Zach Zhang
Explaining Adverse Actions in Credit Decisions Using Shapley Decomposition
Apr 26, 2022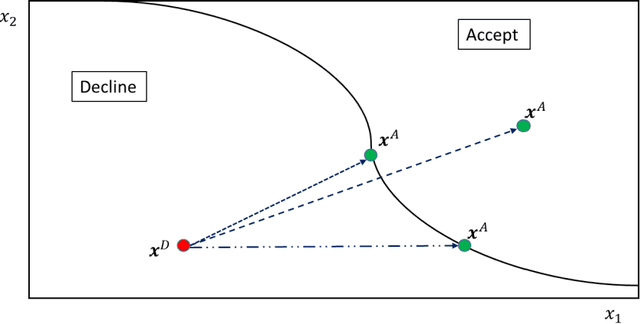
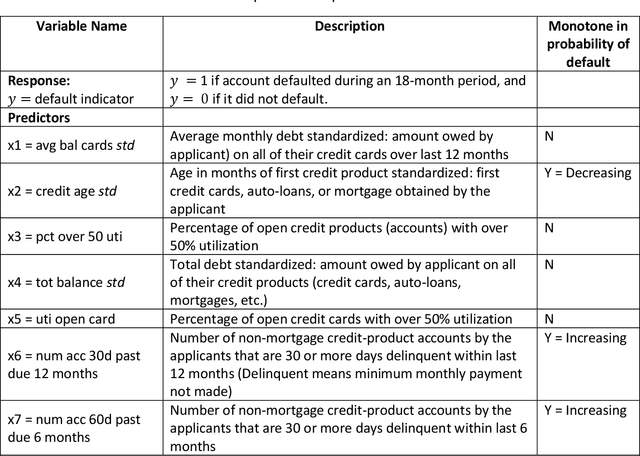
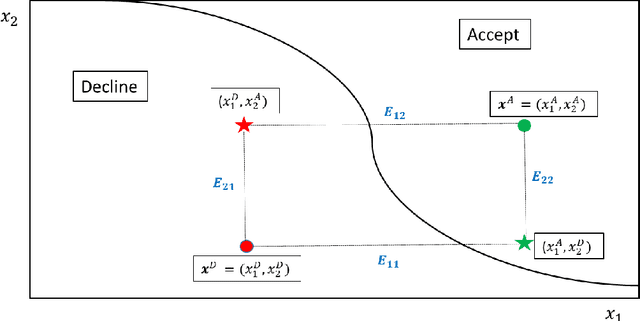
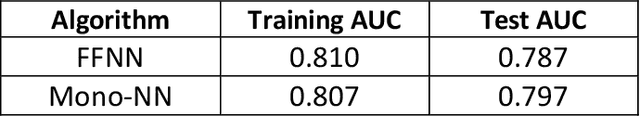
Abstract:When a financial institution declines an application for credit, an adverse action (AA) is said to occur. The applicant is then entitled to an explanation for the negative decision. This paper focuses on credit decisions based on a predictive model for probability of default and proposes a methodology for AA explanation. The problem involves identifying the important predictors responsible for the negative decision and is straightforward when the underlying model is additive. However, it becomes non-trivial even for linear models with interactions. We consider models with low-order interactions and develop a simple and intuitive approach based on first principles. We then show how the methodology generalizes to the well-known Shapely decomposition and the recently proposed concept of Baseline Shapley (B-Shap). Unlike other Shapley techniques in the literature for local interpretability of machine learning results, B-Shap is computationally tractable since it involves just function evaluations. An illustrative case study is used to demonstrate the usefulness of the method. The paper also discusses situations with highly correlated predictors and desirable properties of fitted models in the credit-lending context, such as monotonicity and continuity.
Bias, Fairness, and Accountability with AI and ML Algorithms
May 13, 2021

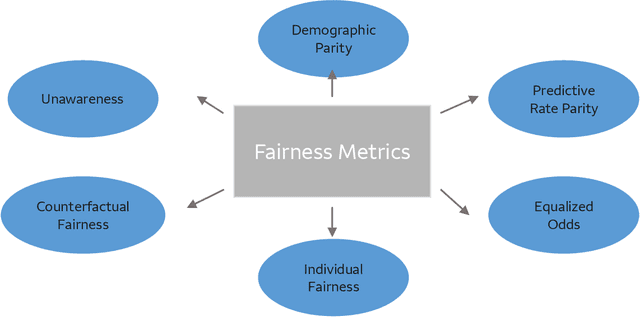
Abstract:The advent of AI and ML algorithms has led to opportunities as well as challenges. In this paper, we provide an overview of bias and fairness issues that arise with the use of ML algorithms. We describe the types and sources of data bias, and discuss the nature of algorithmic unfairness. This is followed by a review of fairness metrics in the literature, discussion of their limitations, and a description of de-biasing (or mitigation) techniques in the model life cycle.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge