Nengfeng Zhou
Towards a framework on tabular synthetic data generation: a minimalist approach: theory, use cases, and limitations
Nov 19, 2024Abstract:We propose and study a minimalist approach towards synthetic tabular data generation. The model consists of a minimalistic unsupervised SparsePCA encoder (with contingent clustering step or log transformation to handle nonlinearity) and XGboost decoder which is SOTA for structured data regression and classification tasks. We study and contrast the methodologies with (variational) autoencoders in several toy low dimensional scenarios to derive necessary intuitions. The framework is applied to high dimensional simulated credit scoring data which parallels real-life financial applications. We applied the method to robustness testing to demonstrate practical use cases. The case study result suggests that the method provides an alternative to raw and quantile perturbation for model robustness testing. We show that the method is simplistic, guarantees interpretability all the way through, does not require extra tuning and provide unique benefits.
Multi-resolution Interpretation and Diagnostics Tool for Natural Language Classifiers
Mar 06, 2023Abstract:Developing explainability methods for Natural Language Processing (NLP) models is a challenging task, for two main reasons. First, the high dimensionality of the data (large number of tokens) results in low coverage and in turn small contributions for the top tokens, compared to the overall model performance. Second, owing to their textual nature, the input variables, after appropriate transformations, are effectively binary (presence or absence of a token in an observation), making the input-output relationship difficult to understand. Common NLP interpretation techniques do not have flexibility in resolution, because they usually operate at word-level and provide fully local (message level) or fully global (over all messages) summaries. The goal of this paper is to create more flexible model explainability summaries by segments of observation or clusters of words that are semantically related to each other. In addition, we introduce a root cause analysis method for NLP models, by analyzing representative False Positive and False Negative examples from different segments. At the end, we illustrate, using a Yelp review data set with three segments (Restaurant, Hotel, and Beauty), that exploiting group/cluster structures in words and/or messages can aid in the interpretation of decisions made by NLP models and can be utilized to assess the model's sensitivity or bias towards gender, syntax, and word meanings.
Model Explainability in Deep Learning Based Natural Language Processing
Jun 14, 2021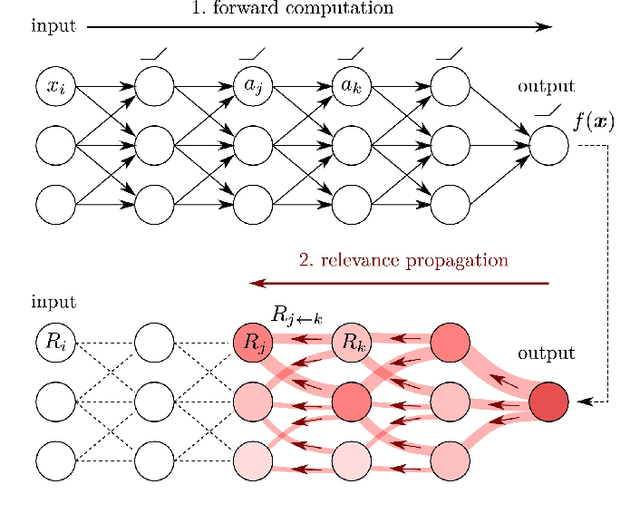
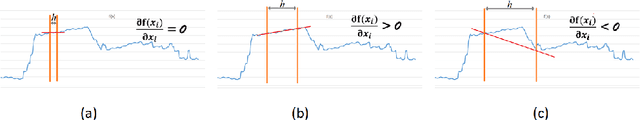
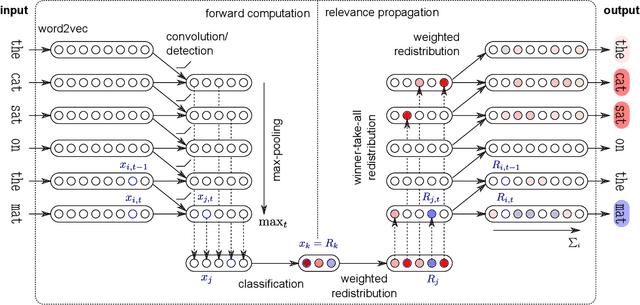
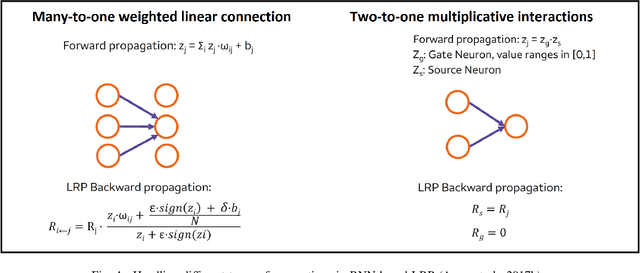
Abstract:Machine learning (ML) model explainability has received growing attention, especially in the area related to model risk and regulations. In this paper, we reviewed and compared some popular ML model explainability methodologies, especially those related to Natural Language Processing (NLP) models. We then applied one of the NLP explainability methods Layer-wise Relevance Propagation (LRP) to a NLP classification model. We used the LRP method to derive a relevance score for each word in an instance, which is a local explainability. The relevance scores are then aggregated together to achieve global variable importance of the model. Through the case study, we also demonstrated how to apply the local explainability method to false positive and false negative instances to discover the weakness of a NLP model. These analysis can help us to understand NLP models better and reduce the risk due to the black-box nature of NLP models. We also identified some common issues due to the special natures of NLP models and discussed how explainability analysis can act as a control to detect these issues after the model has been trained.
Bias, Fairness, and Accountability with AI and ML Algorithms
May 13, 2021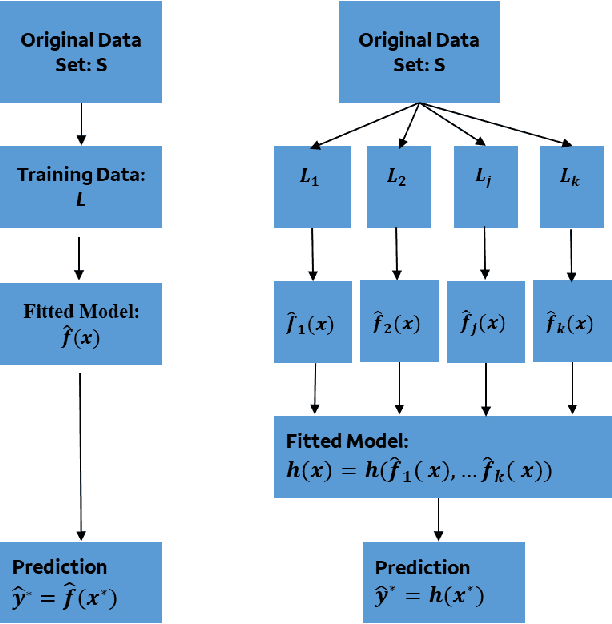

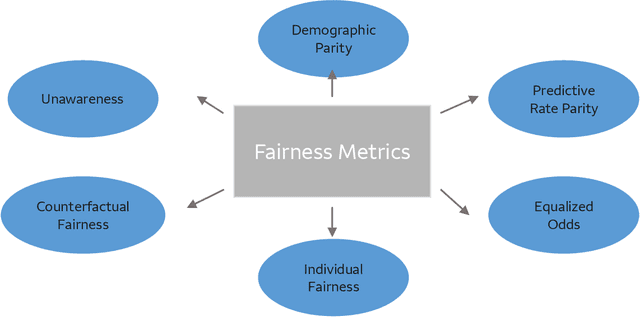
Abstract:The advent of AI and ML algorithms has led to opportunities as well as challenges. In this paper, we provide an overview of bias and fairness issues that arise with the use of ML algorithms. We describe the types and sources of data bias, and discuss the nature of algorithmic unfairness. This is followed by a review of fairness metrics in the literature, discussion of their limitations, and a description of de-biasing (or mitigation) techniques in the model life cycle.
Survey of Imbalanced Data Methodologies
Apr 06, 2021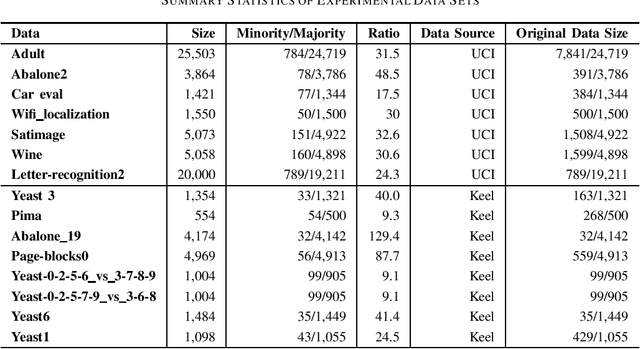

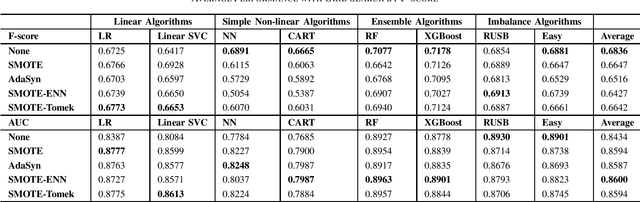
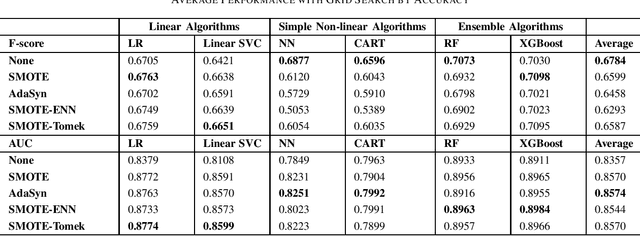
Abstract:Imbalanced data set is a problem often found and well-studied in financial industry. In this paper, we reviewed and compared some popular methodologies handling data imbalance. We then applied the under-sampling/over-sampling methodologies to several modeling algorithms on UCI and Keel data sets. The performance was analyzed for class-imbalance methods, modeling algorithms and grid search criteria comparison.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge