Jul 11, 2022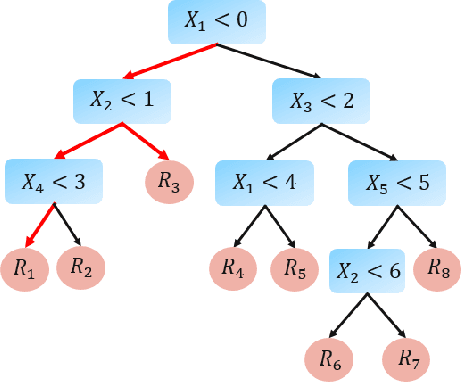

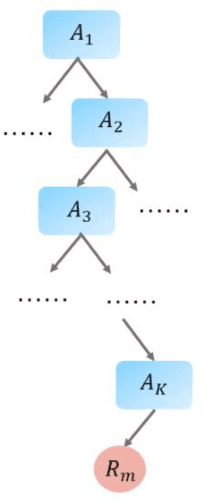
Abstract:Shapley-related techniques have gained attention as both global and local interpretation tools because of their desirable properties. However, their computation using conditional expectations is computationally expensive. Approximation methods suggested in the literature have limitations. This paper proposes the use of a surrogate model-based tree to compute Shapley and SHAP values based on conditional expectation. Simulation studies show that the proposed algorithm provides improvements in accuracy, unifies global Shapley and SHAP interpretation, and the thresholding method provides a way to trade-off running time and accuracy.
Performance and Interpretability Comparisons of Supervised Machine Learning Algorithms: An Empirical Study
May 05, 2022
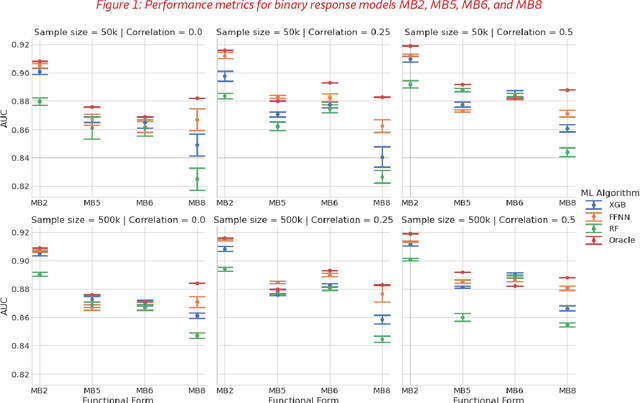
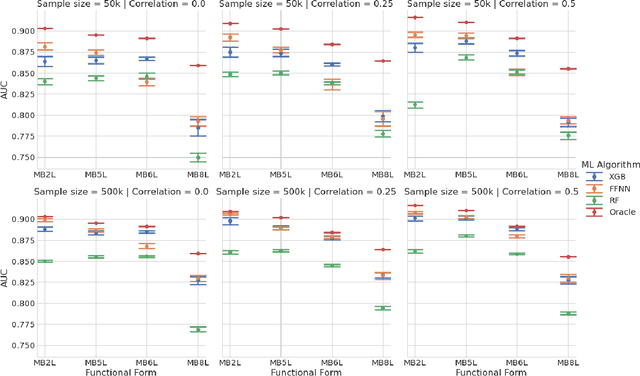
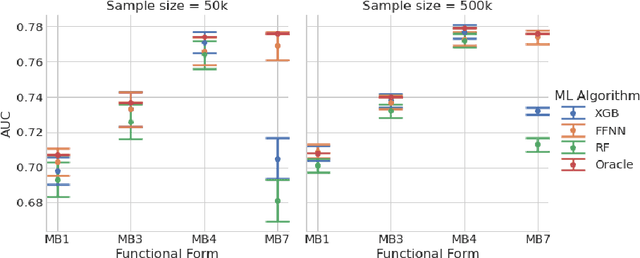
Abstract:This paper compares the performances of three supervised machine learning algorithms in terms of predictive ability and model interpretation on structured or tabular data. The algorithms considered were scikit-learn implementations of extreme gradient boosting machines (XGB) and random forests (RFs), and feedforward neural networks (FFNNs) from TensorFlow. The paper is organized in a findings-based manner, with each section providing general conclusions supported by empirical results from simulation studies that cover a wide range of model complexity and correlation structures among predictors. We considered both continuous and binary responses of different sample sizes. Overall, XGB and FFNNs were competitive, with FFNNs showing better performance in smooth models and tree-based boosting algorithms performing better in non-smooth models. This conclusion held generally for predictive performance, identification of important variables, and determining correct input-output relationships as measured by partial dependence plots (PDPs). FFNNs generally had less over-fitting, as measured by the difference in performance between training and testing datasets. However, the difference with XGB was often small. RFs did not perform well in general, confirming the findings in the literature. All models exhibited different degrees of bias seen in PDPs, but the bias was especially problematic for RFs. The extent of the biases varied with correlation among predictors, response type, and data set sample size. In general, tree-based models tended to over-regularize the fitted model in the tails of predictor distributions. Finally, as to be expected, performances were better for continuous responses compared to binary data and with larger samples.
Explaining Adverse Actions in Credit Decisions Using Shapley Decomposition
Apr 26, 2022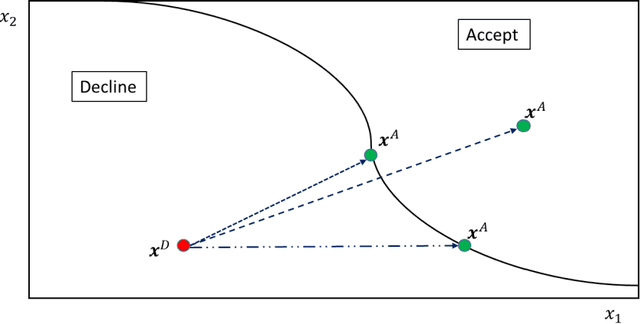
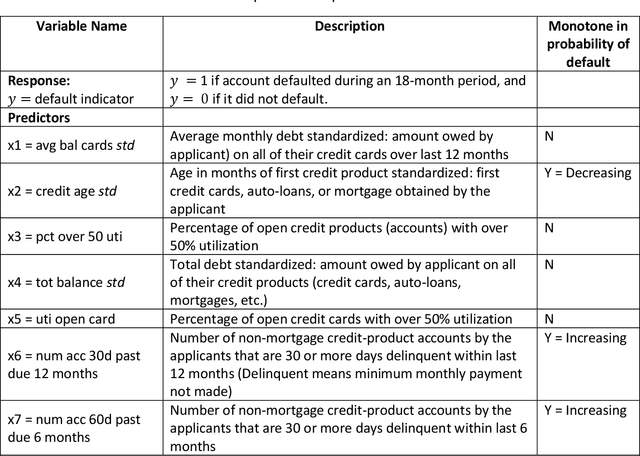
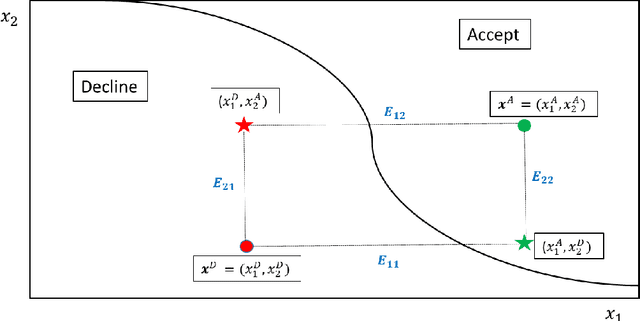
Abstract:When a financial institution declines an application for credit, an adverse action (AA) is said to occur. The applicant is then entitled to an explanation for the negative decision. This paper focuses on credit decisions based on a predictive model for probability of default and proposes a methodology for AA explanation. The problem involves identifying the important predictors responsible for the negative decision and is straightforward when the underlying model is additive. However, it becomes non-trivial even for linear models with interactions. We consider models with low-order interactions and develop a simple and intuitive approach based on first principles. We then show how the methodology generalizes to the well-known Shapely decomposition and the recently proposed concept of Baseline Shapley (B-Shap). Unlike other Shapley techniques in the literature for local interpretability of machine learning results, B-Shap is computationally tractable since it involves just function evaluations. An illustrative case study is used to demonstrate the usefulness of the method. The paper also discusses situations with highly correlated predictors and desirable properties of fitted models in the credit-lending context, such as monotonicity and continuity.
Surrogate Locally-Interpretable Models with Supervised Machine Learning Algorithms
Jul 28, 2020



Abstract:Supervised Machine Learning (SML) algorithms, such as Gradient Boosting, Random Forest, and Neural Networks, have become popular in recent years due to their superior predictive performance over traditional statistical methods. However, their complexity makes the results hard to interpret without additional tools. There has been a lot of recent work in developing global and local diagnostics for interpreting SML models. In this paper, we propose a locally-interpretable model that takes the fitted ML response surface, partitions the predictor space using model-based regression trees, and fits interpretable main-effects models at each of the nodes. We adapt the algorithm to be efficient in dealing with high-dimensional predictors. While the main focus is on interpretability, the resulting surrogate model also has reasonably good predictive performance.
Supervised Machine Learning Techniques: An Overview with Applications to Banking
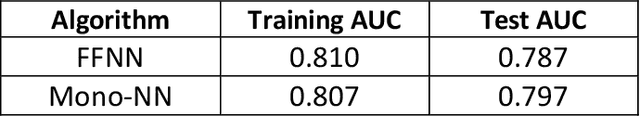
Jul 28, 2020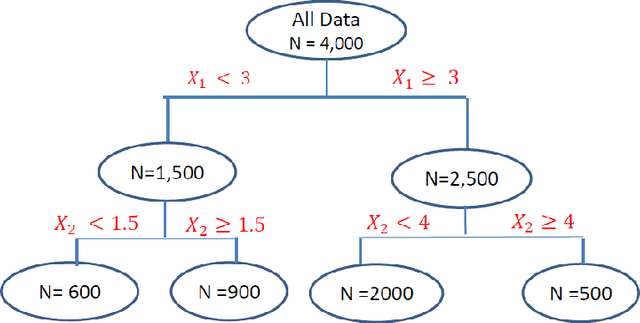
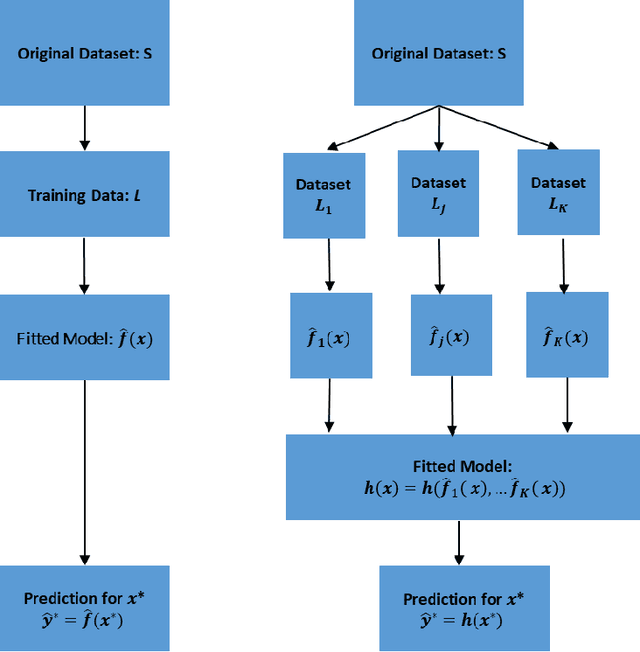
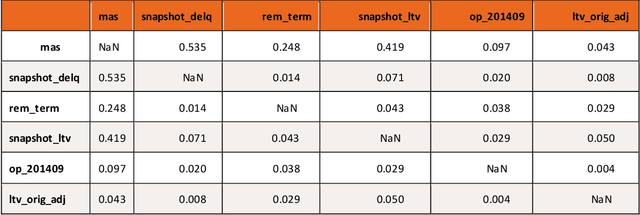
Abstract:This article provides an overview of Supervised Machine Learning (SML) with a focus on applications to banking. The SML techniques covered include Bagging (Random Forest or RF), Boosting (Gradient Boosting Machine or GBM) and Neural Networks (NNs). We begin with an introduction to ML tasks and techniques. This is followed by a description of: i) tree-based ensemble algorithms including Bagging with RF and Boosting with GBMs, ii) Feedforward NNs, iii) a discussion of hyper-parameter optimization techniques, and iv) machine learning interpretability. The paper concludes with a comparison of the features of different ML algorithms. Examples taken from credit risk modeling in banking are used throughout the paper to illustrate the techniques and interpret the results of the algorithms.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge